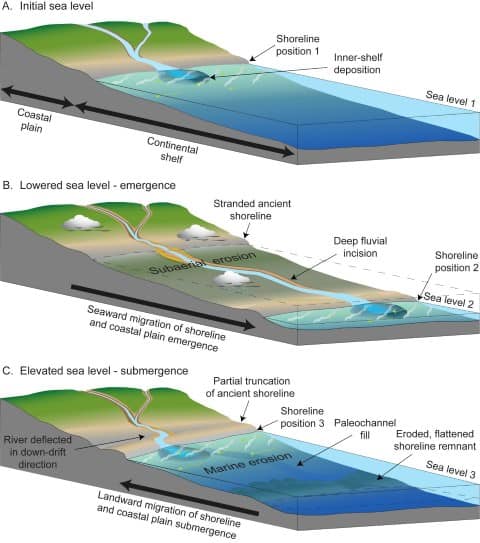
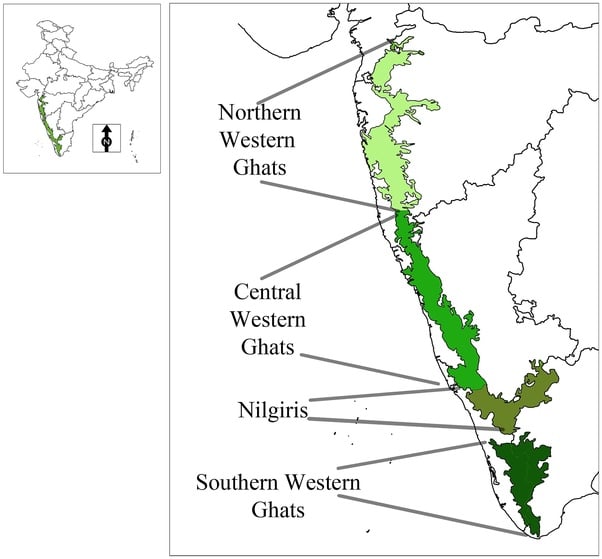
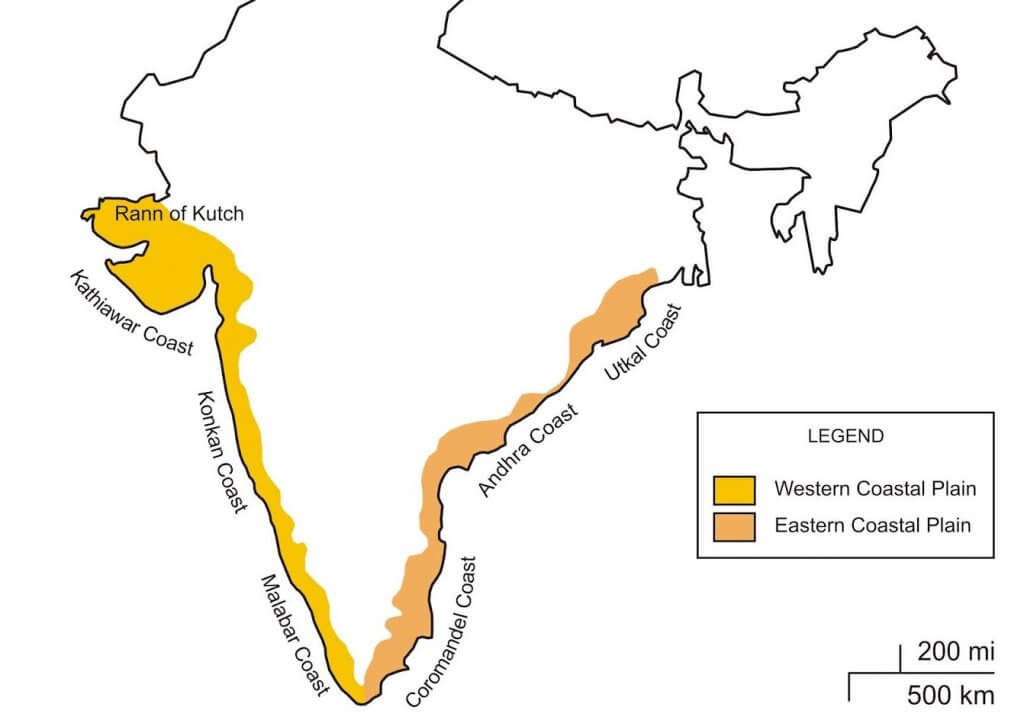
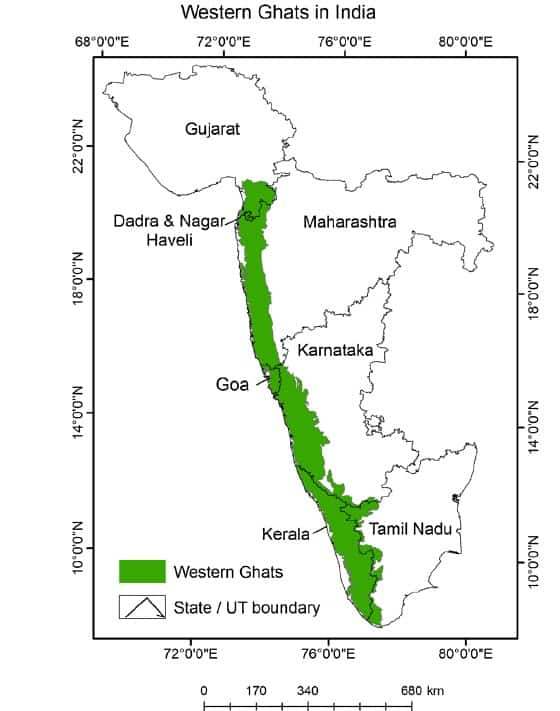
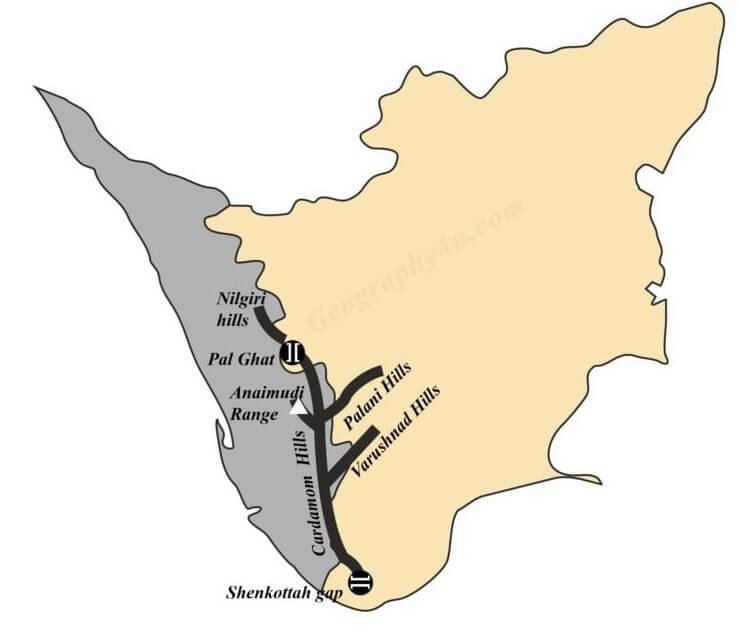
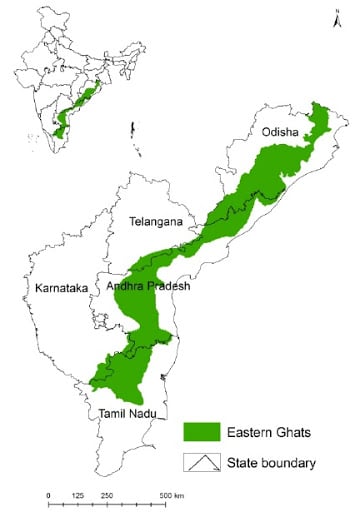
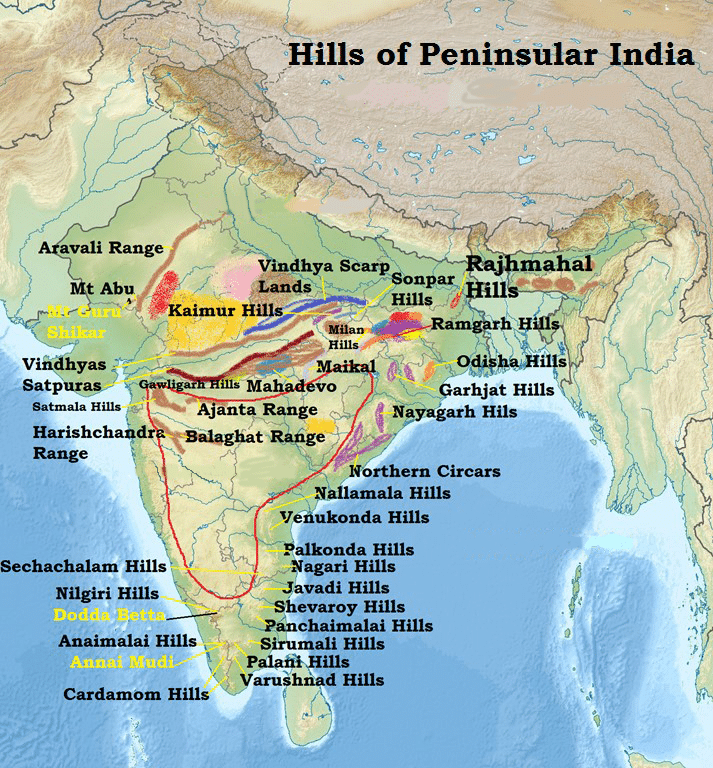
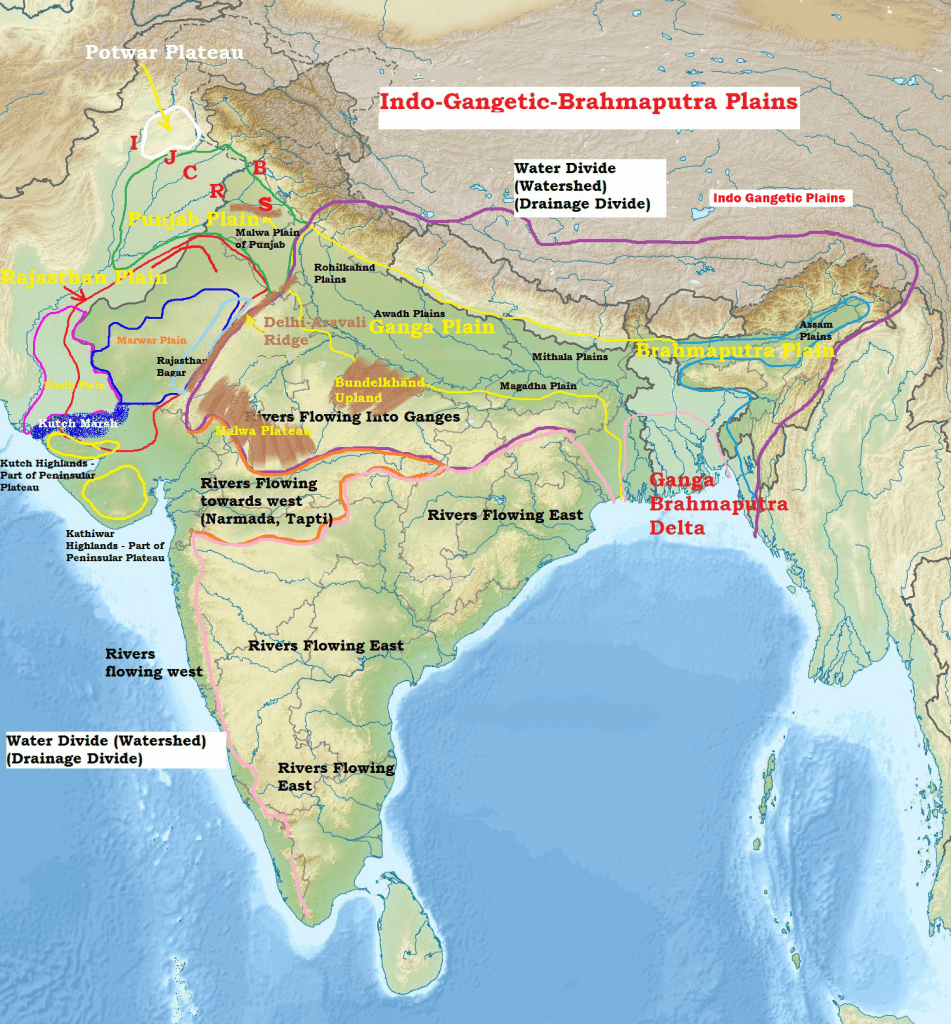
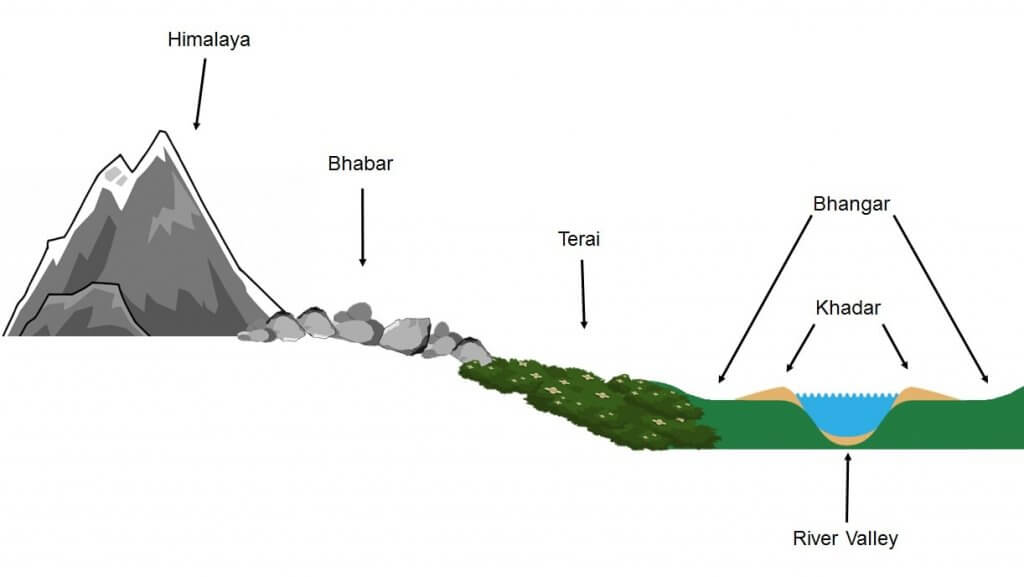
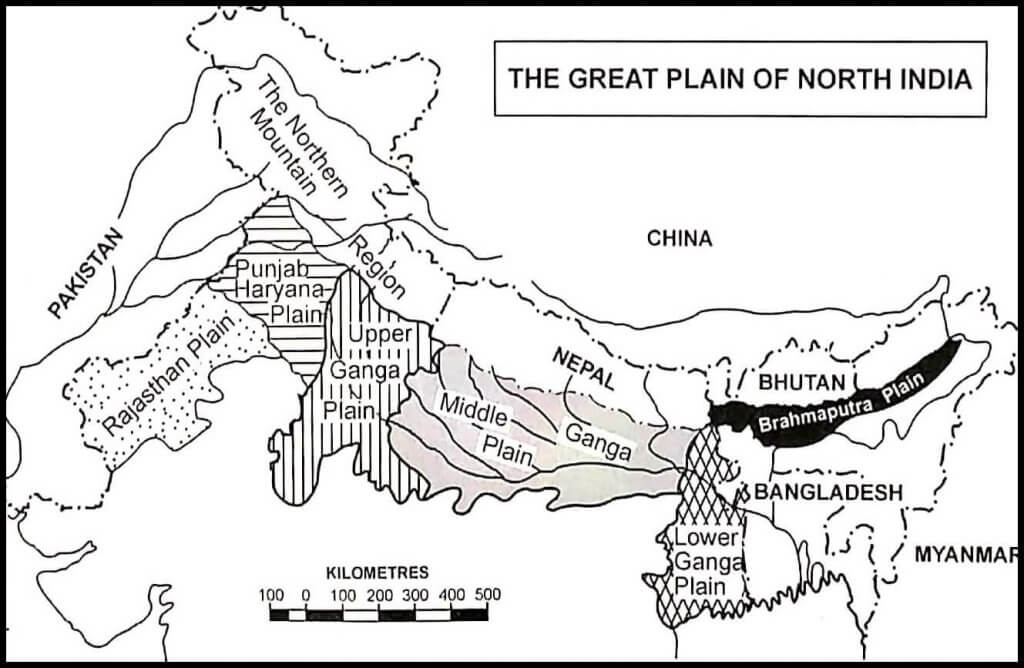
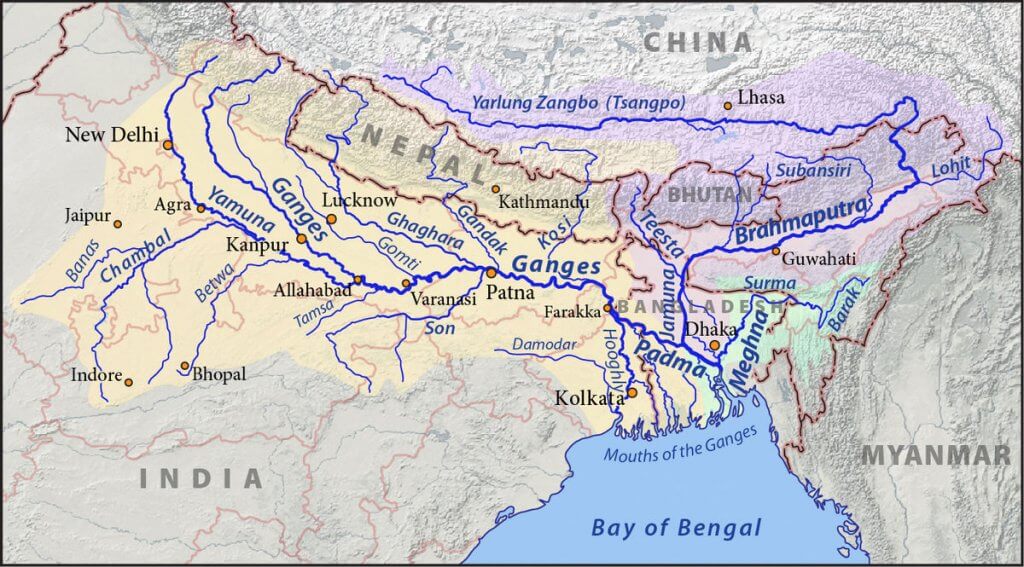
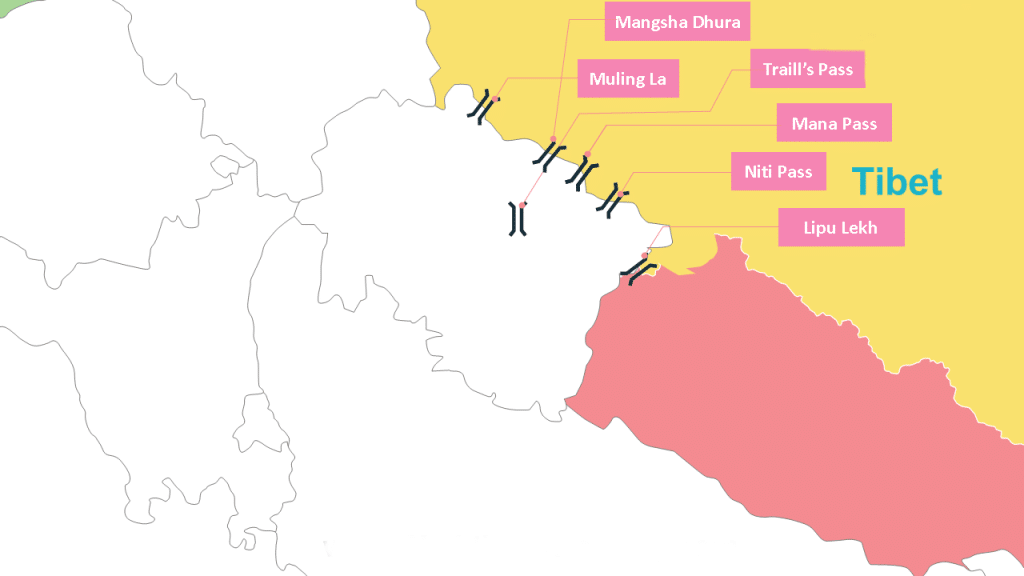
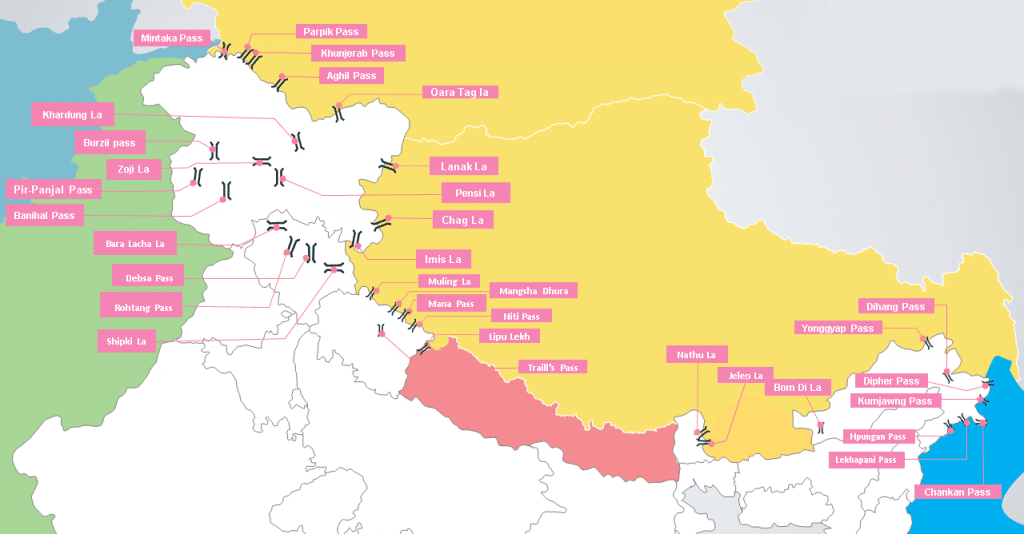
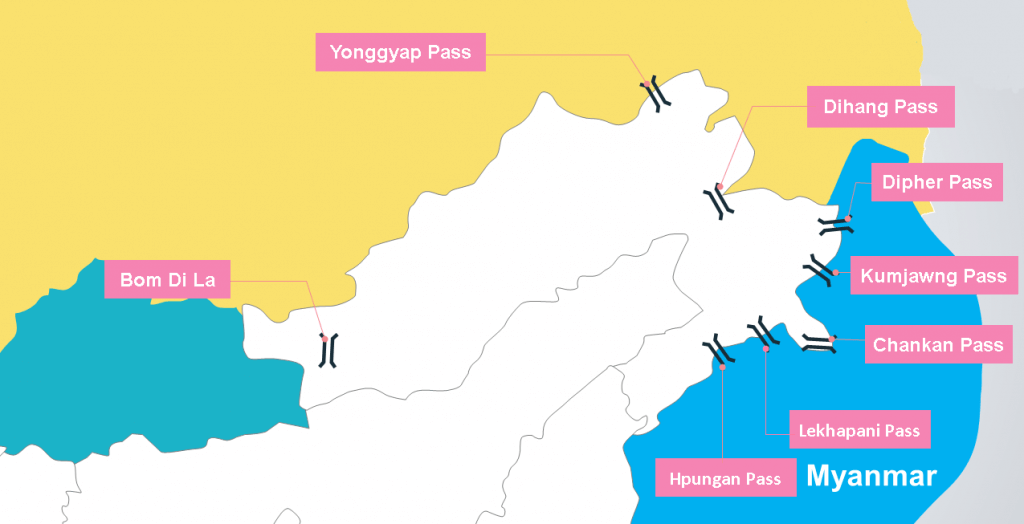
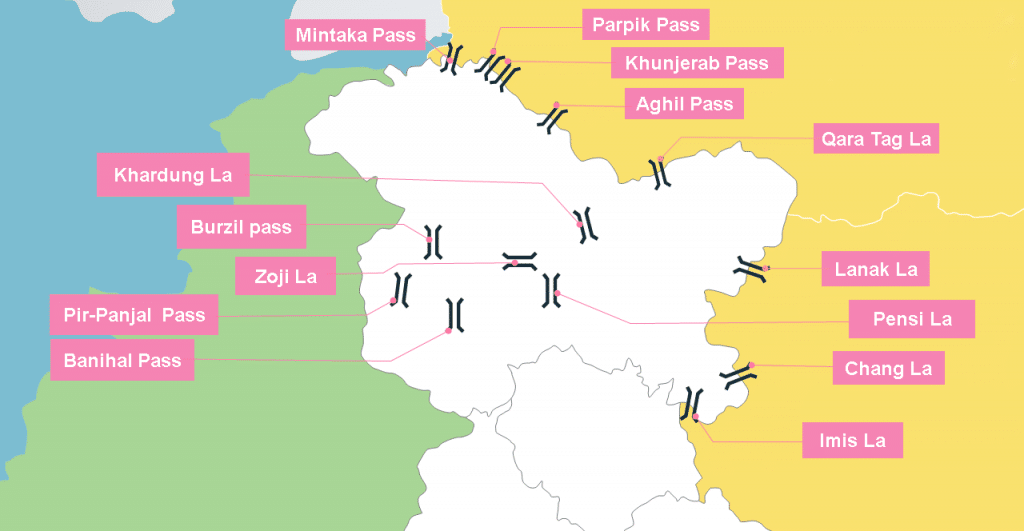
Introduction to Geography
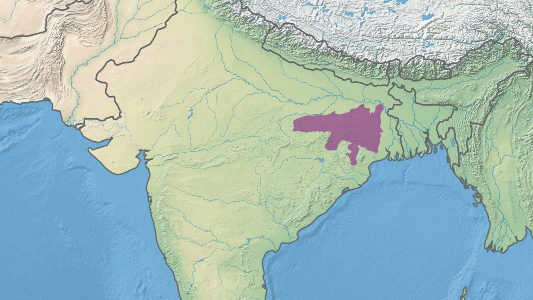
Geography, a field of science that bridges the gap between the natural world and human society, provides a framework for understanding the world around us and our place within it. It is divided into two main branches: Physical Geography, which focuses on understanding the Earth’s natural environment, and Human Geography, which is concerned with the study of people, their communities, cultures, economies, and interactions with the environment. Geography also encompasses the study of spatial relationships and plays a vital role in understanding global issues such as climate change, deforestation, and migration. Geographers use various tools and techniques in their work, including maps, Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and remote sensing. By studying geography, we can better appreciate the complexity of the world we live in and make informed decisions about its future.
Physical Geography delves into the study of the Earth’s atmosphere, biosphere, and hydrosphere, and how these systems interact with each other. It also explores natural disasters, their causes, and effects.
Human Geography examines how human activities affect the physical environment and how the environment influences those activities in return. Topics under this branch include urban development, transportation, population growth, and geopolitics. Spatial relationships in geography investigate how things are distributed on the Earth’s surface and why they are located where they are. This aspect of geography is crucial in fields such as urban planning, transportation, and environmental management. Global issues like climate change, deforestation, and migration can be analyzed from a spatial perspective, helping us comprehend the interconnectedness of the world. Geographic tools like maps, GIS, and remote sensing are used for visualizing and analyzing spatial data.



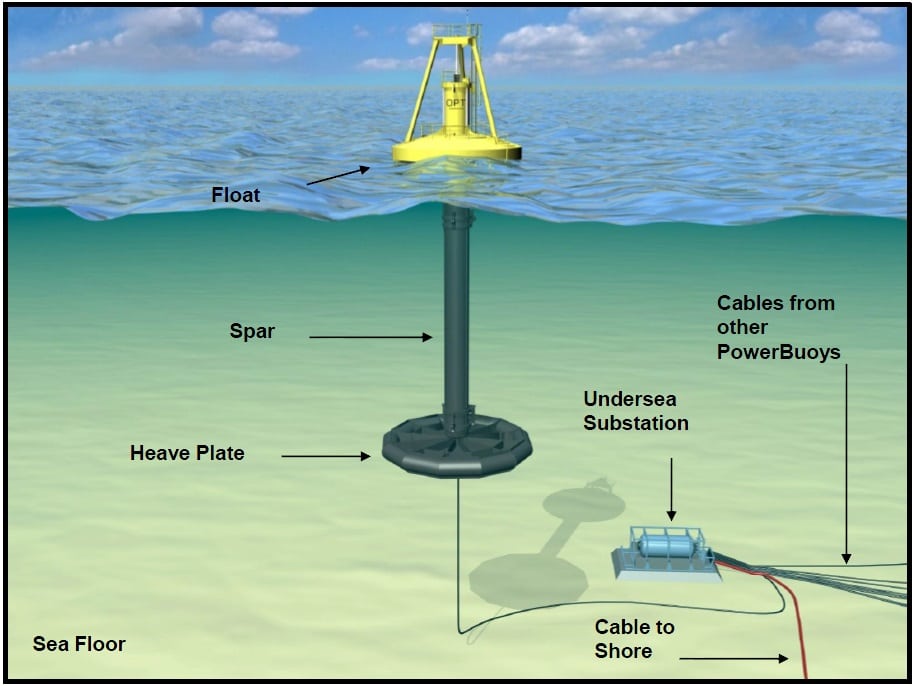
 कहा जाता है। यह ऊष्मा इंजन को संचालित करने के लिए समुद्र की सतह और लूम की गहराई के बीच तापमान के अंतर का उपयोग करता है, जो विद्युत ऊर्जा का उत्पादन करता है।</li></ul></li></ul><div class=)

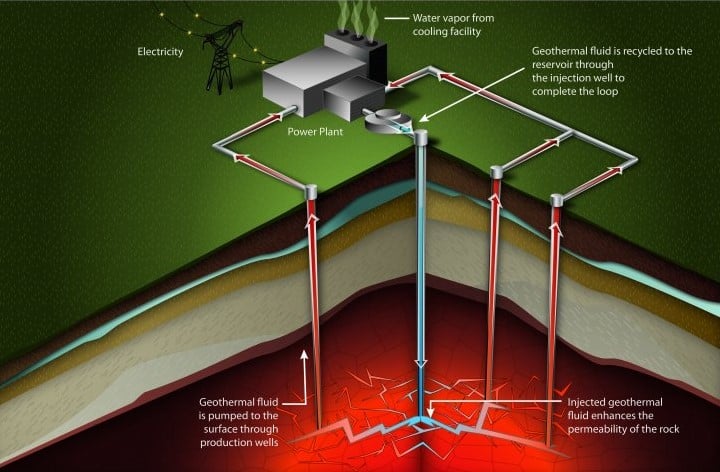
 मुख्य विशेषताएं (Salient Features)
मुख्य विशेषताएं (Salient Features)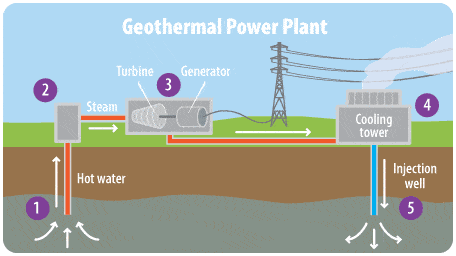
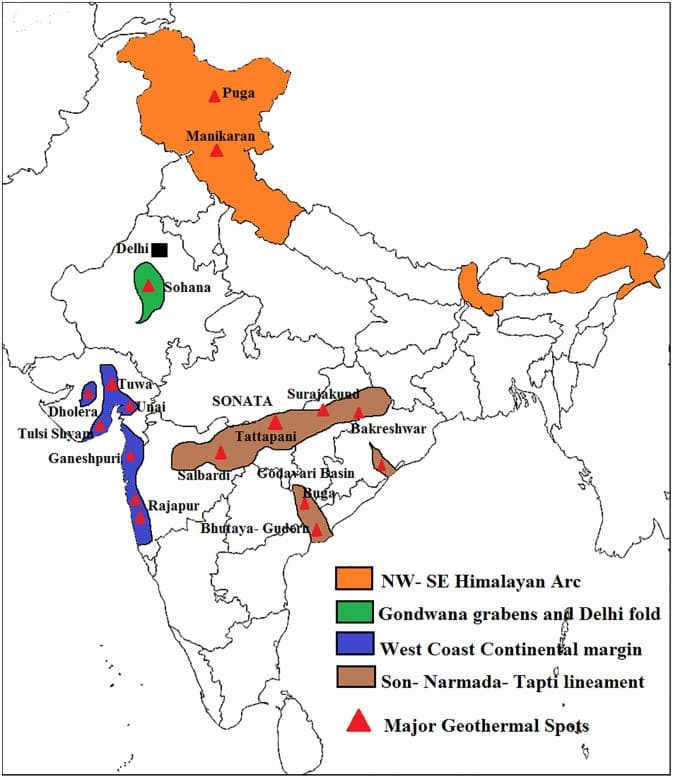
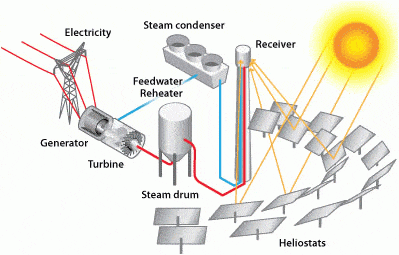
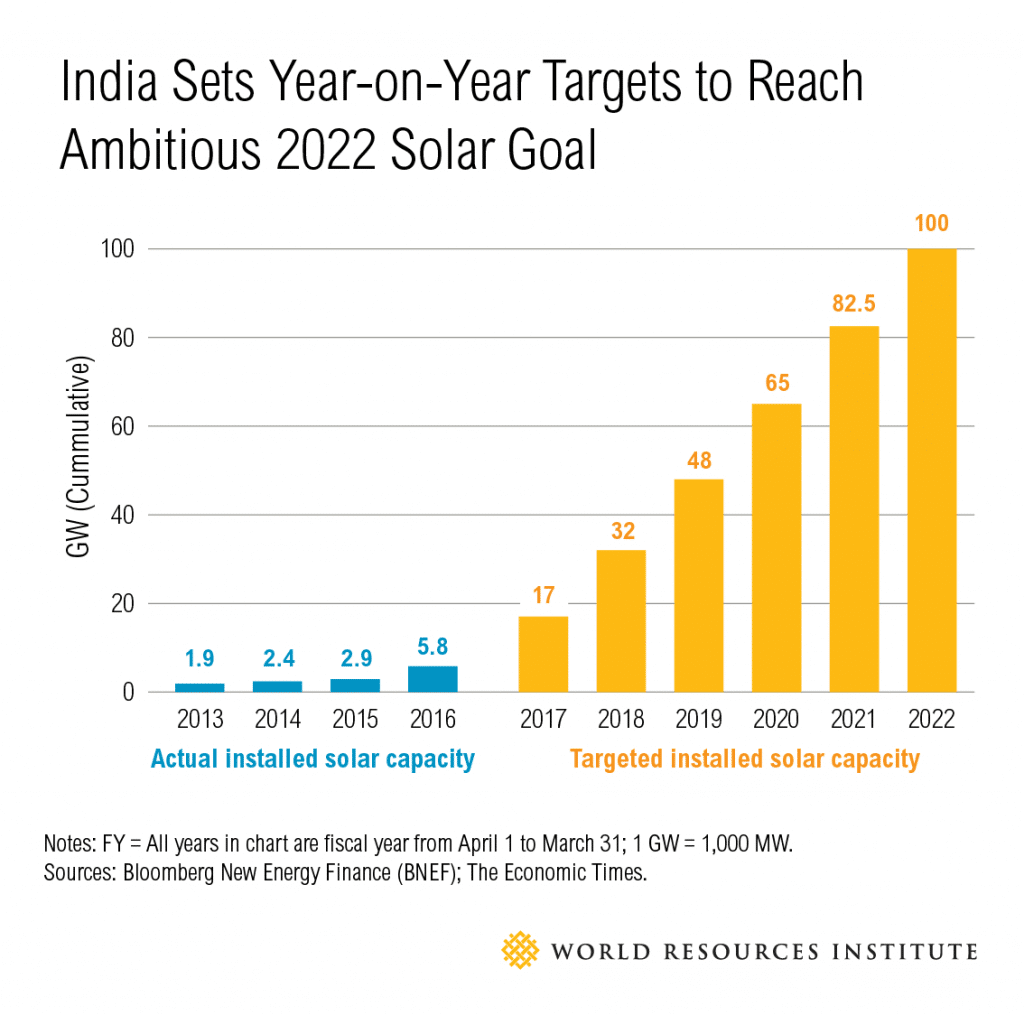
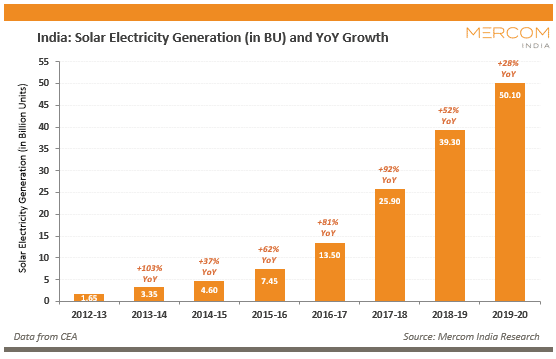
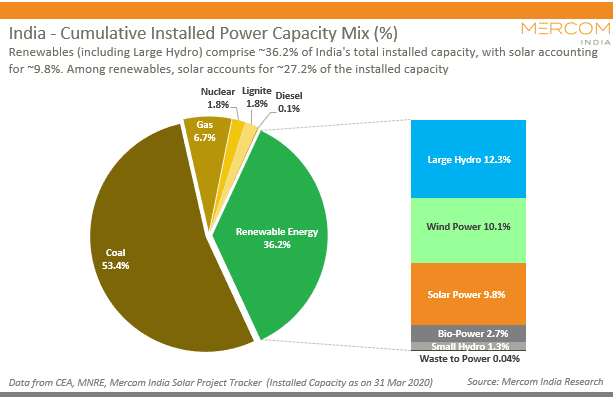

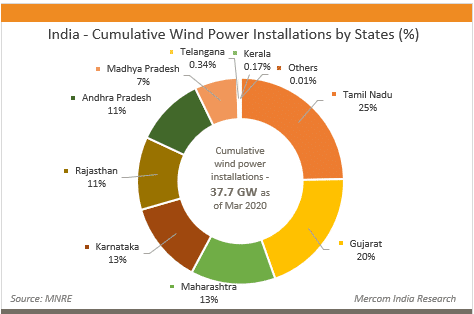
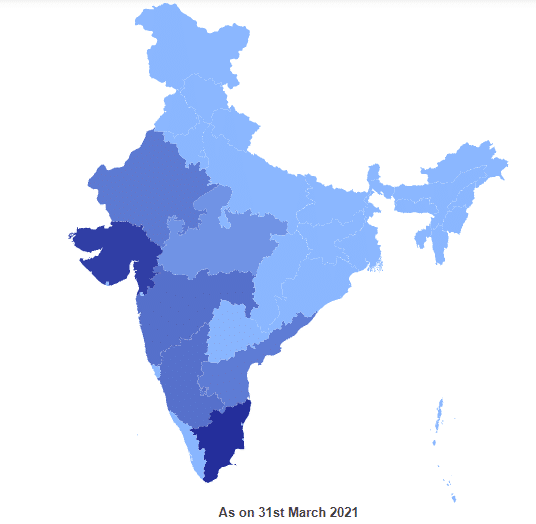
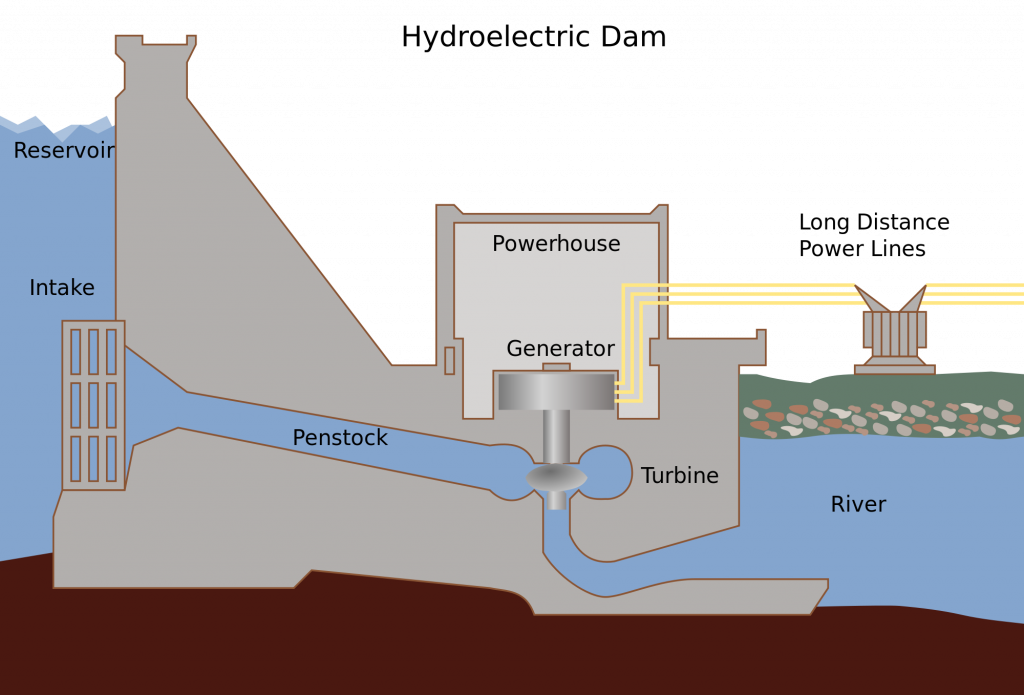
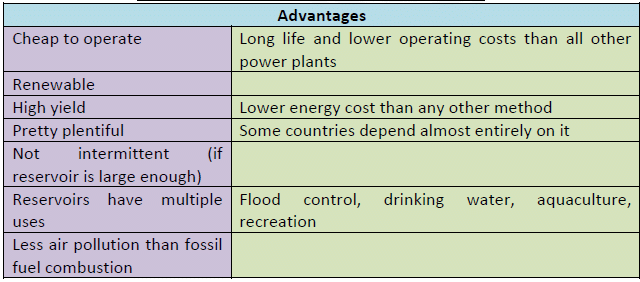
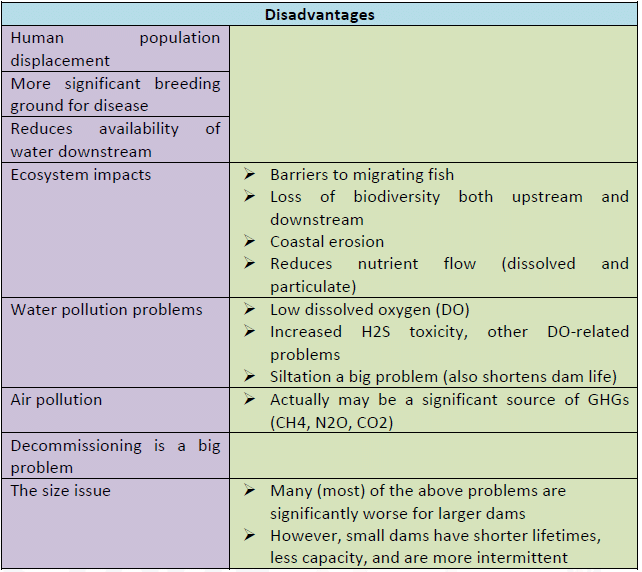
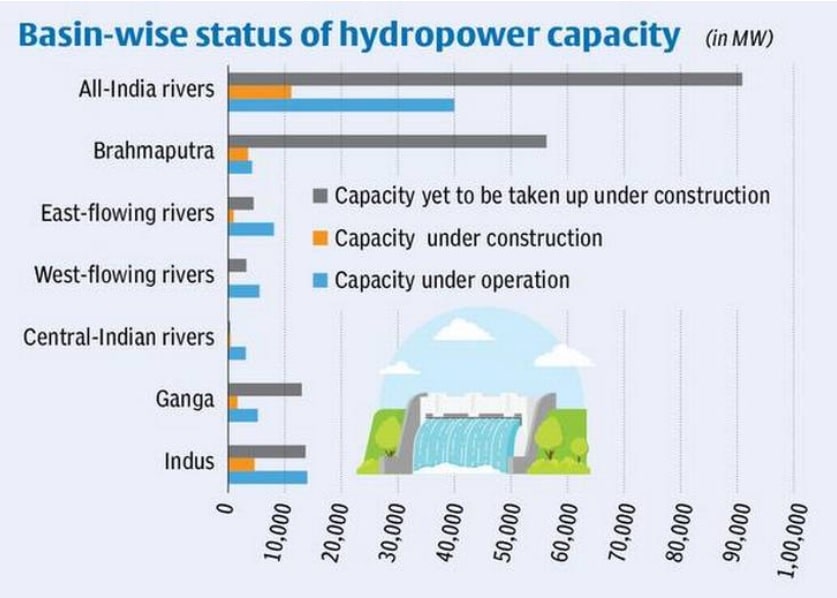
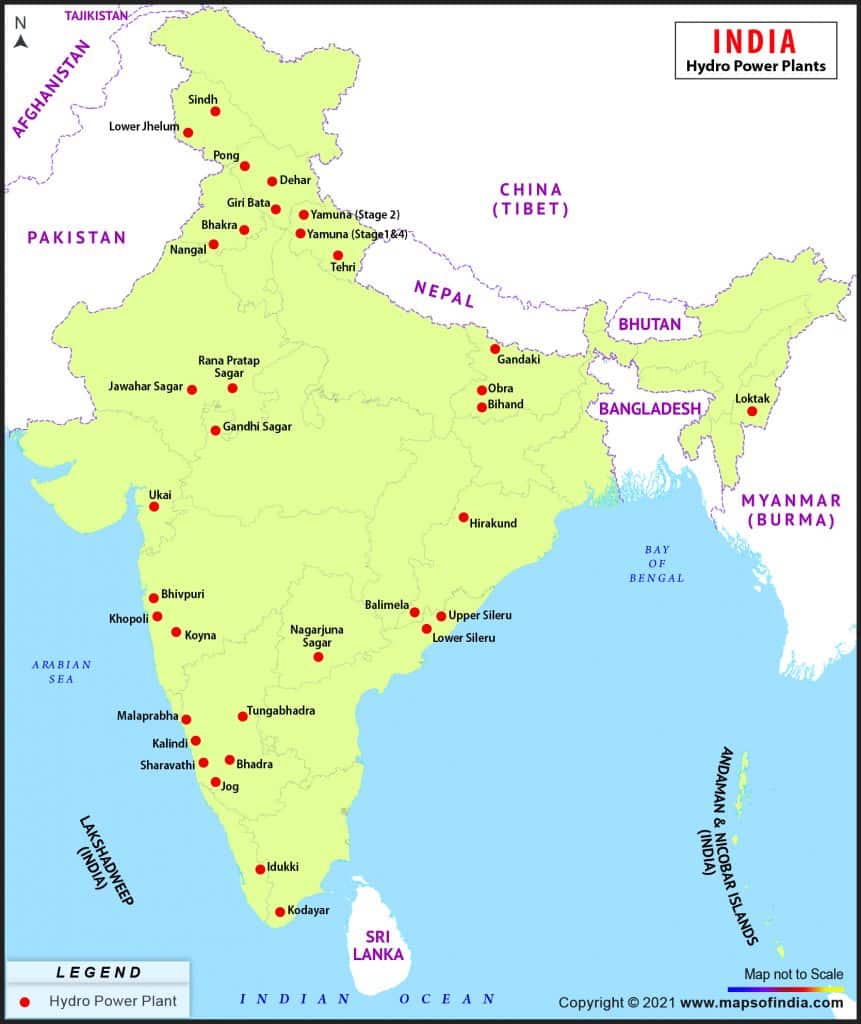
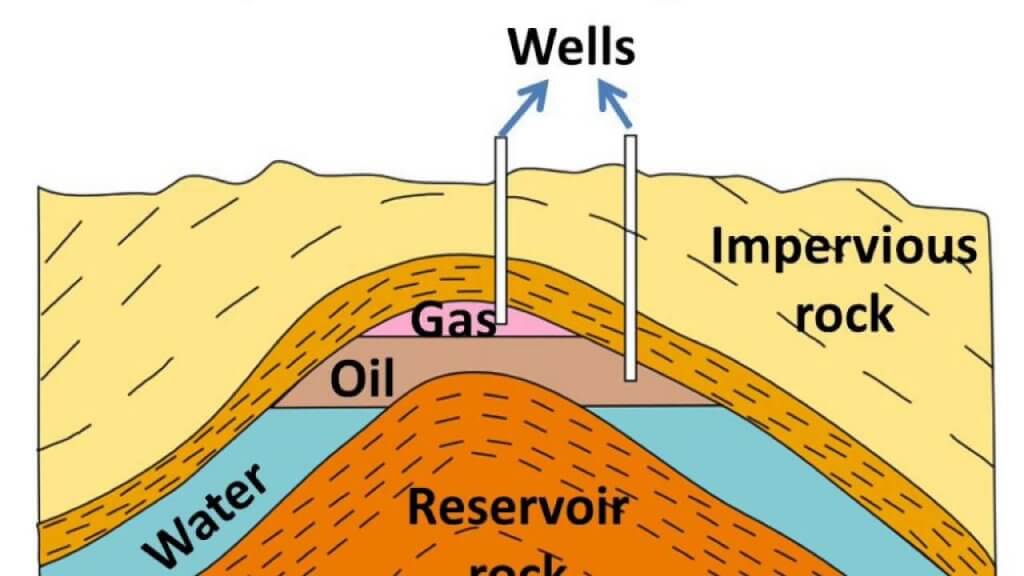
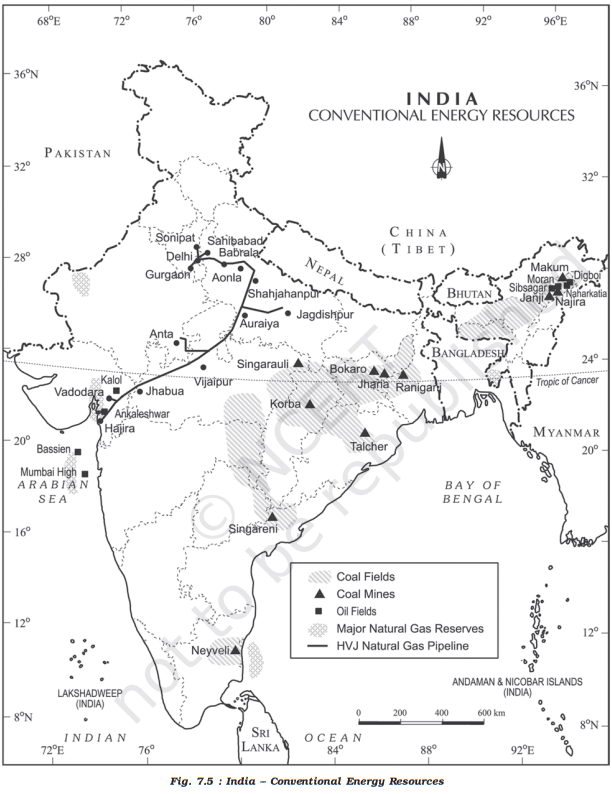
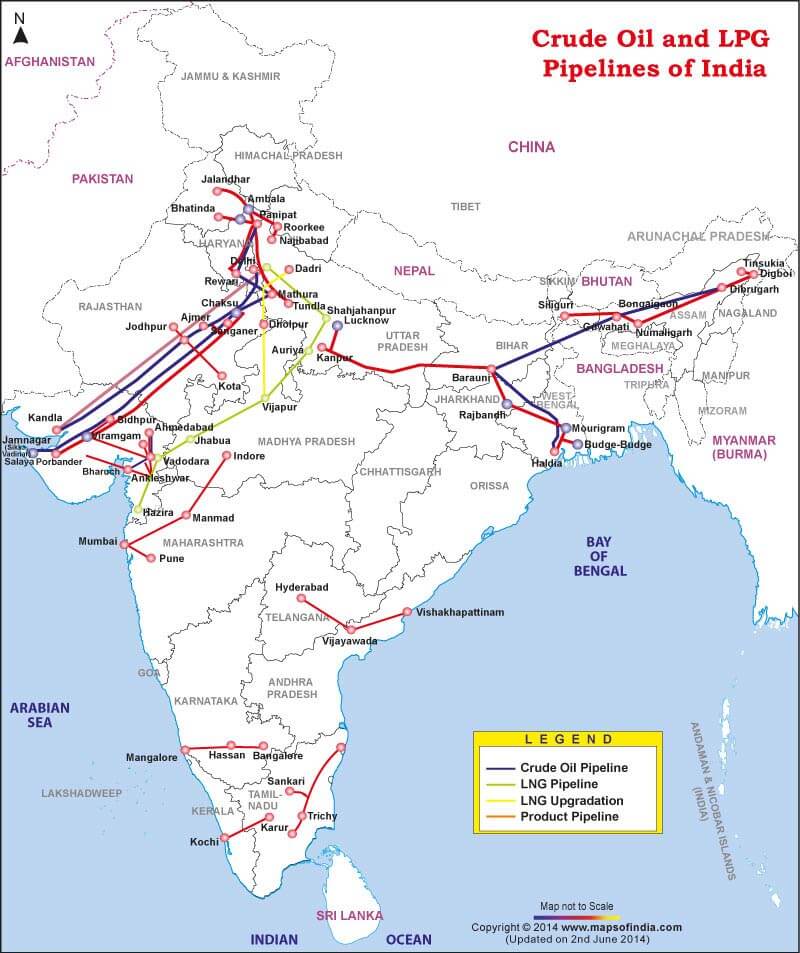
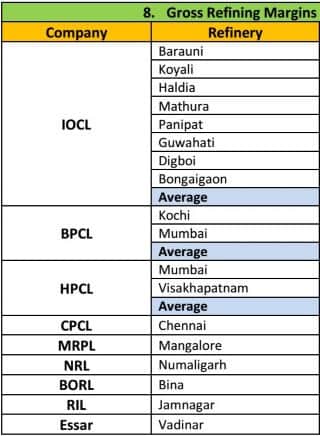
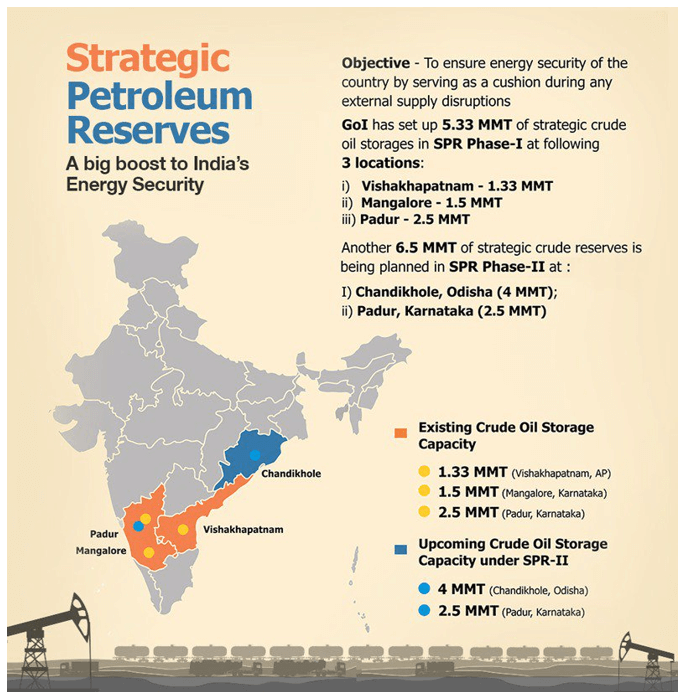
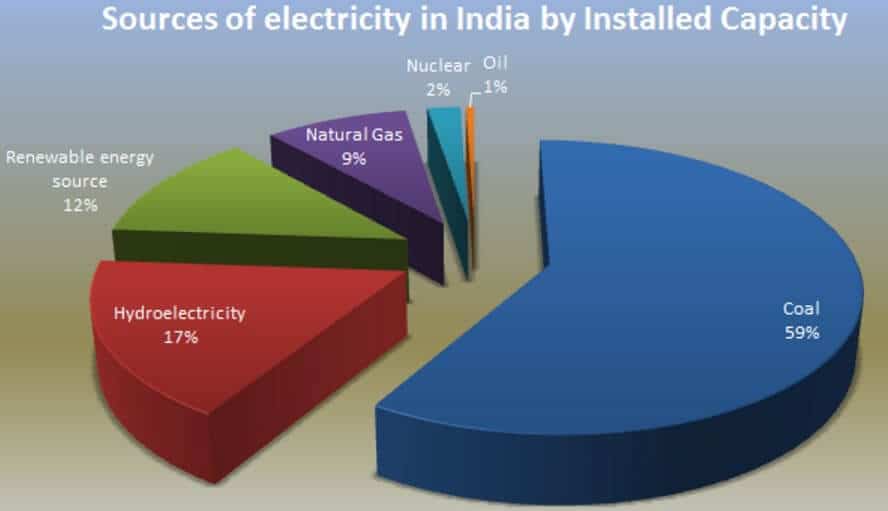
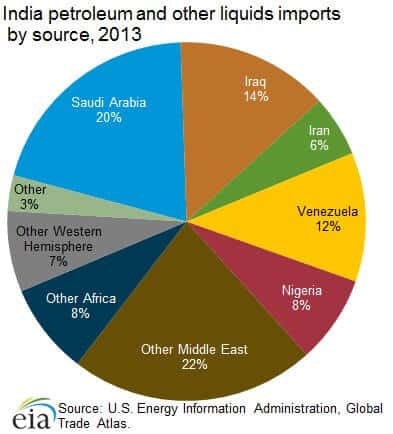
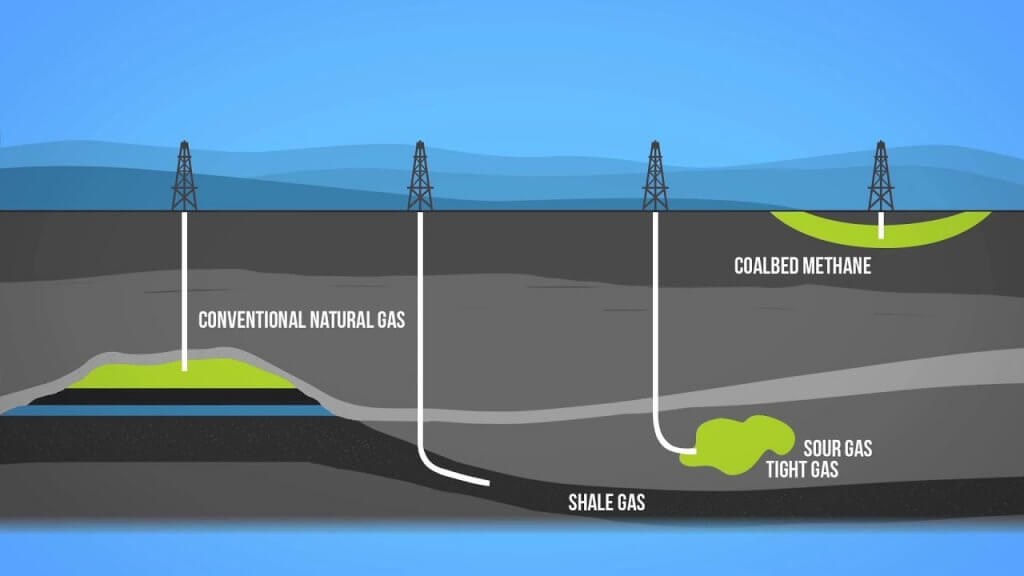
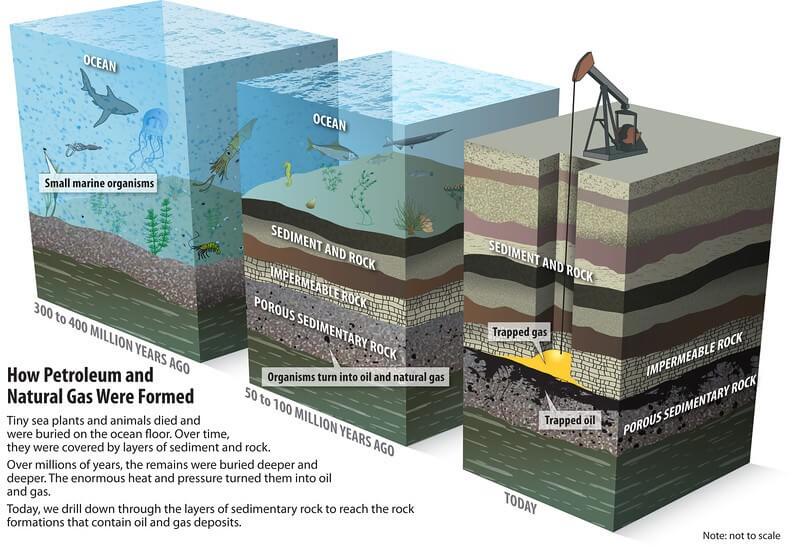
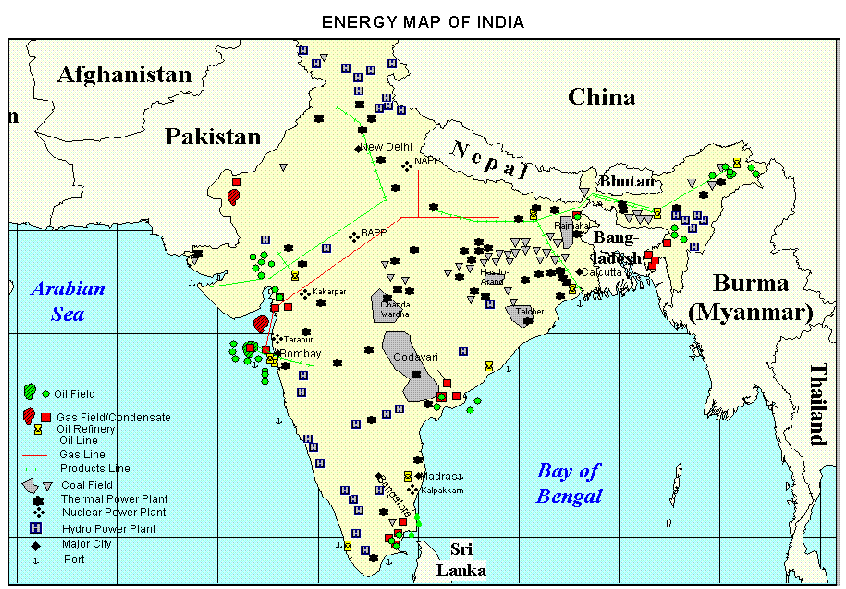
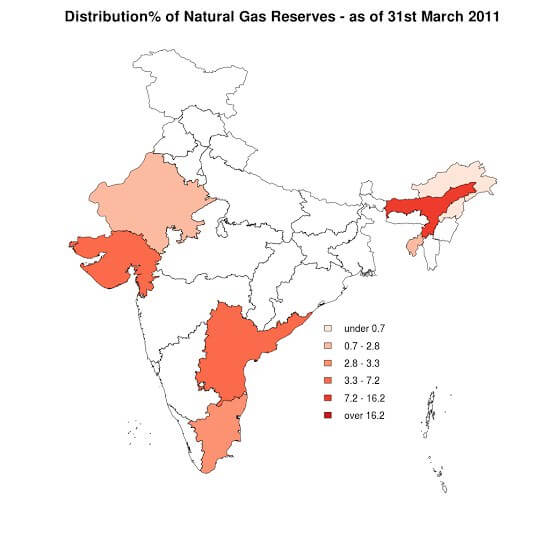
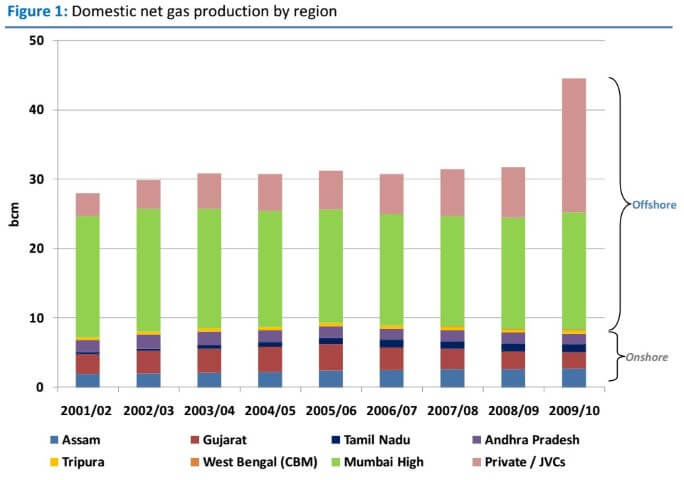
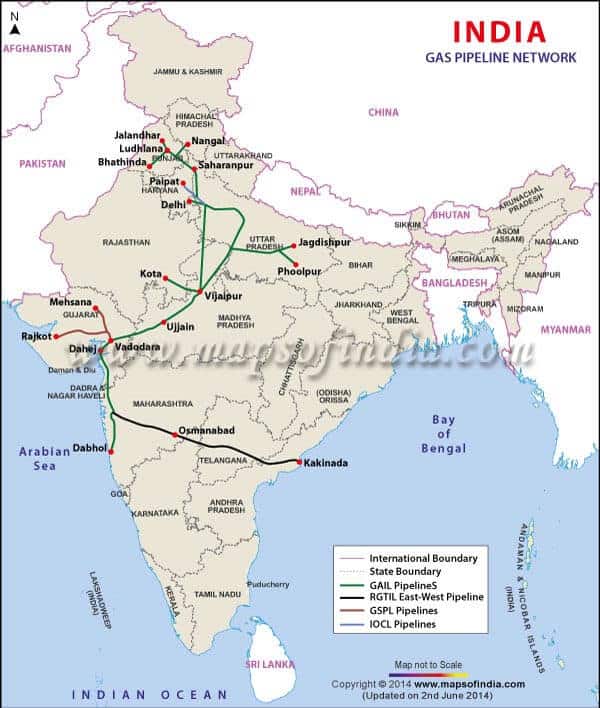
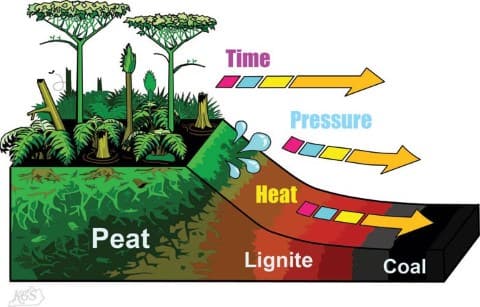
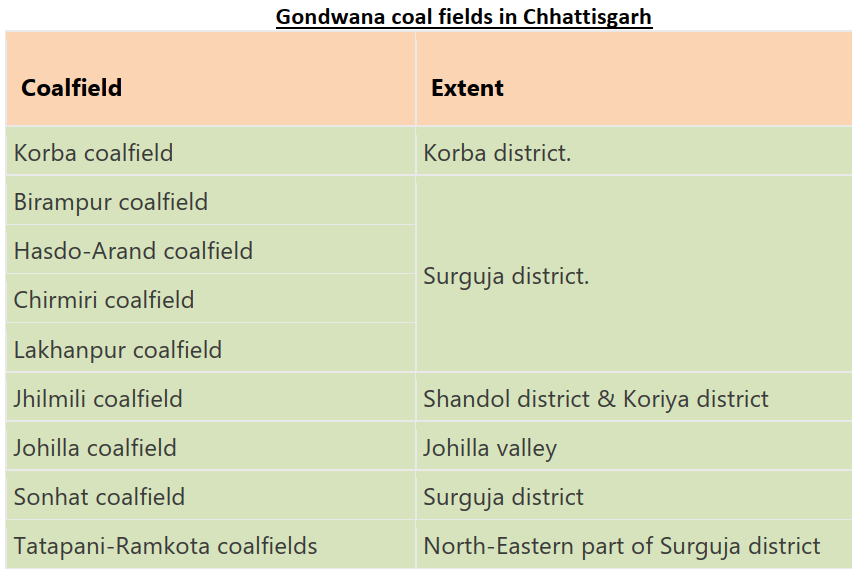
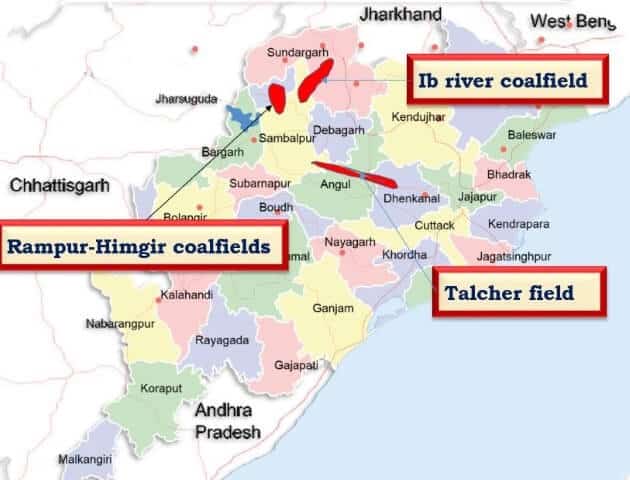
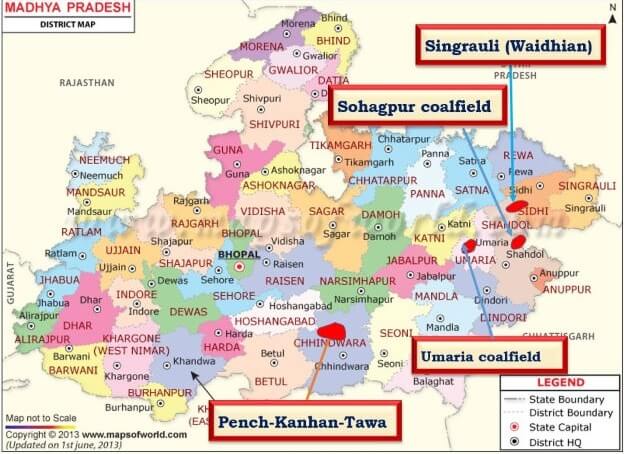
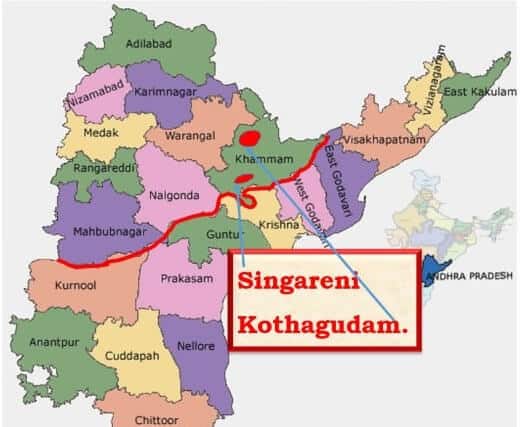
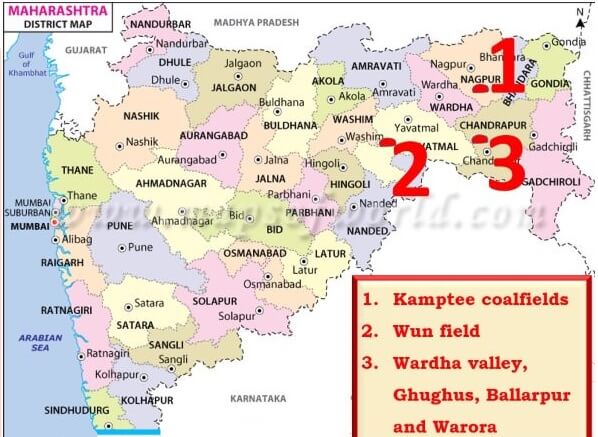
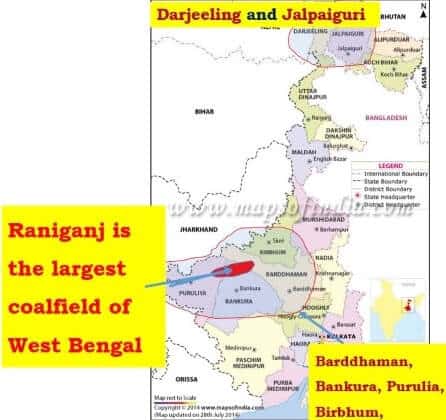
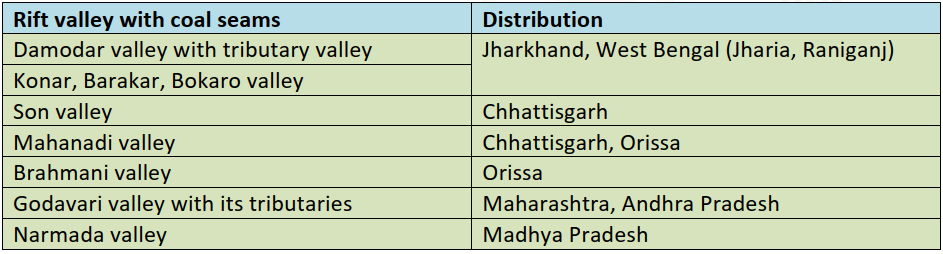
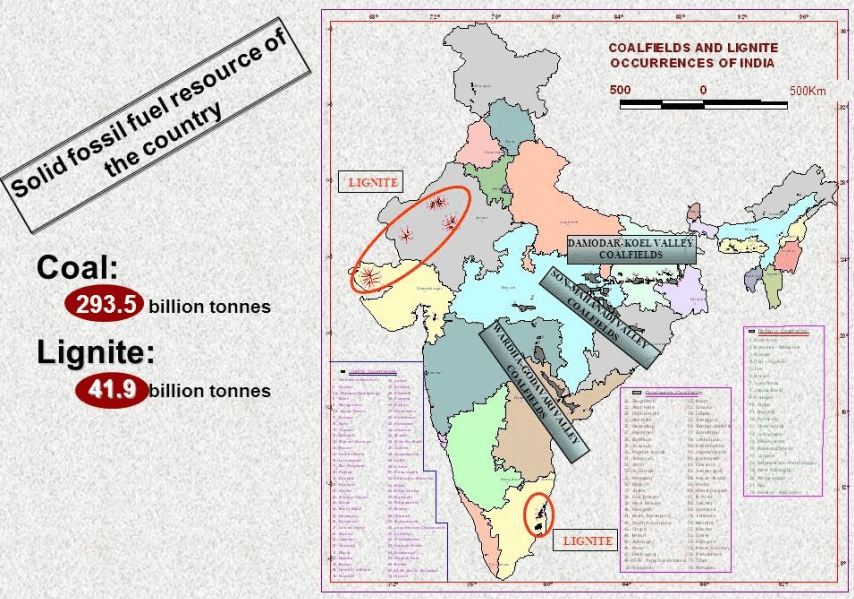
 कोयले के प्रकार (Types of Coal)
कोयले के प्रकार (Types of Coal)
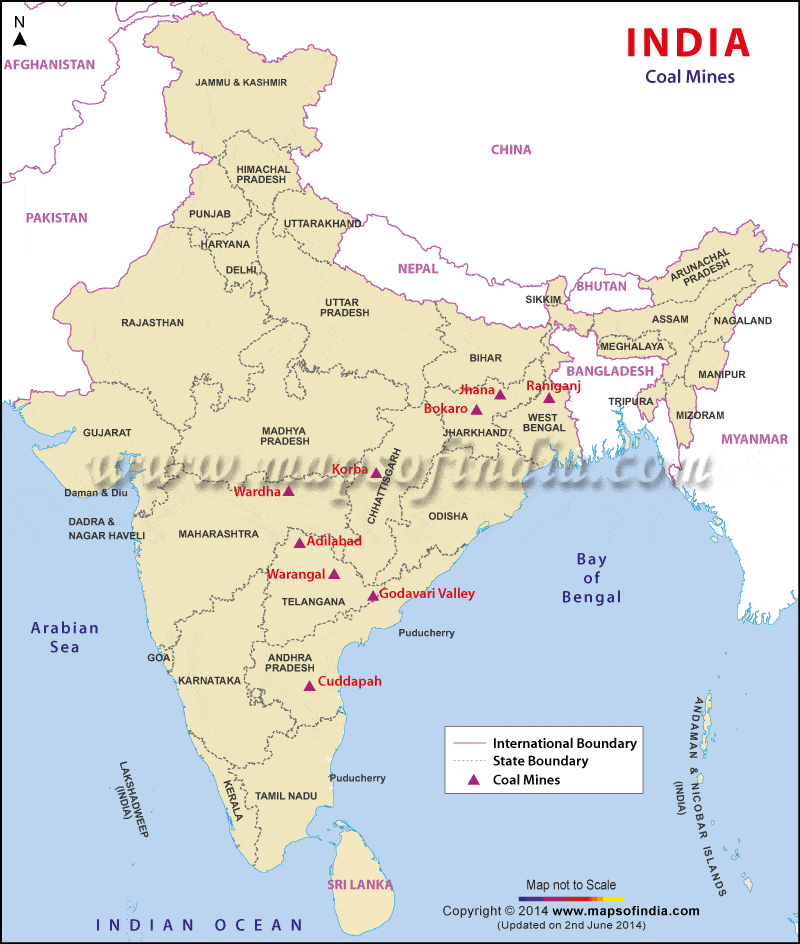
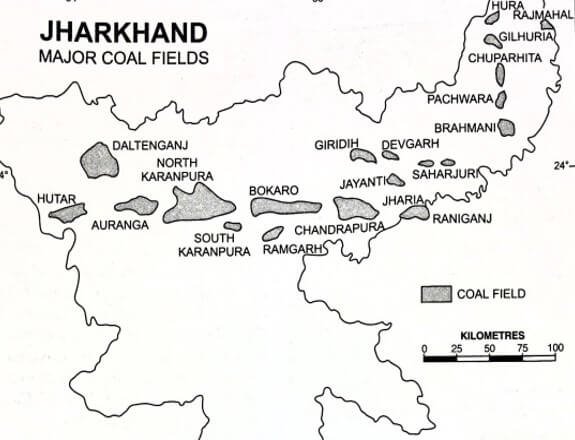
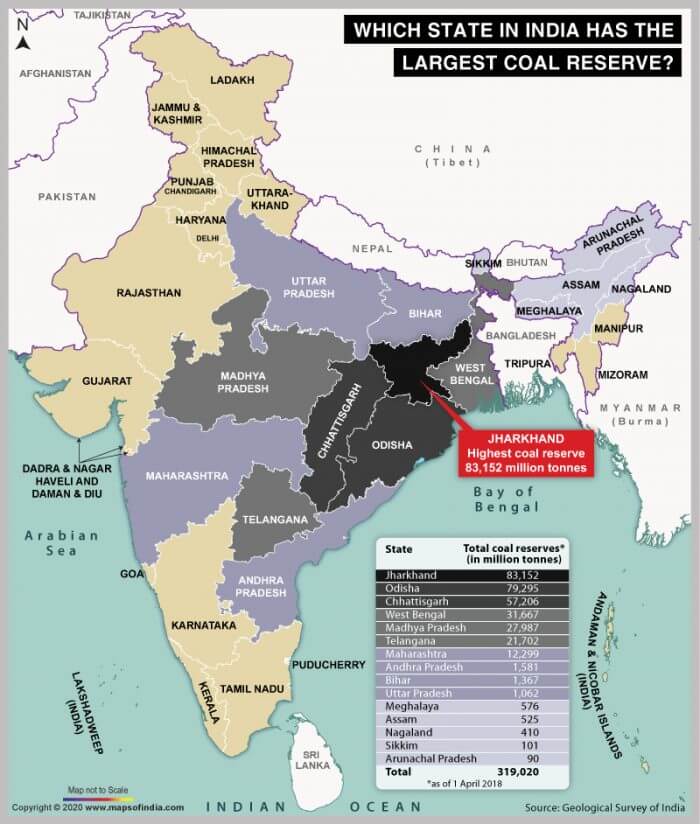
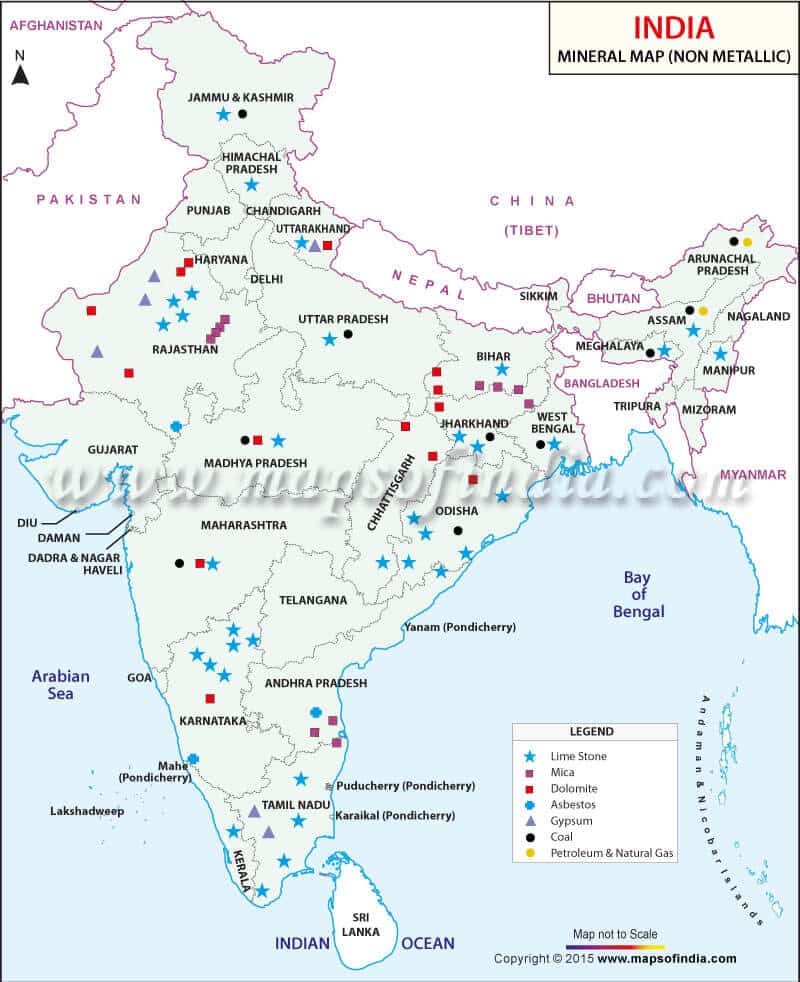
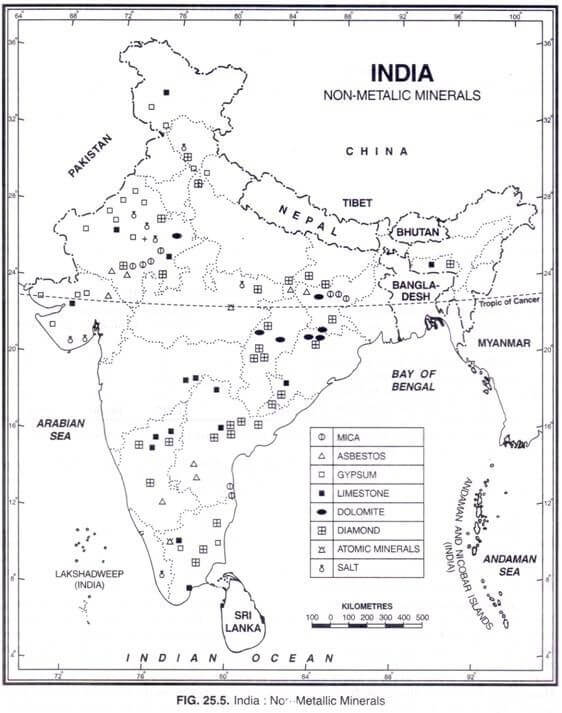
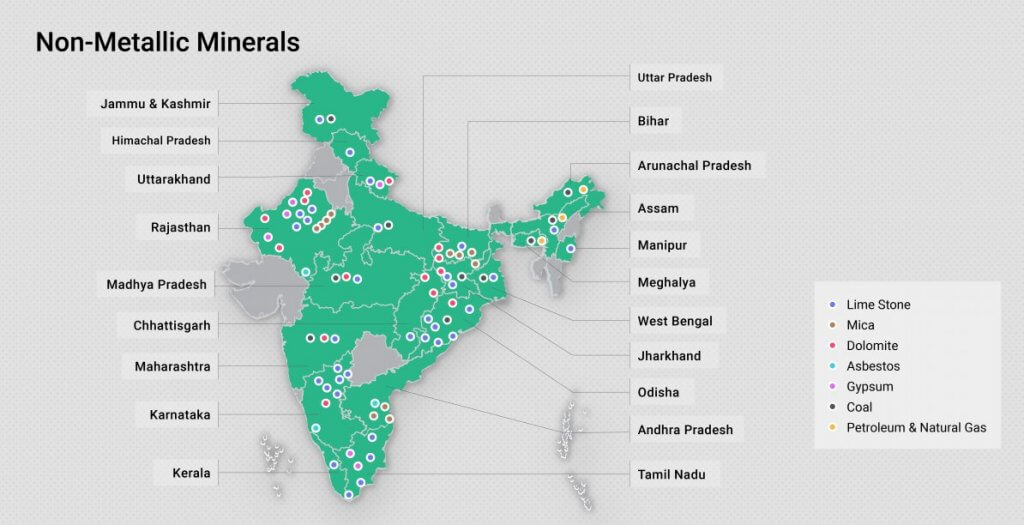
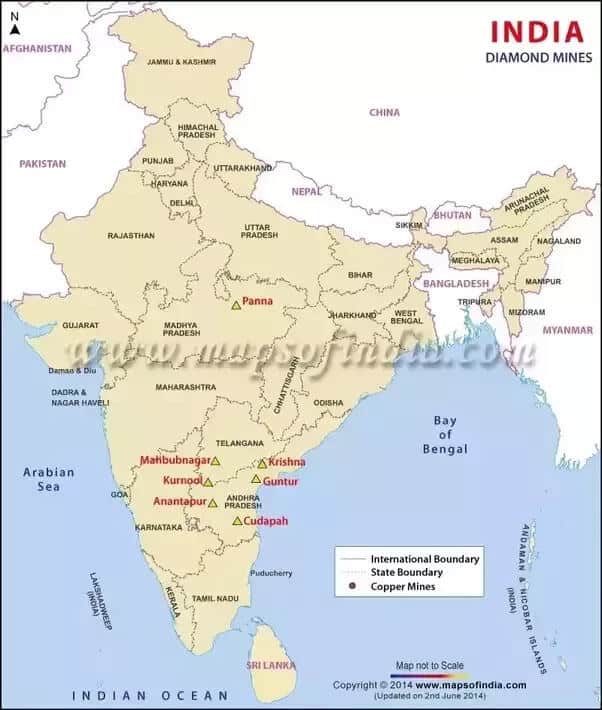
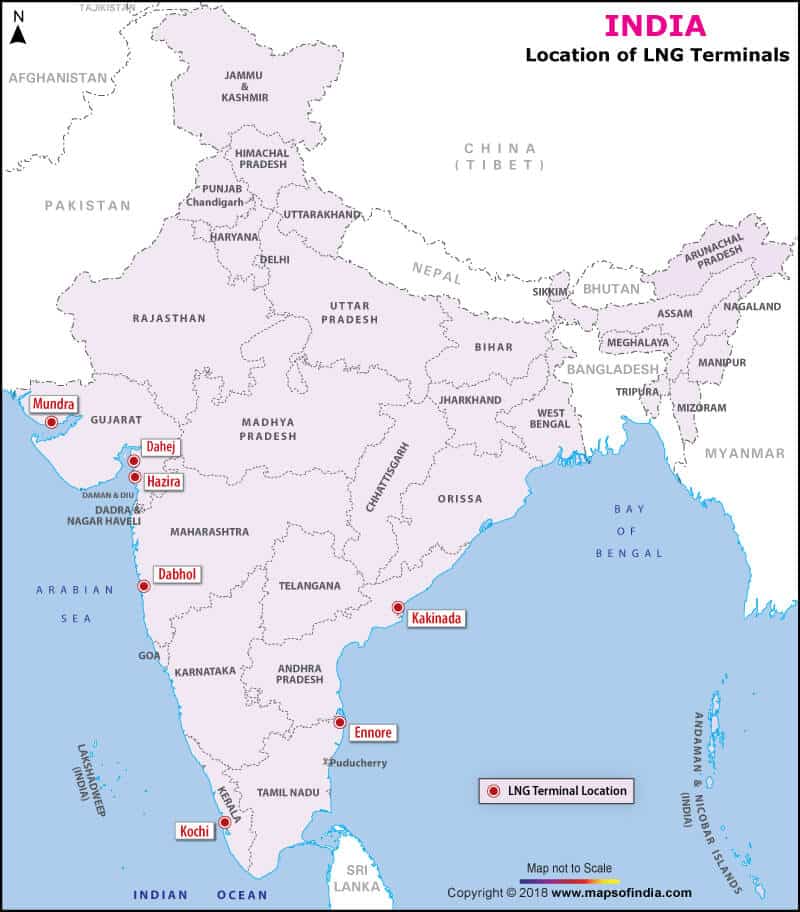
 के मझगांव में</strong>84,000 कैरेट की उत्पादन क्षमता वाली एकमात्र खदान है और इस खदान से अब तक बरामद कुल हीरे 1 मिलियन कैरेट से थोड़ा अधिक हैं।</li></ul></li></ul><div class=)
 ग्रेफाइट (Graphite)
ग्रेफाइट (Graphite)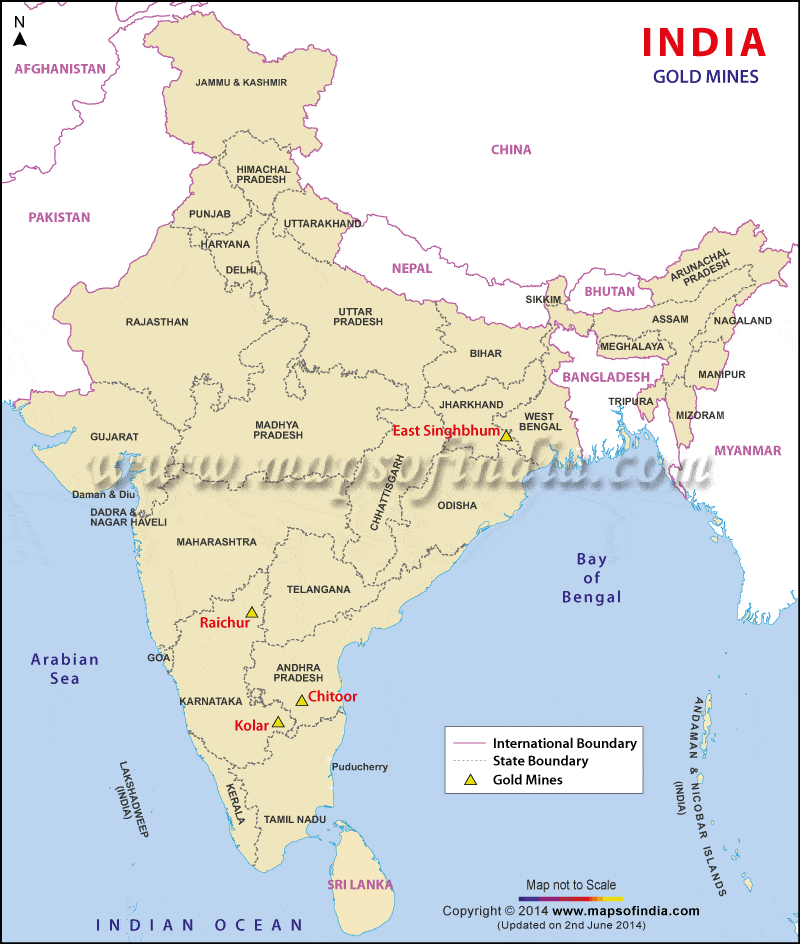
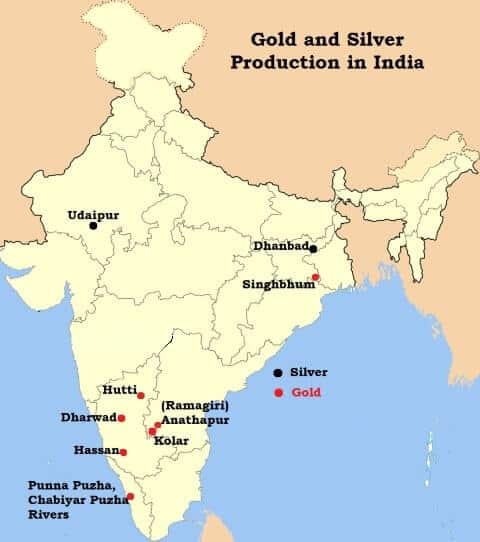
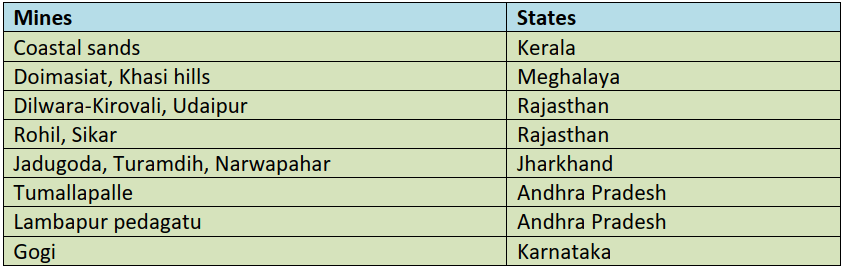

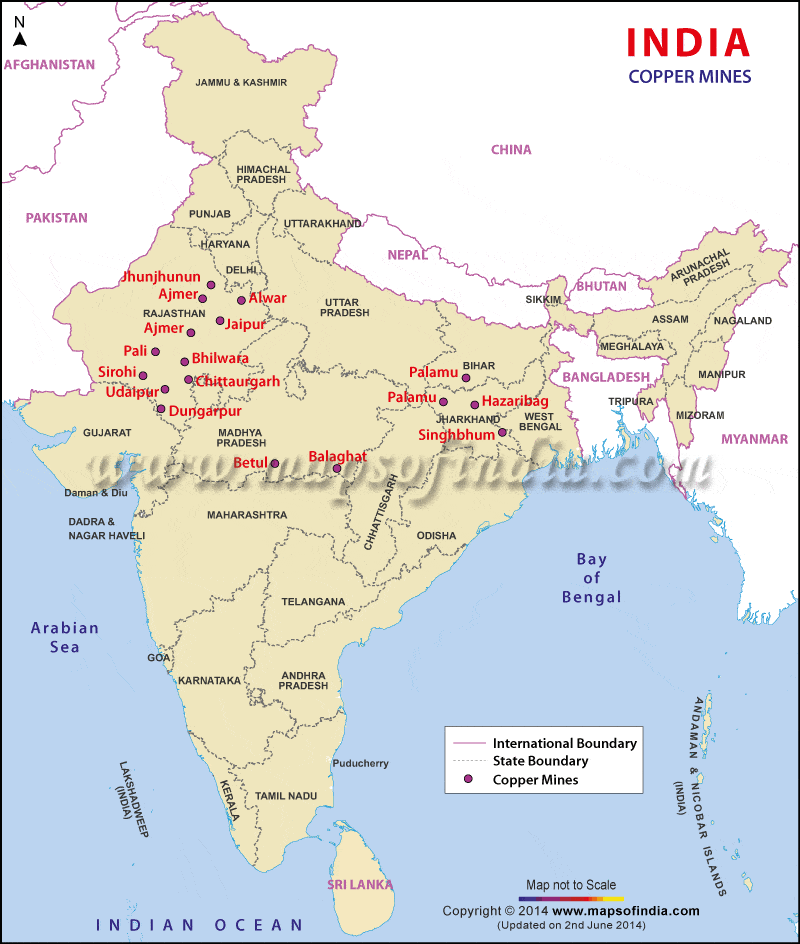
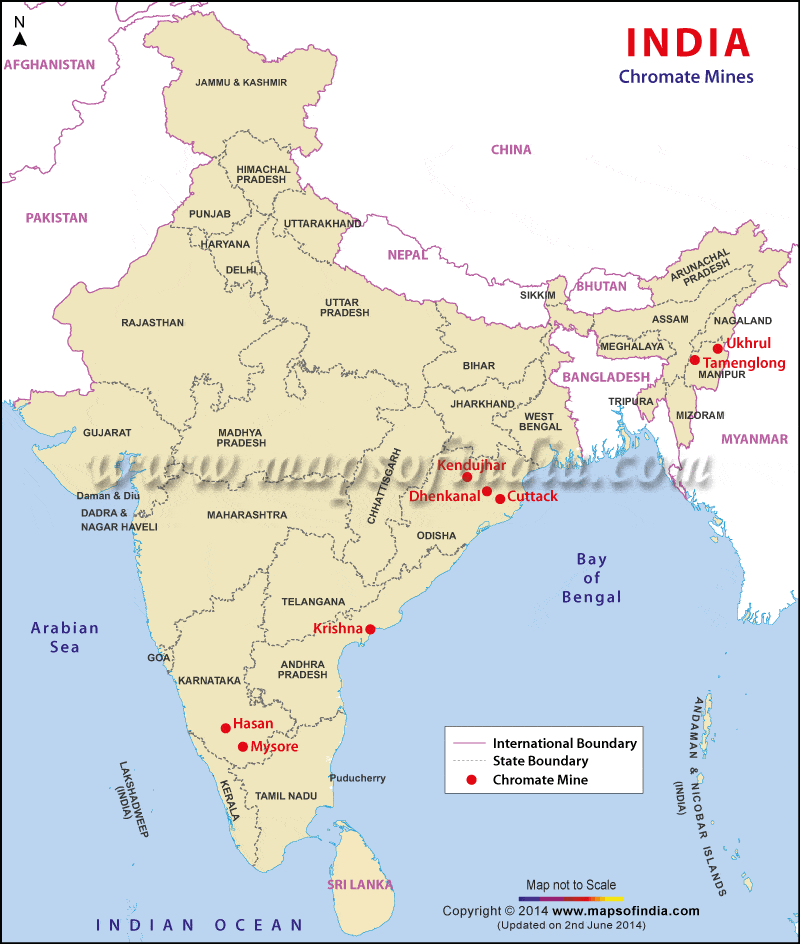
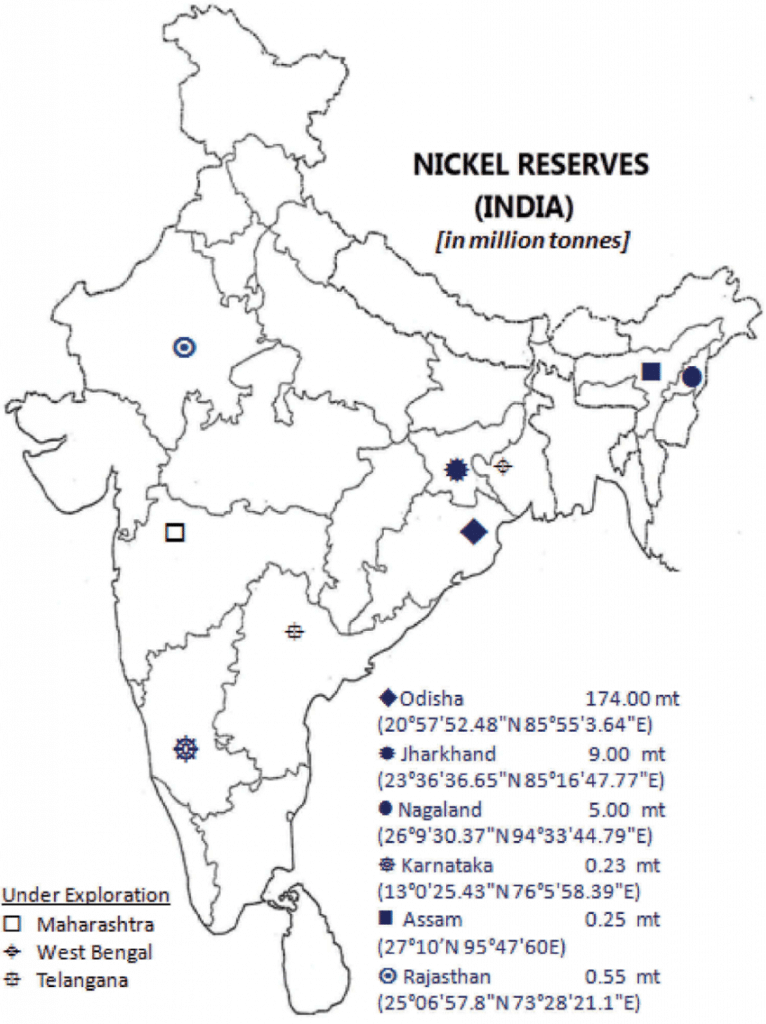


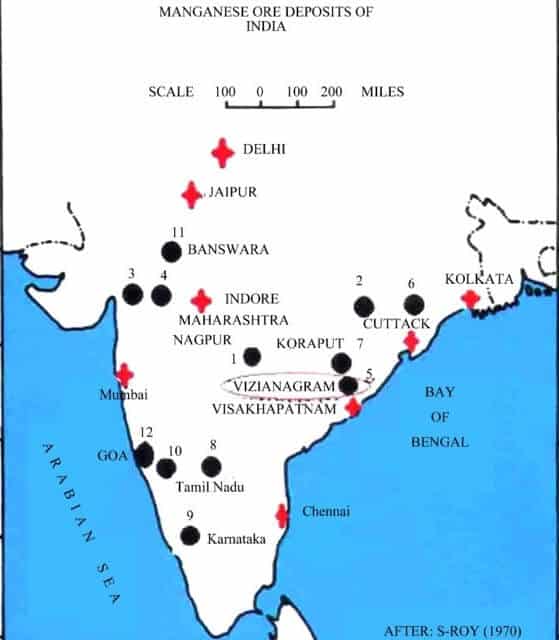

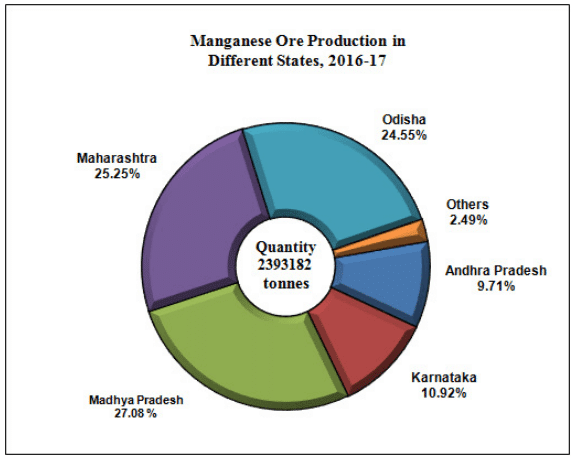
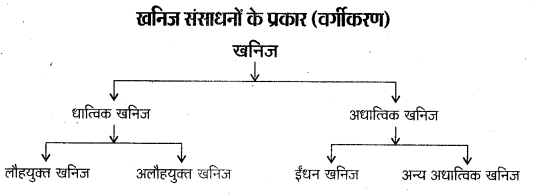
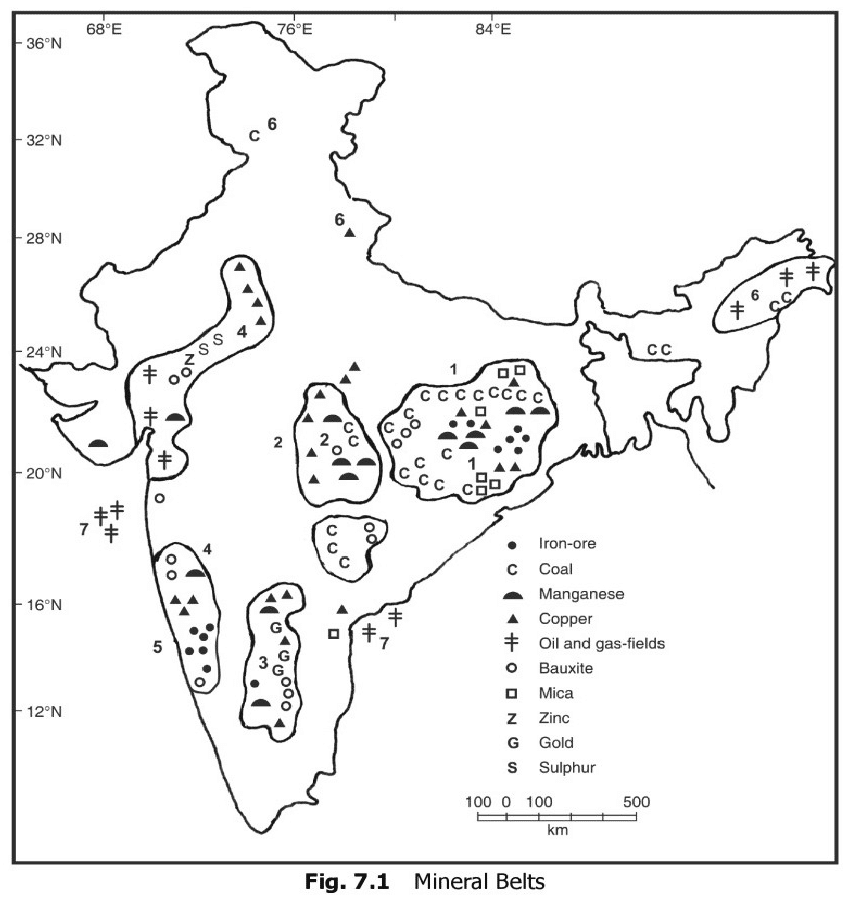
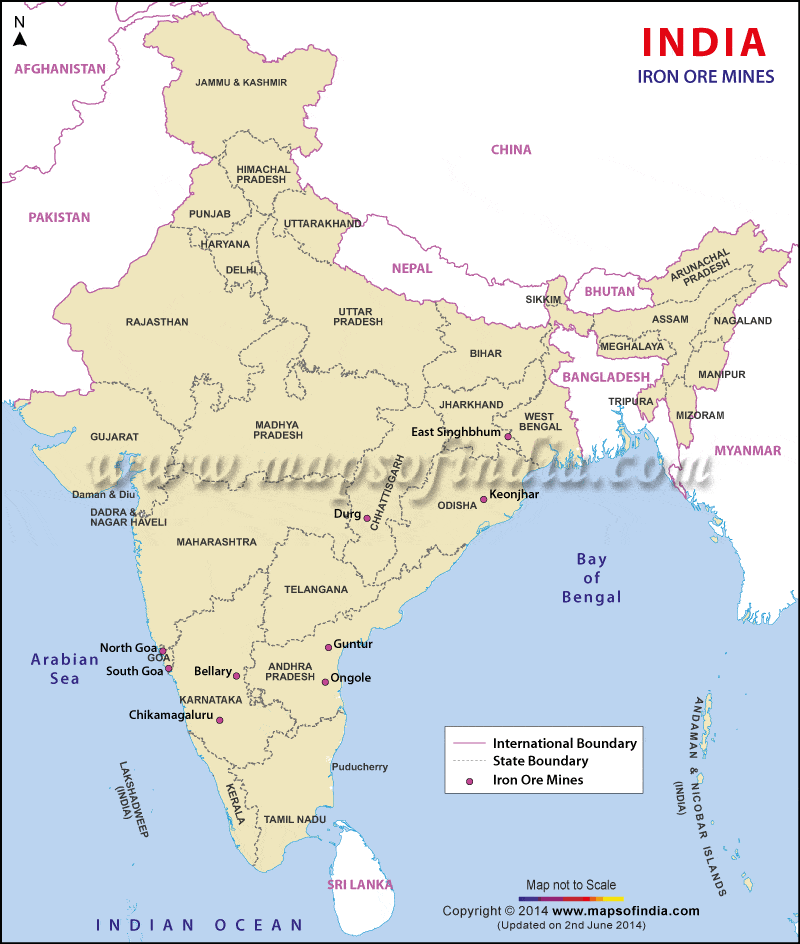
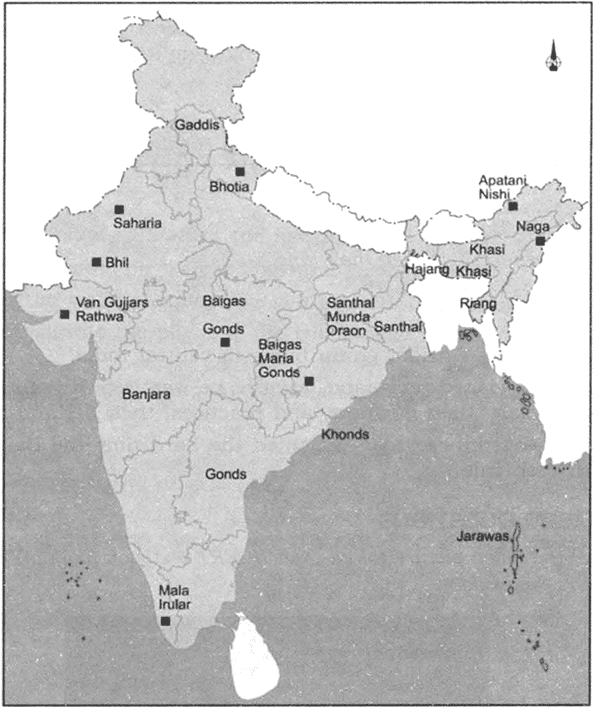
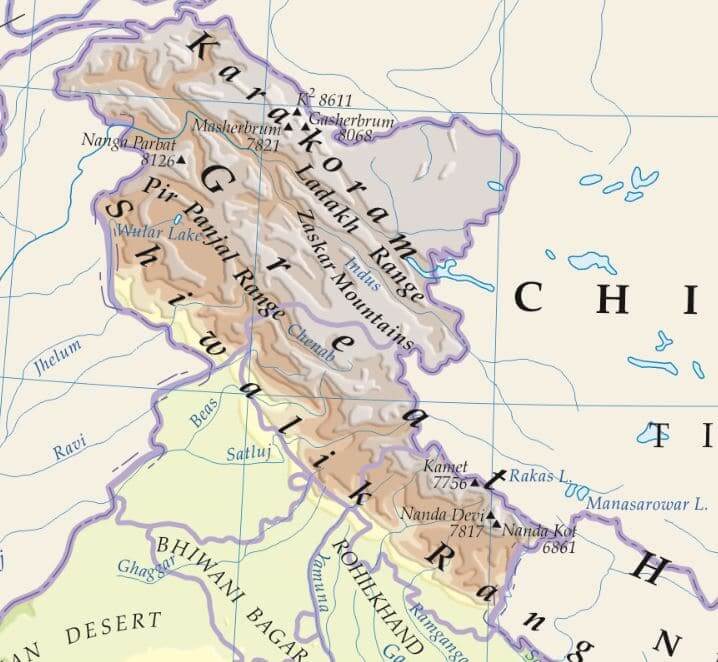
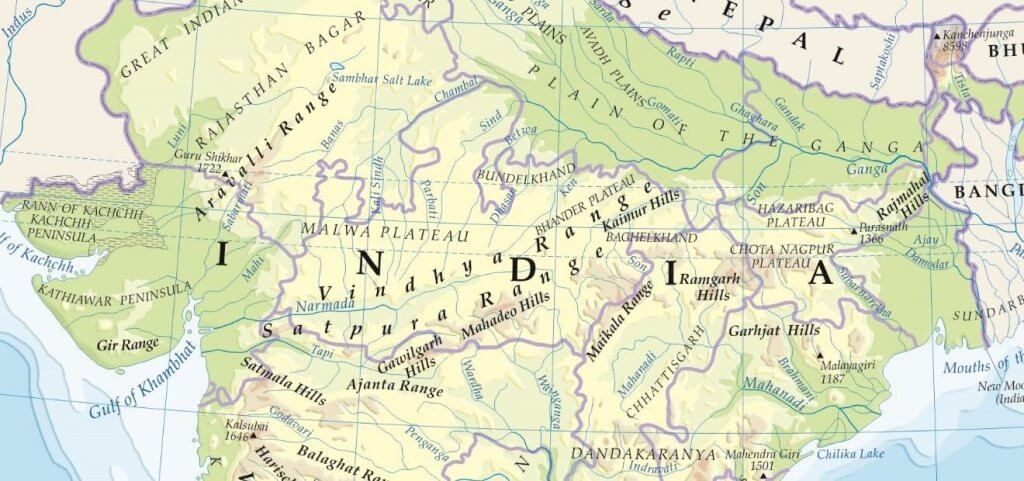
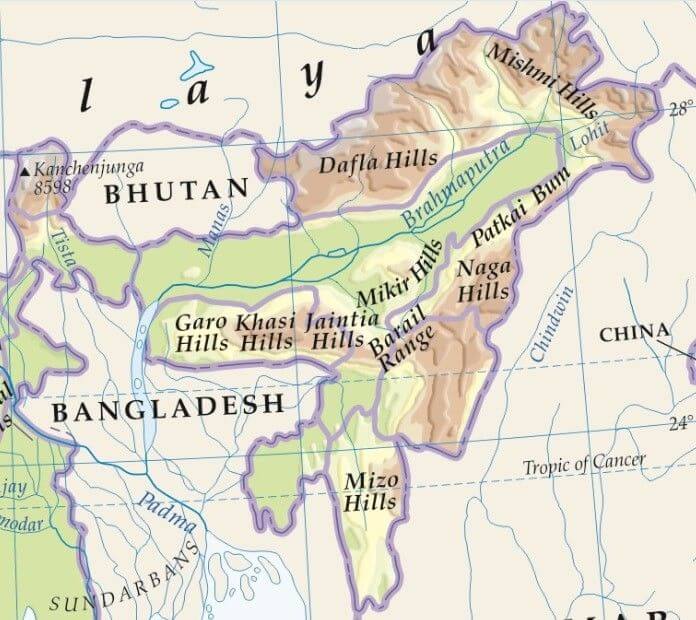
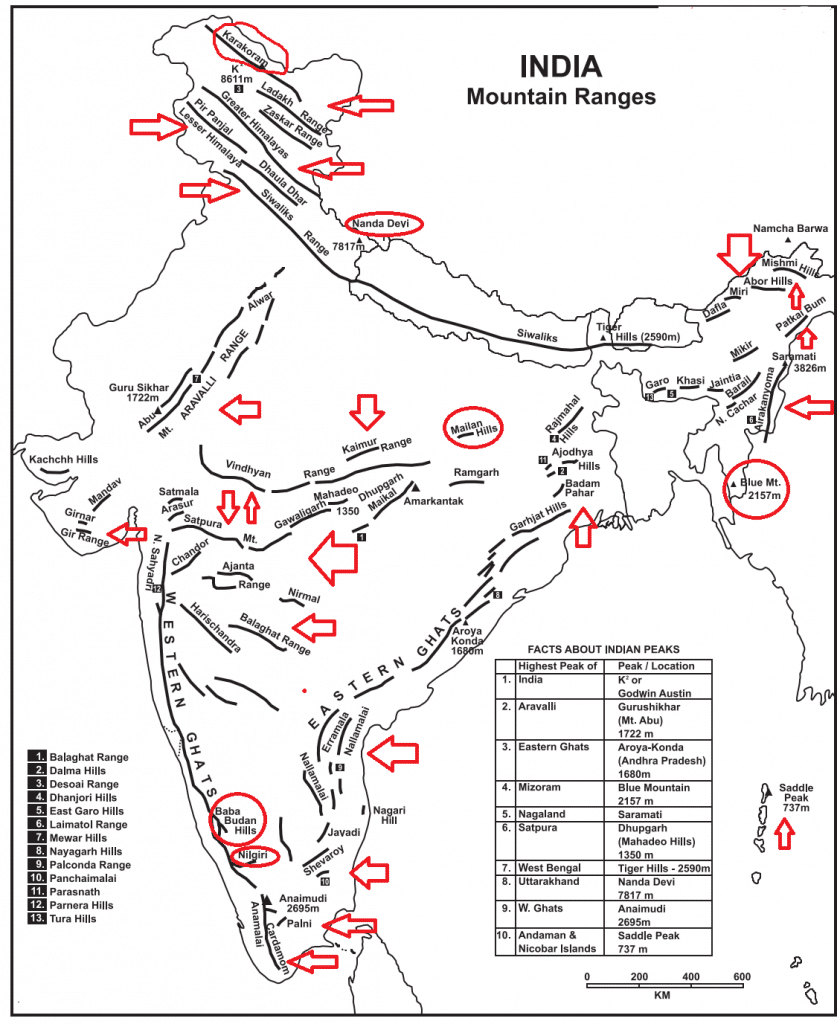
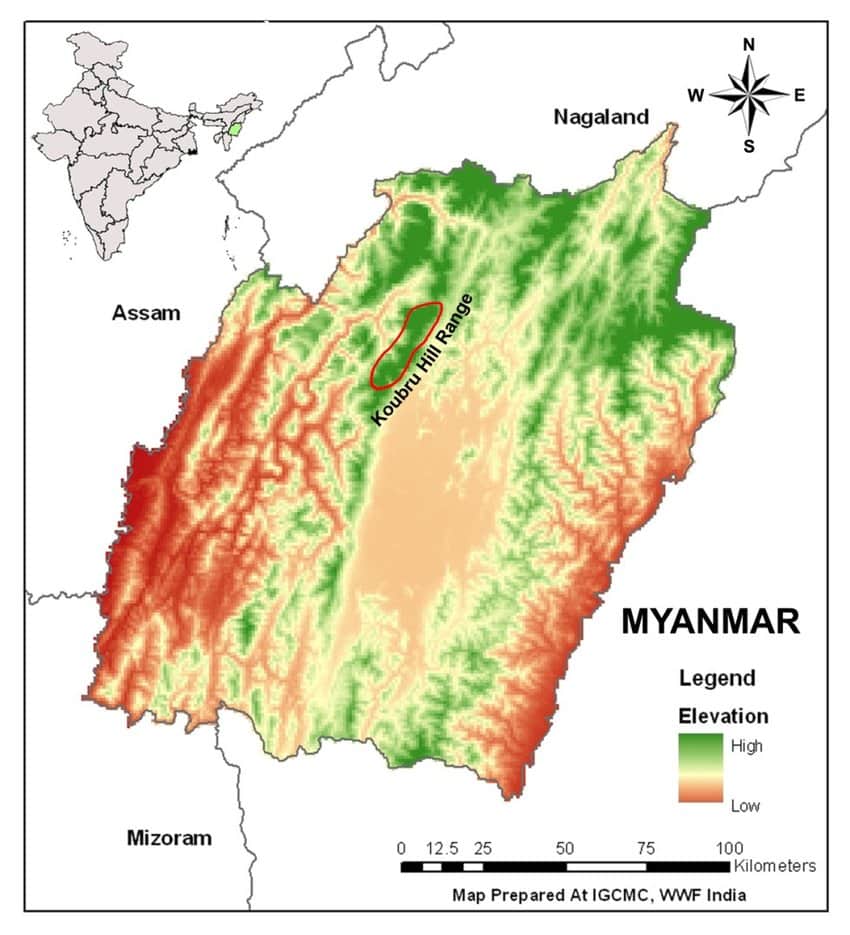
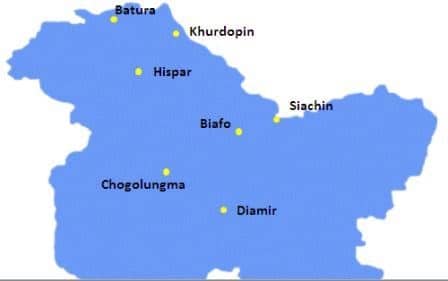
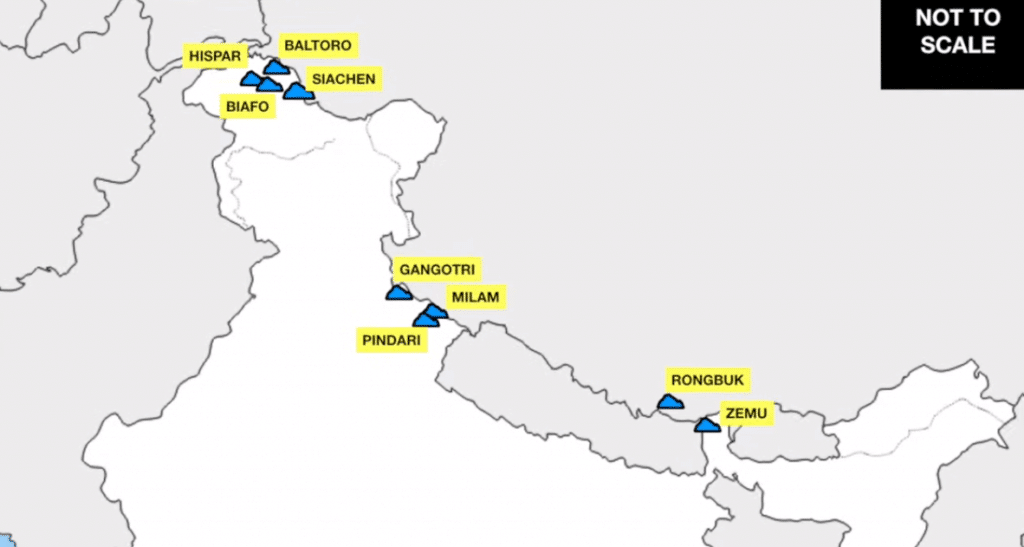
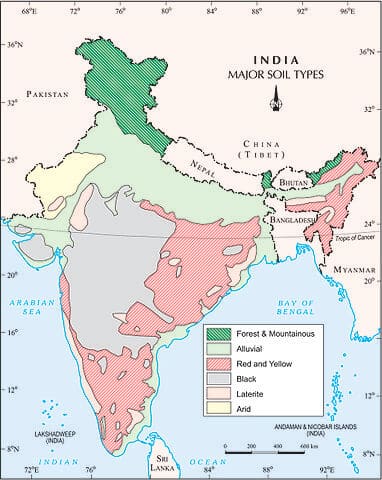
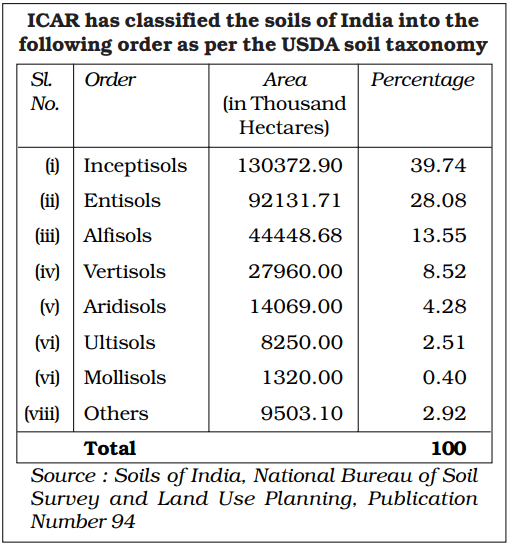
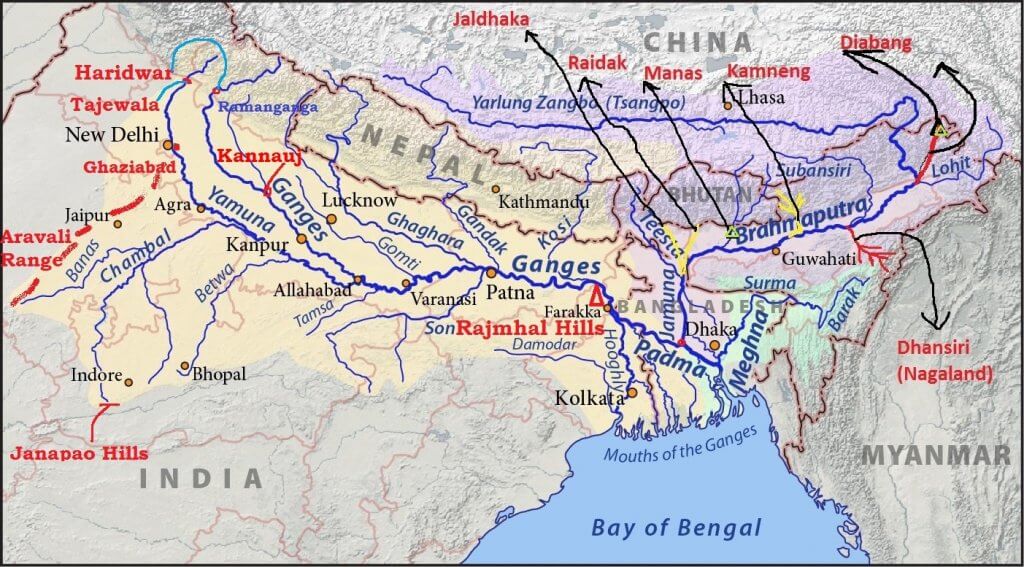
 भारत में महत्वपूर्ण ग्लेशियर
भारत में महत्वपूर्ण ग्लेशियर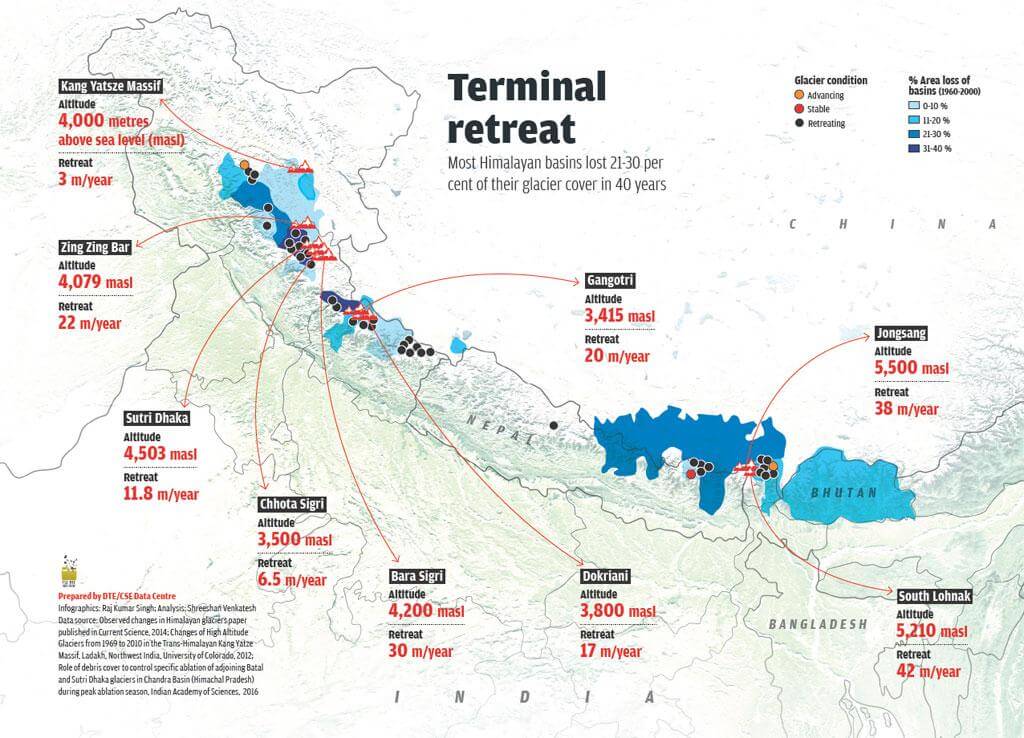
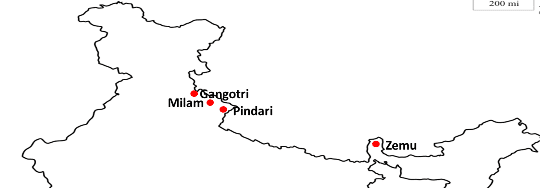





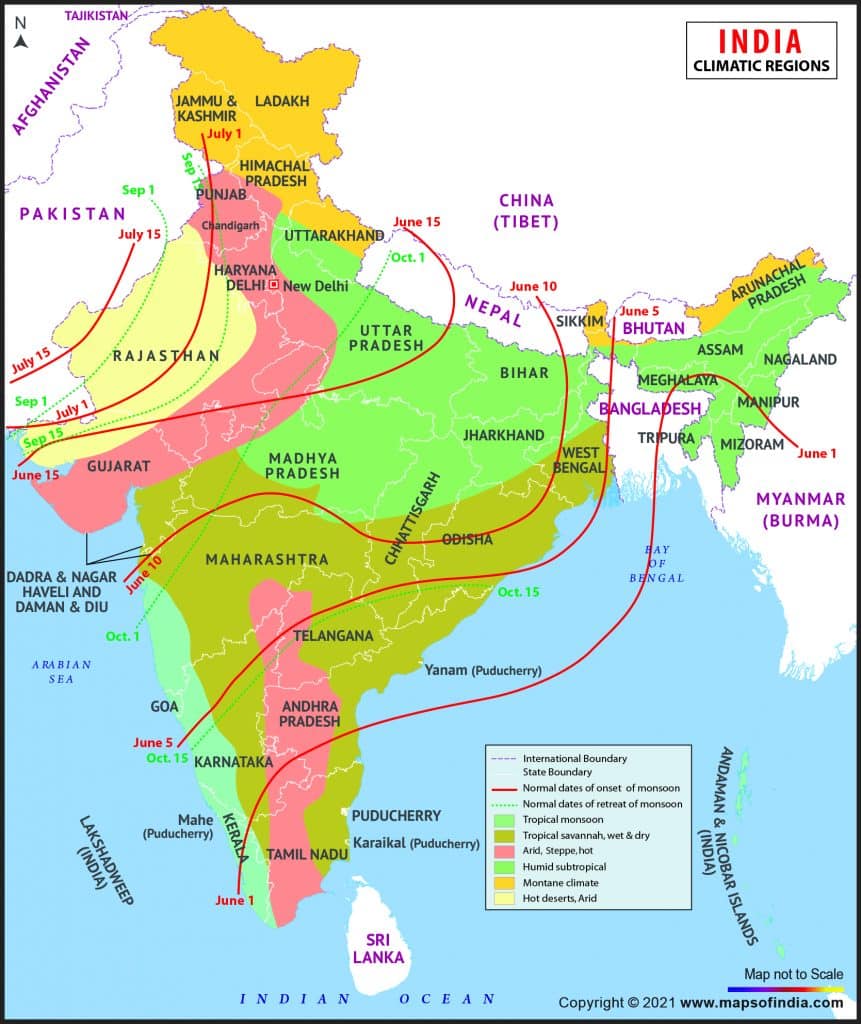
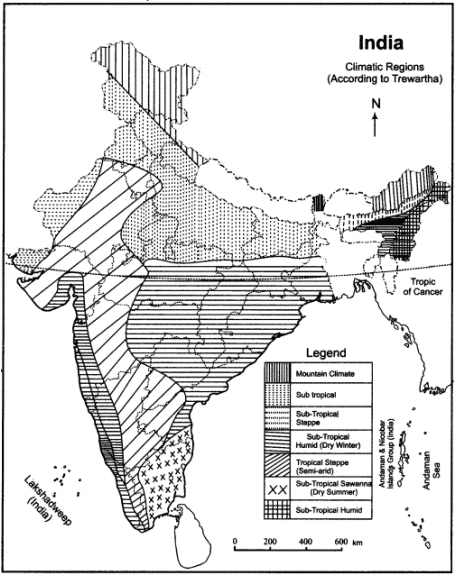
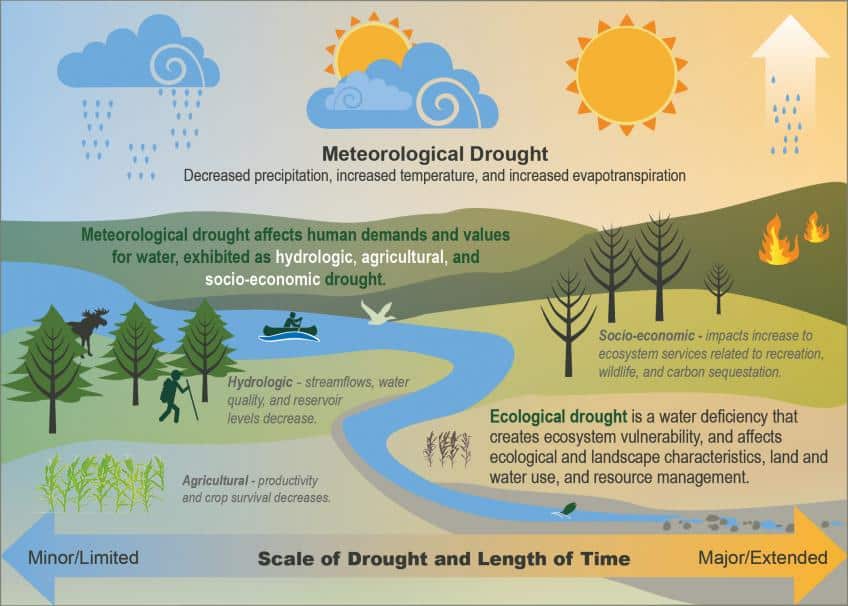

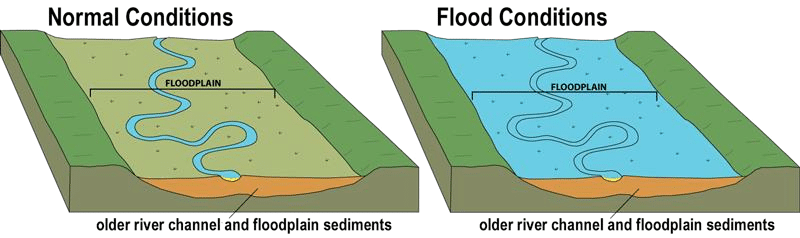
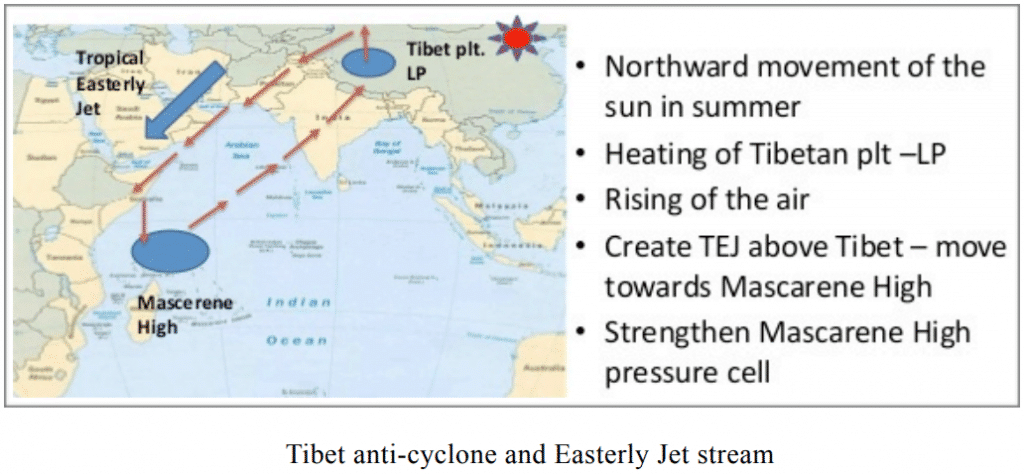
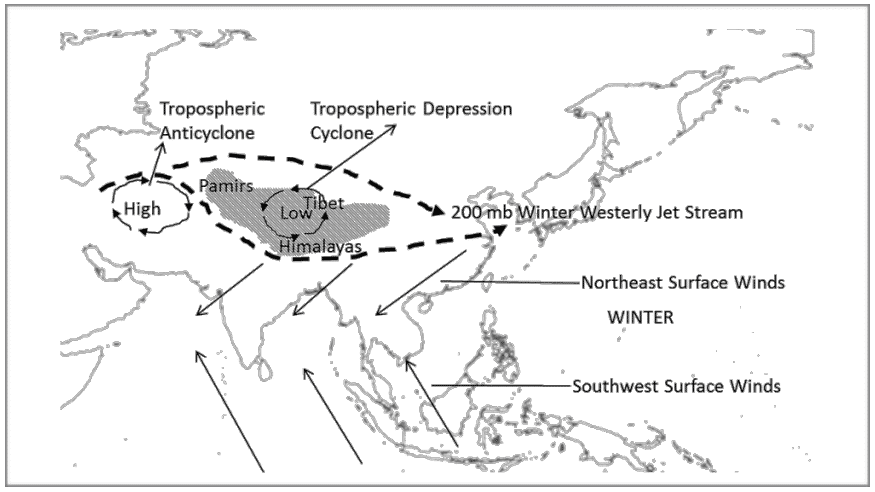
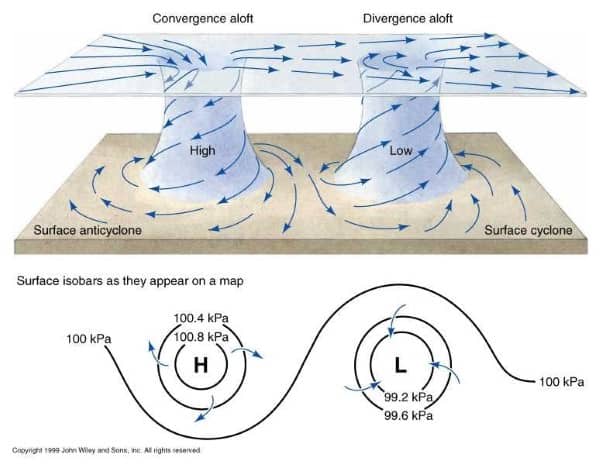
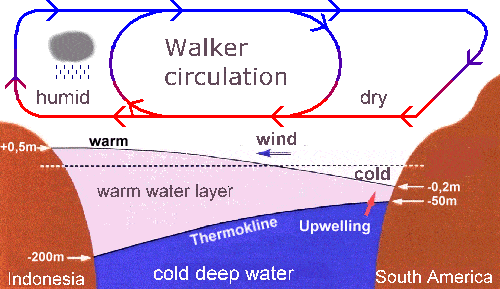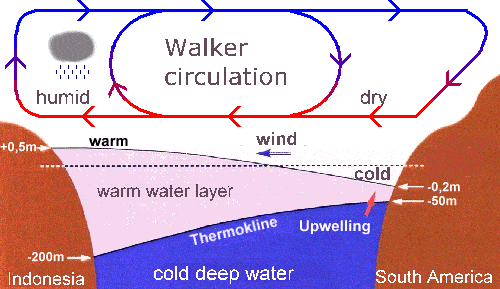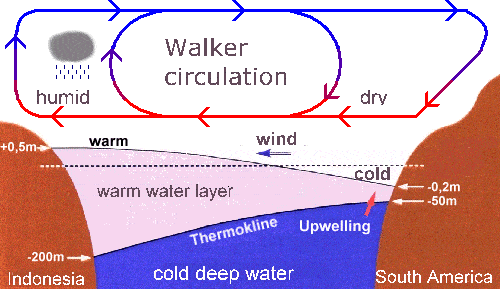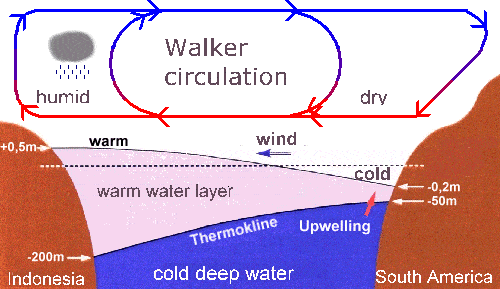
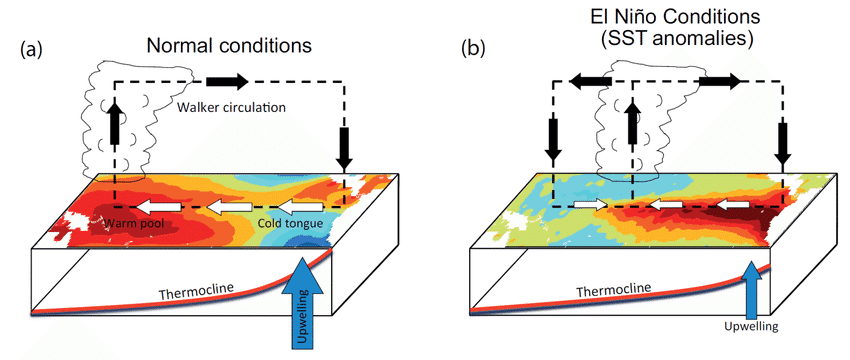
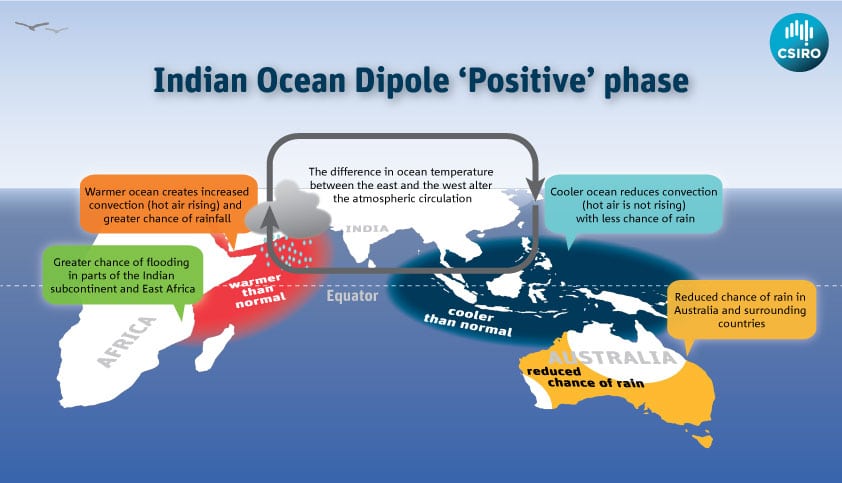
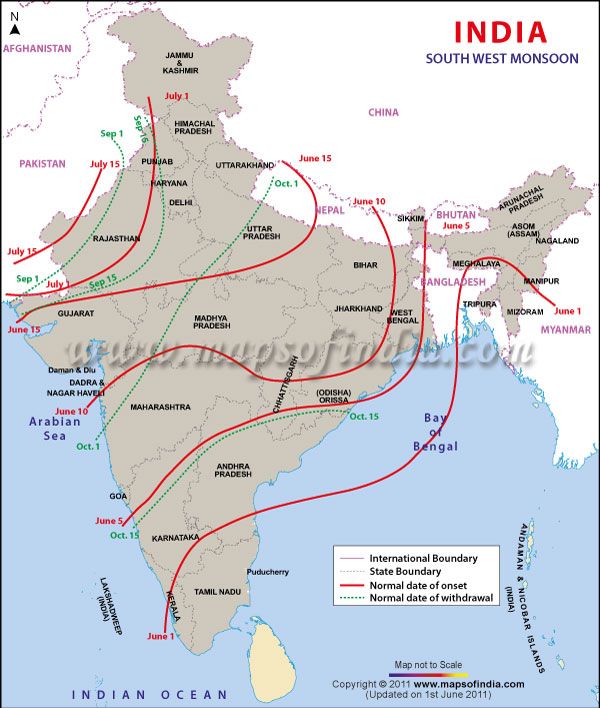
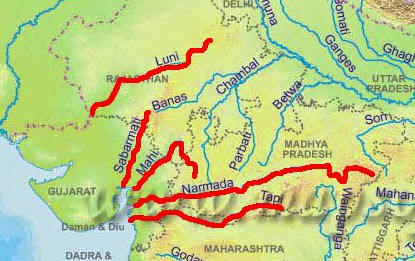
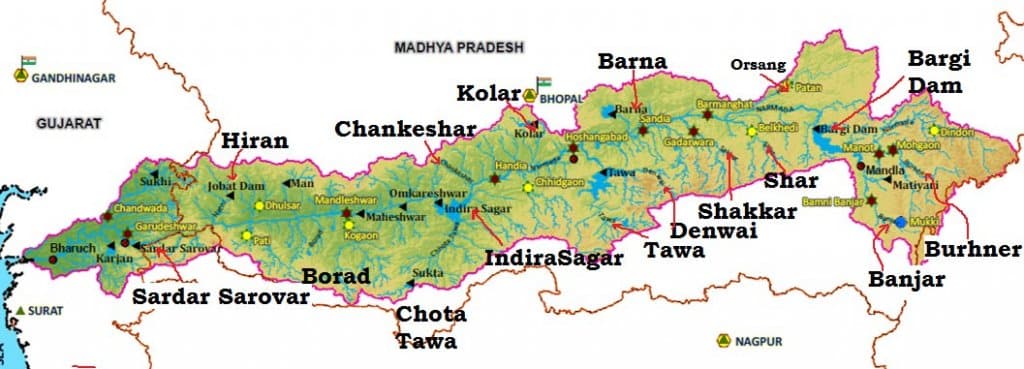
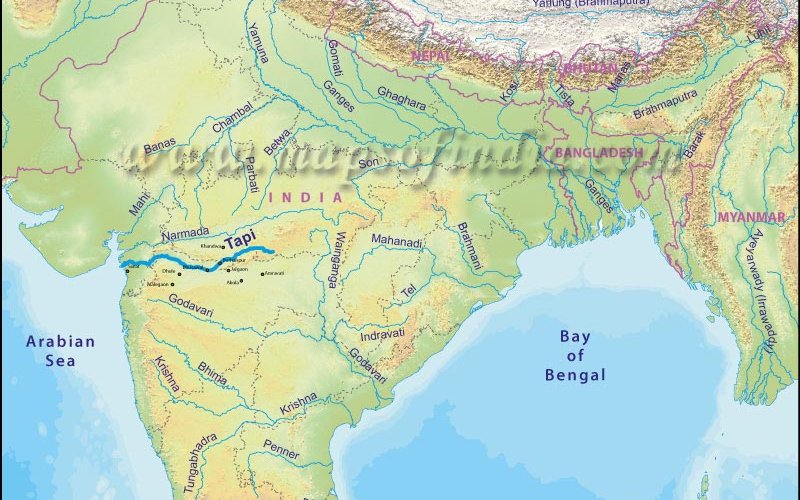
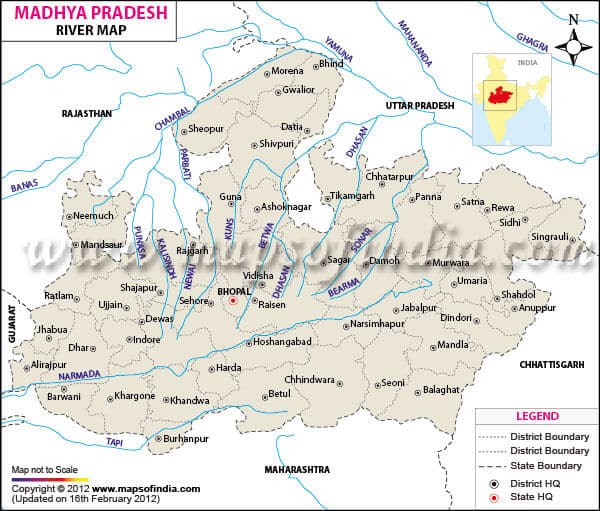
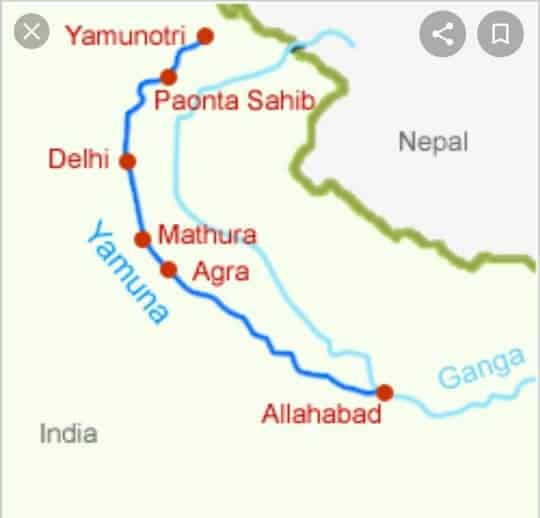
 साबरमती नदी
साबरमती नदी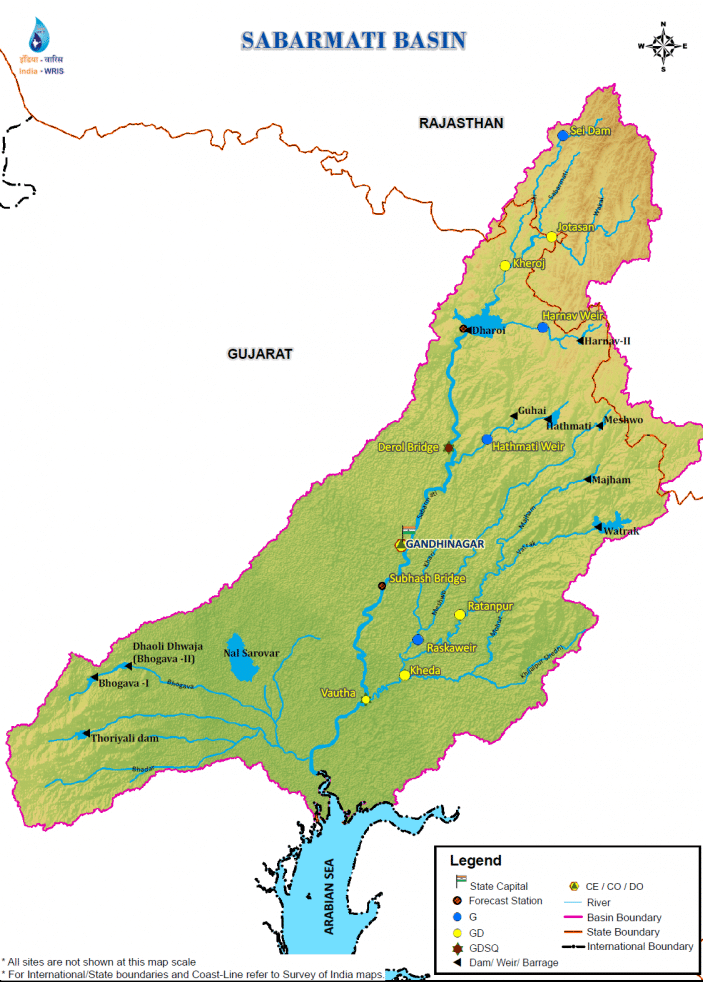
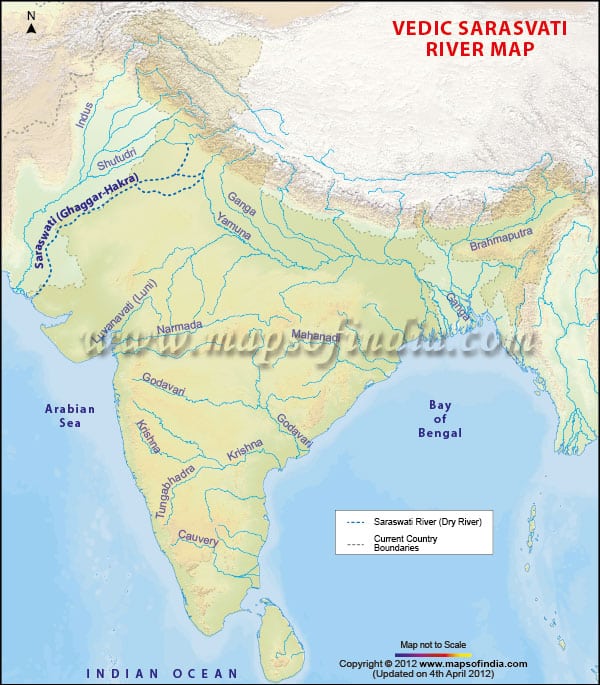
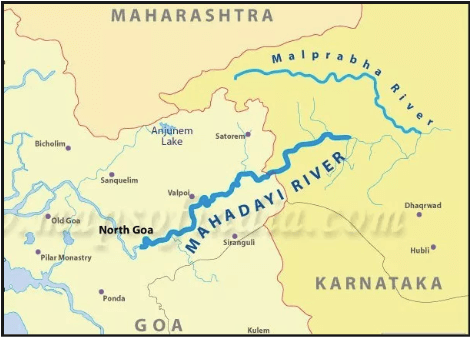
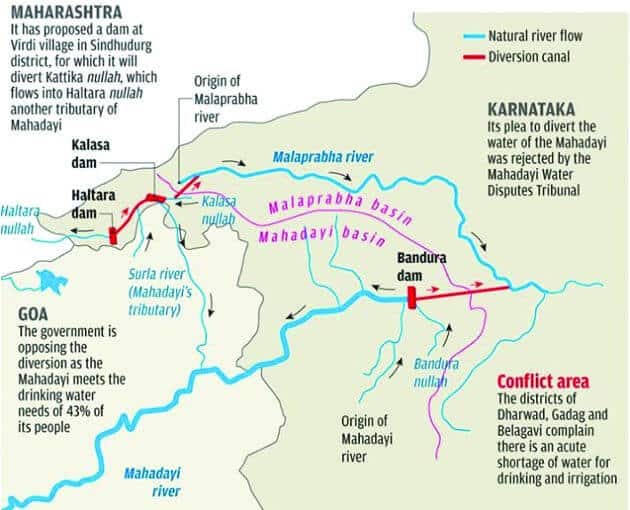
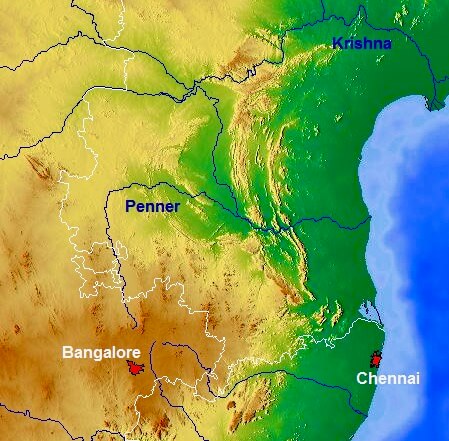
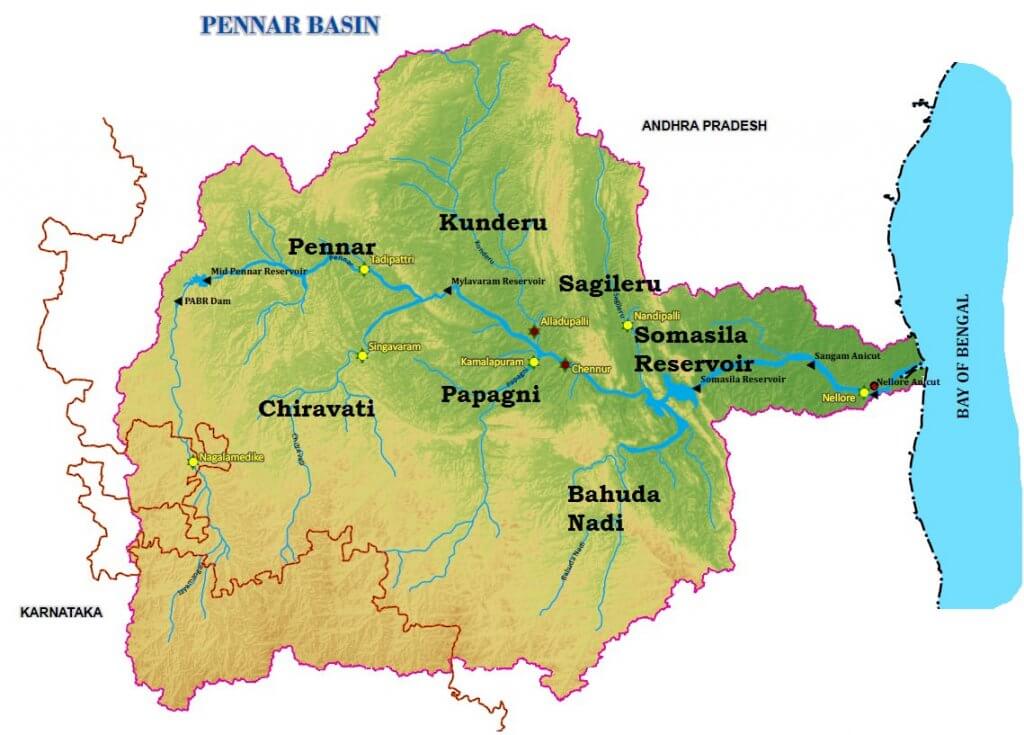
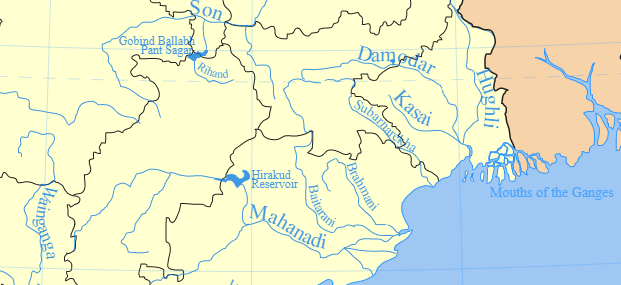
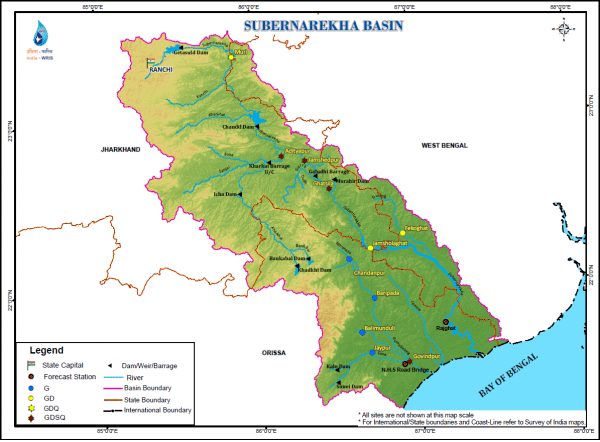
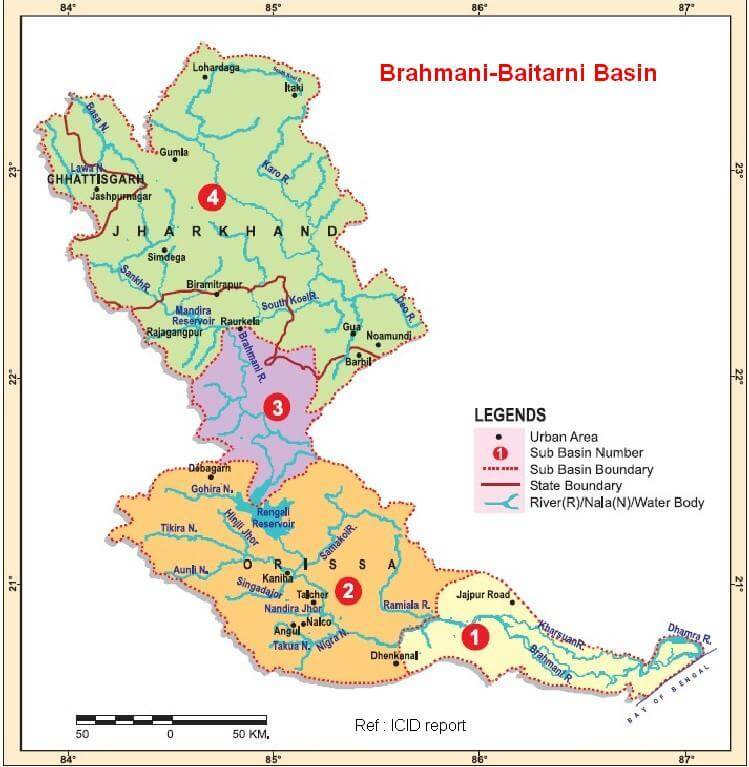
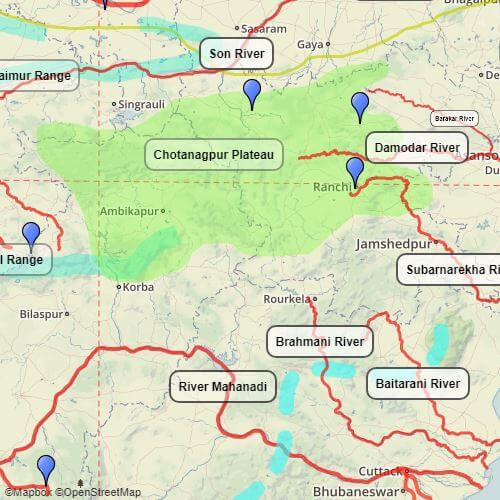
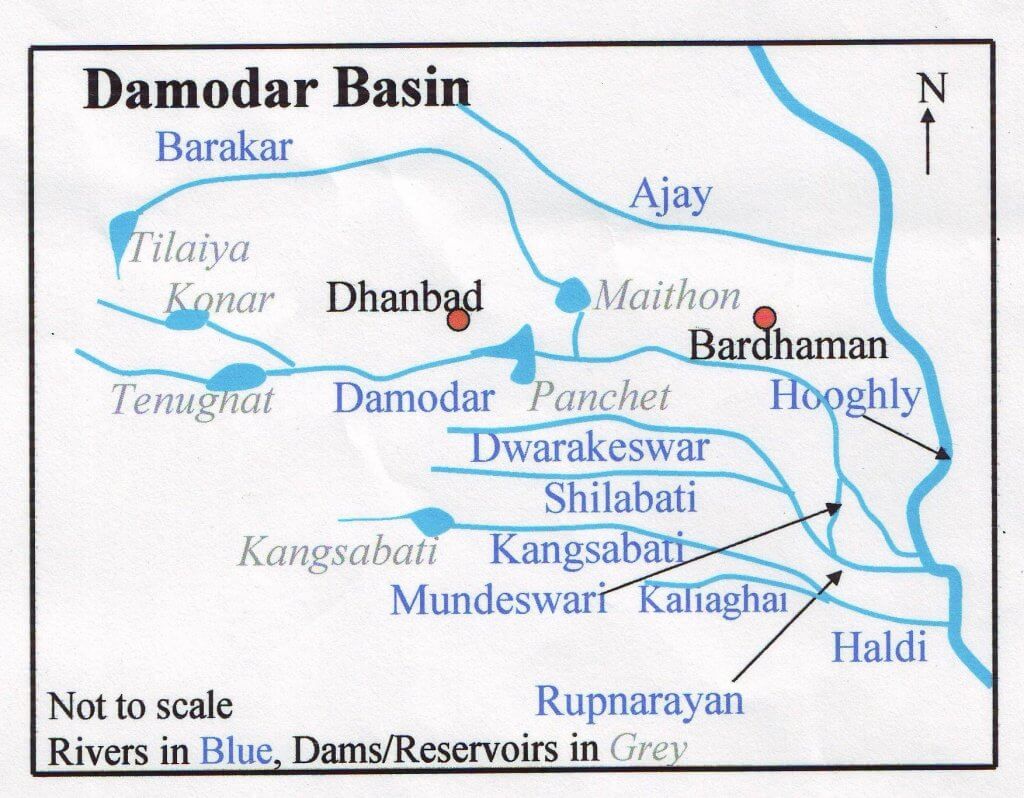
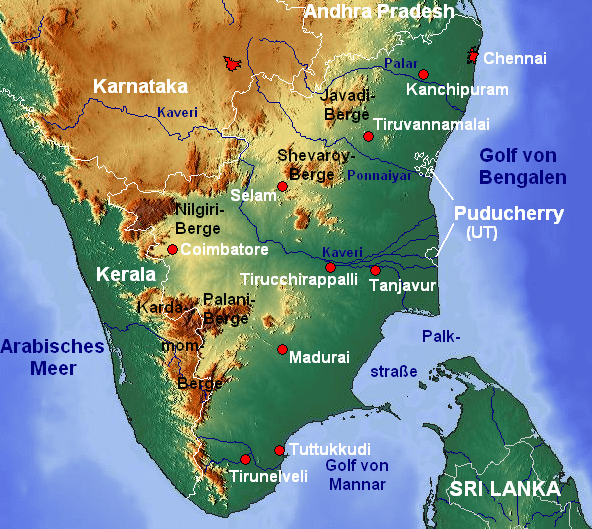
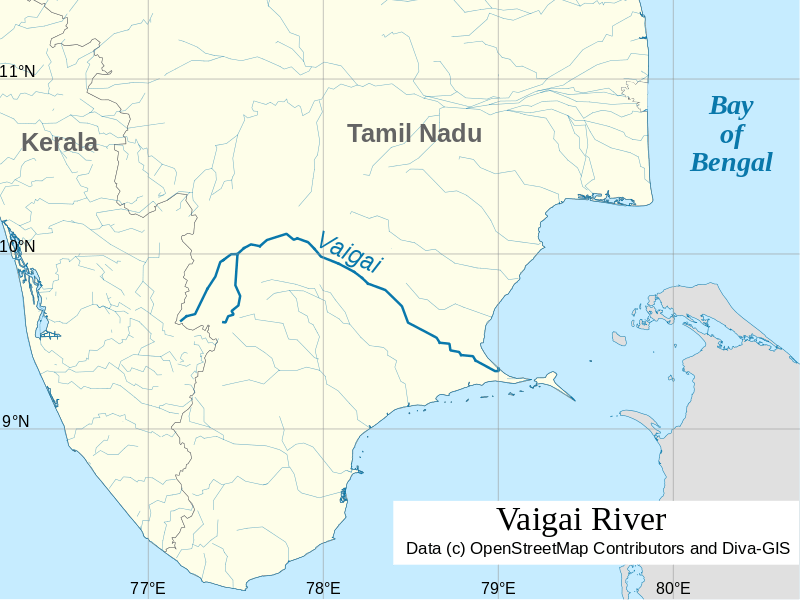
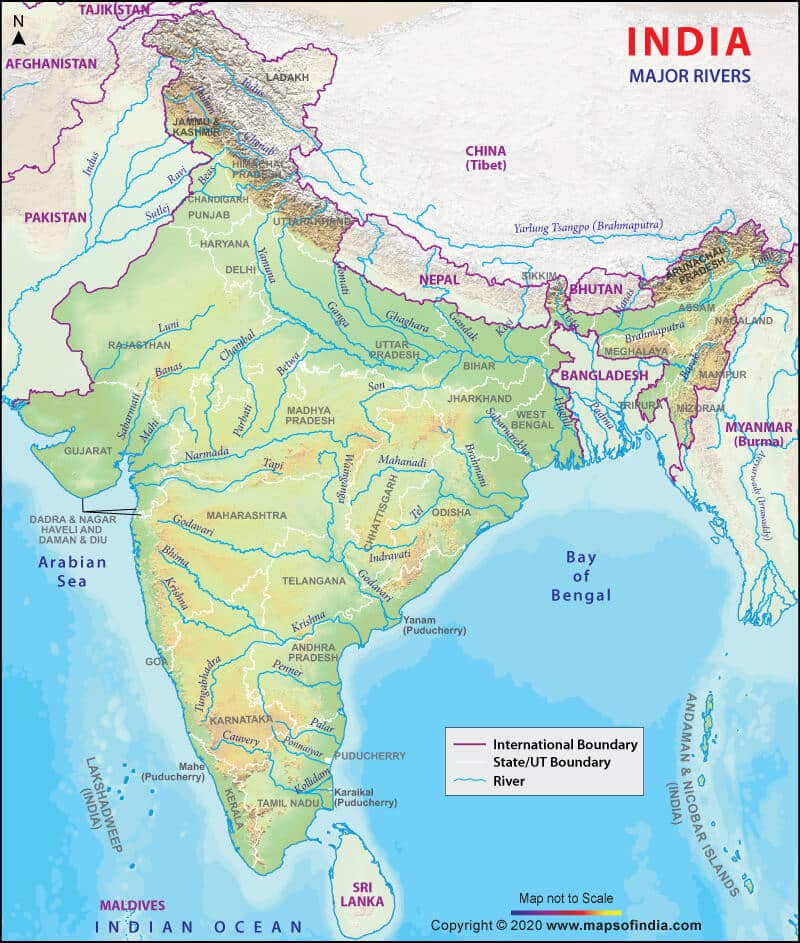
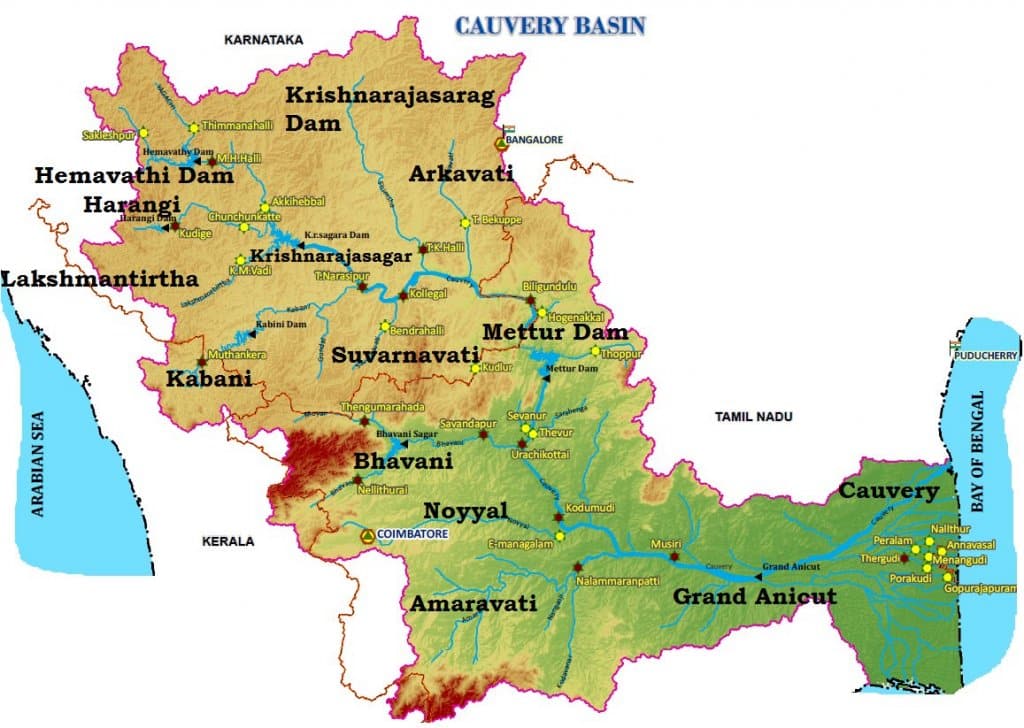
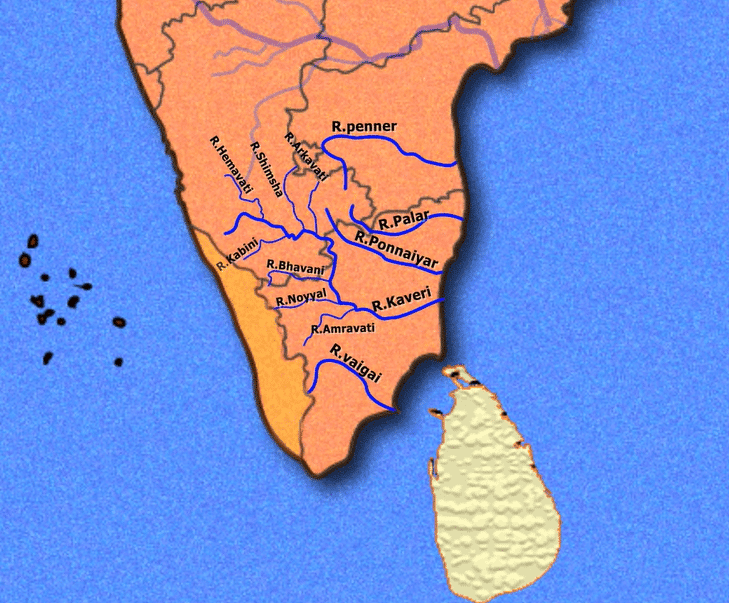
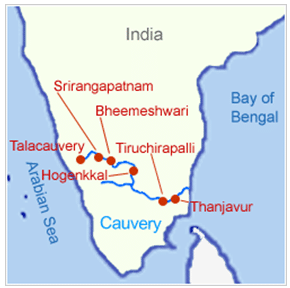
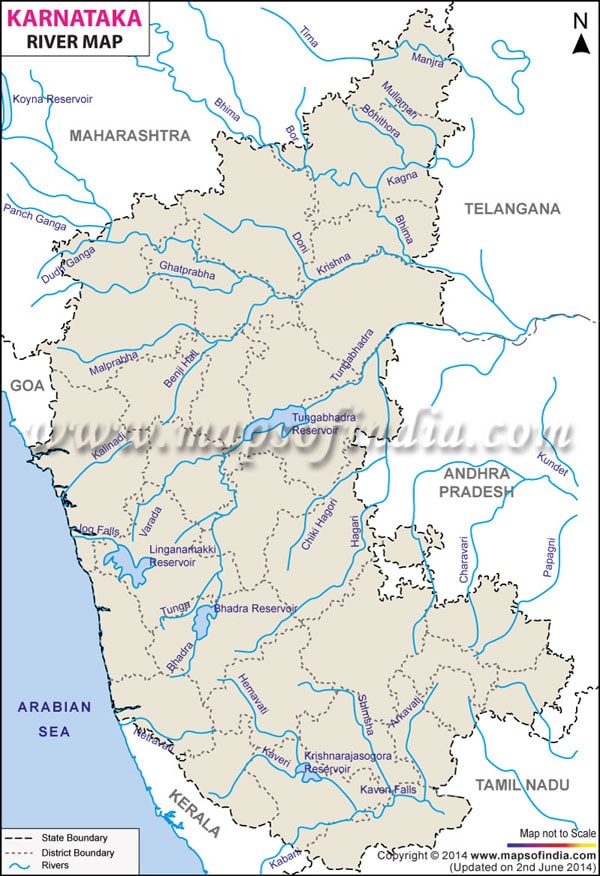
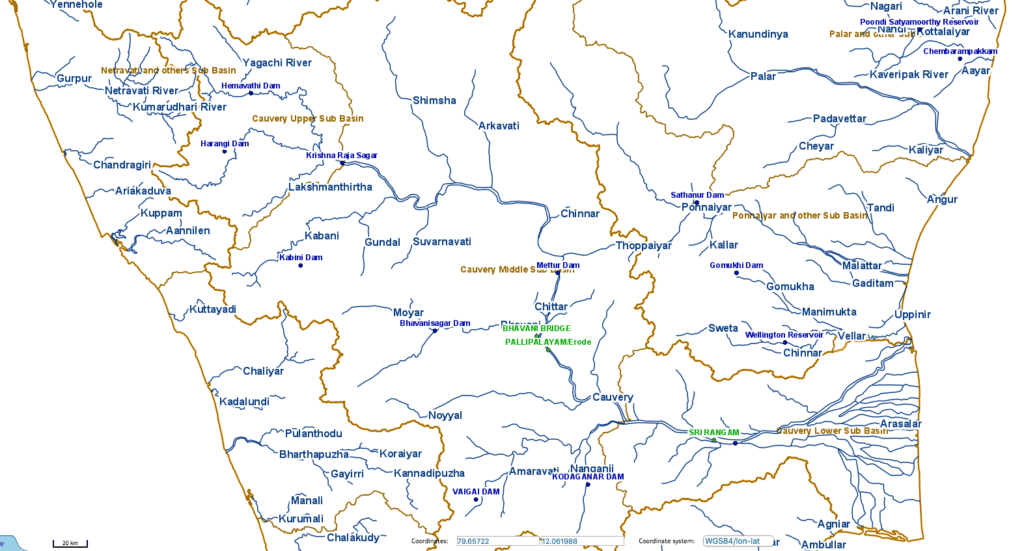
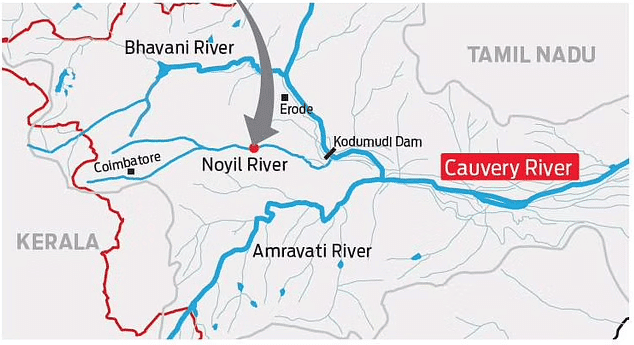
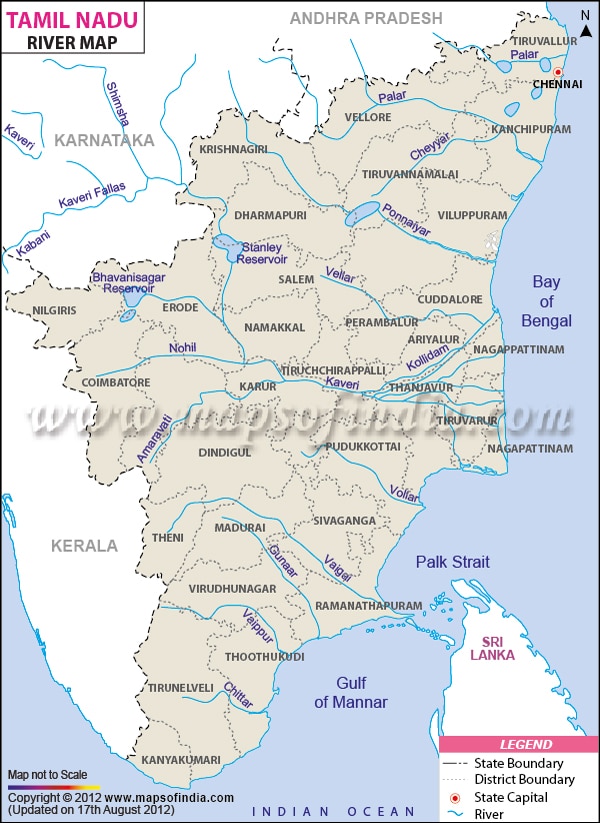
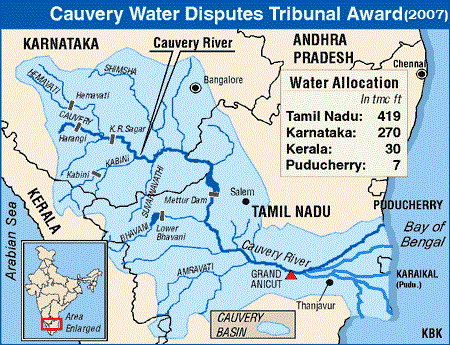
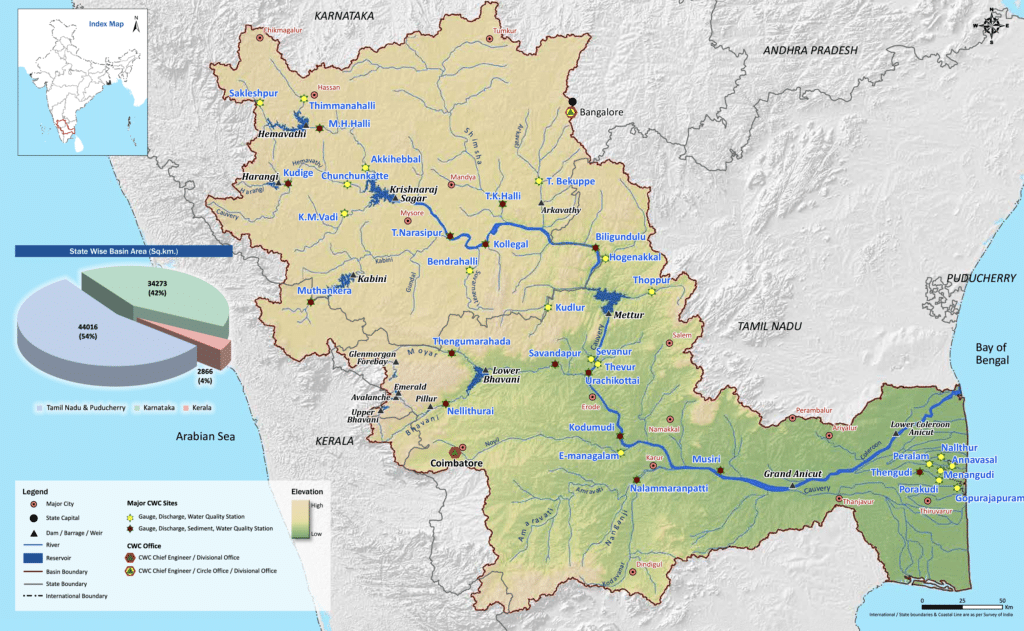
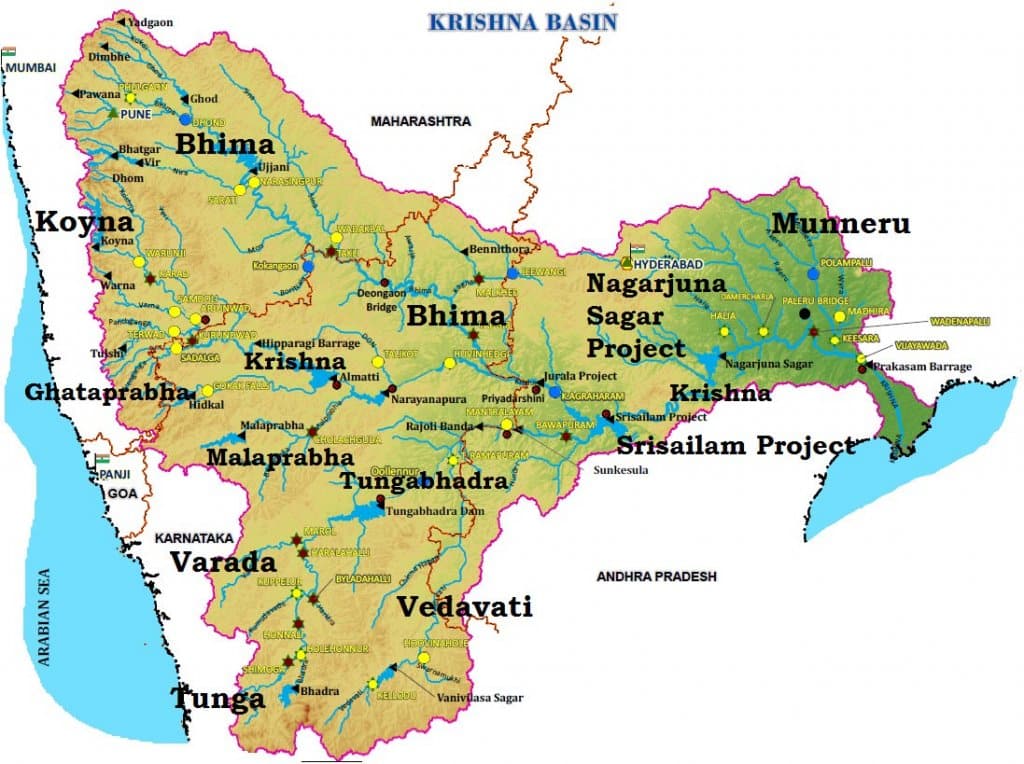
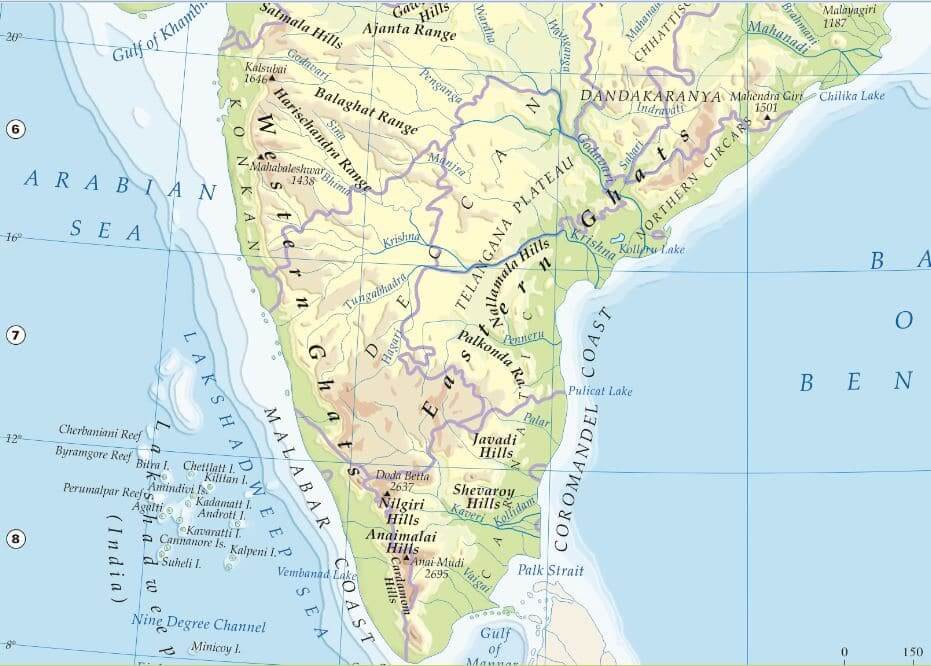
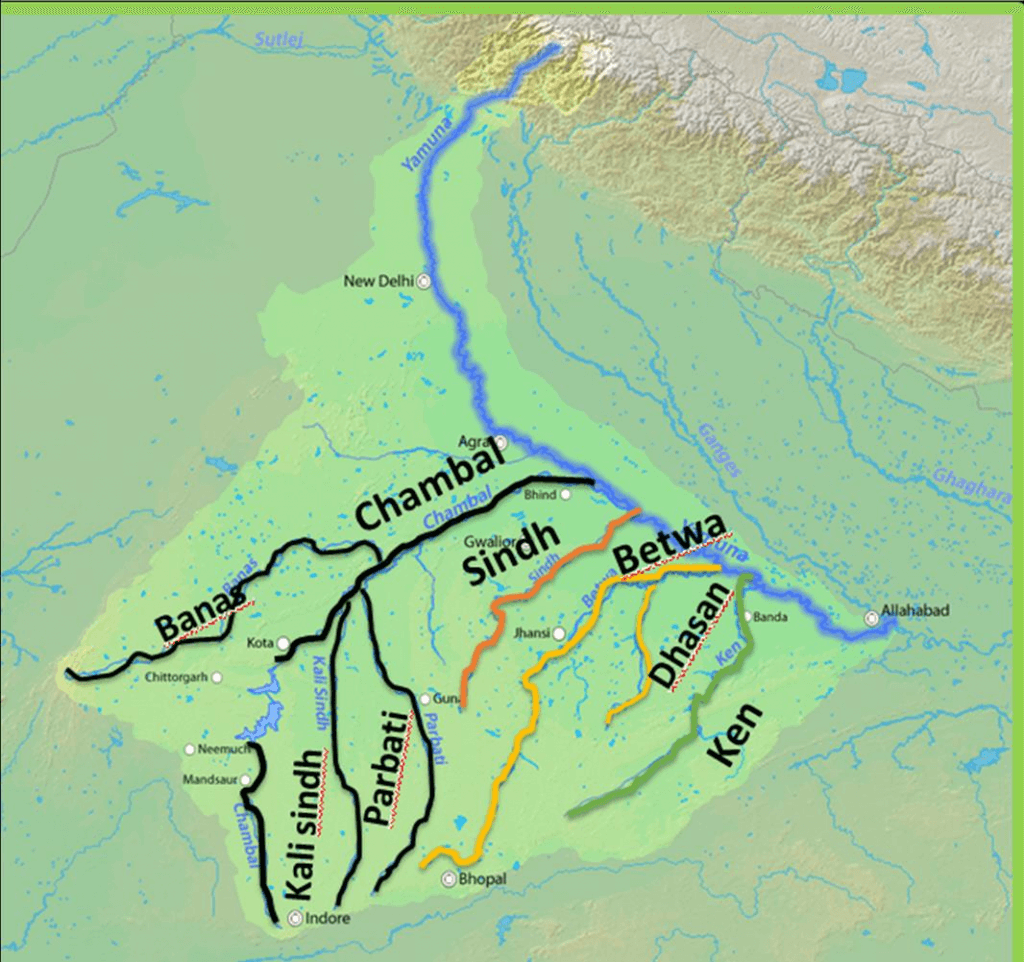
 कृष्णा नदी की सहायक नदियाँ
कृष्णा नदी की सहायक नदियाँ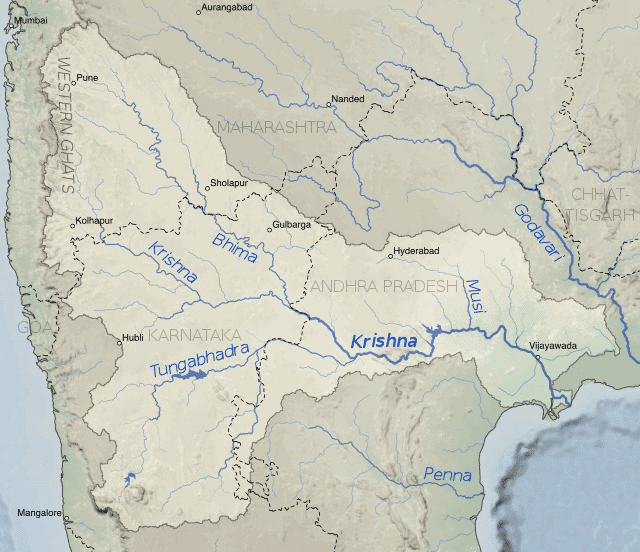
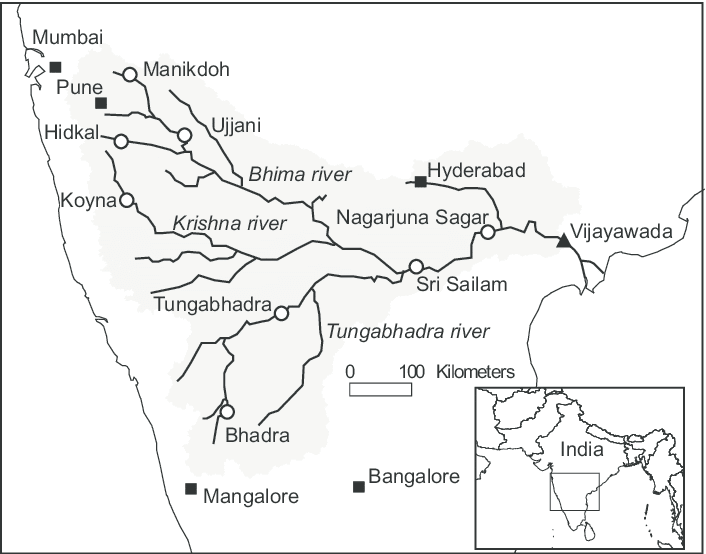
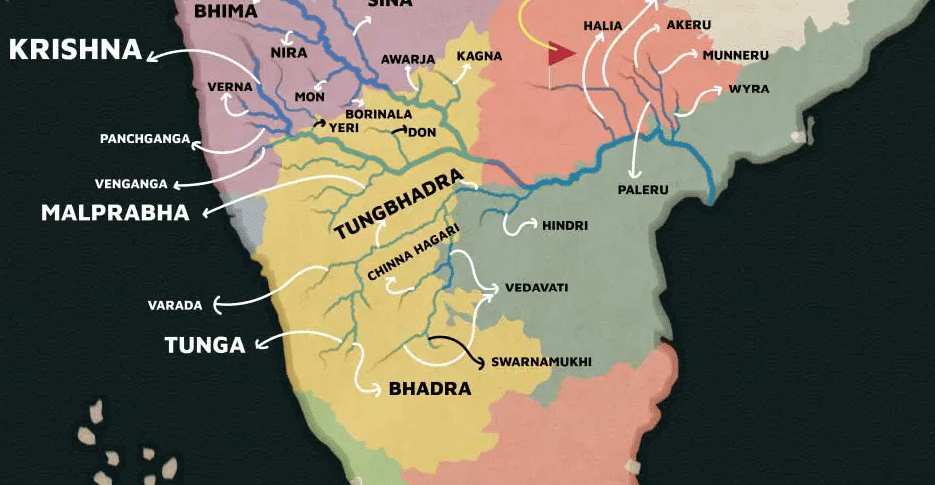
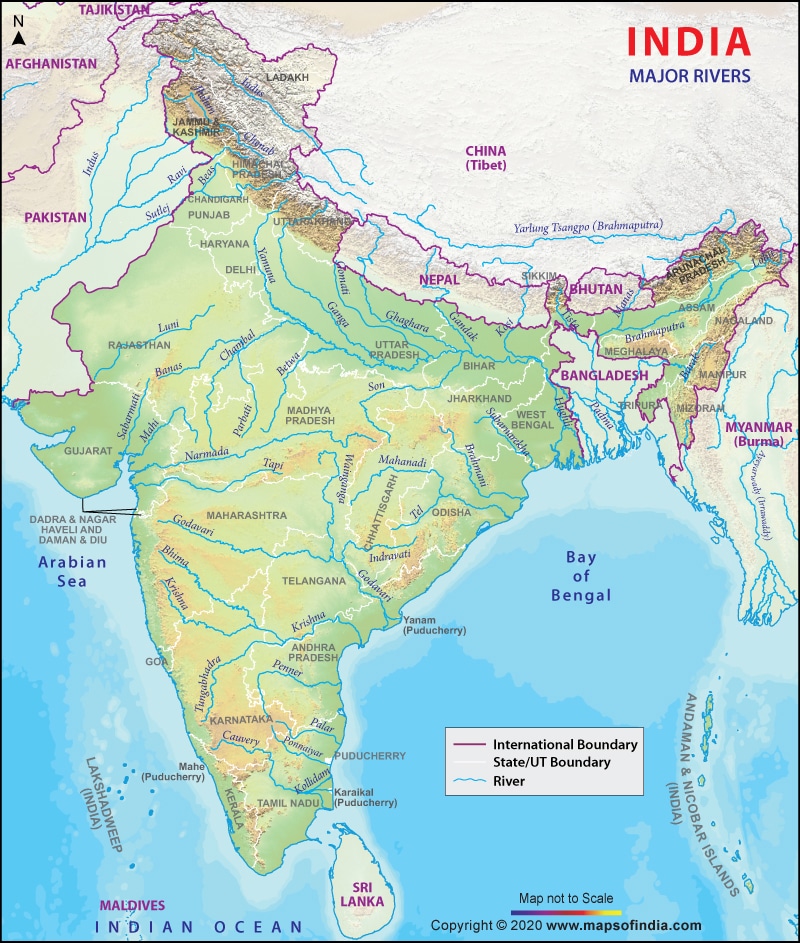
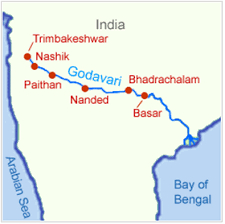

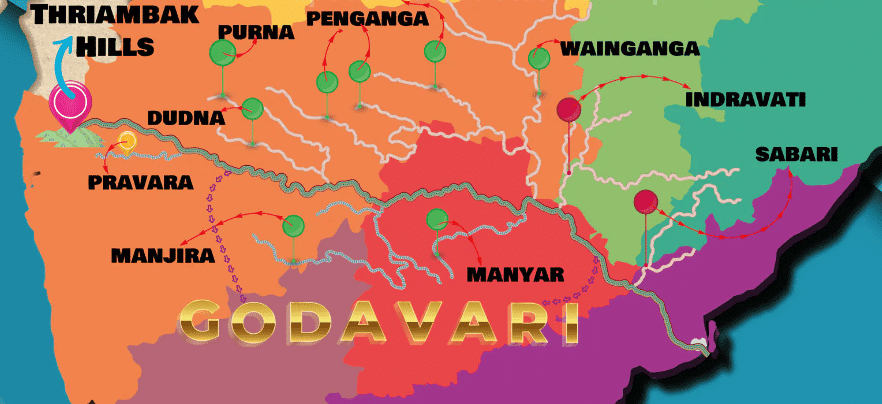
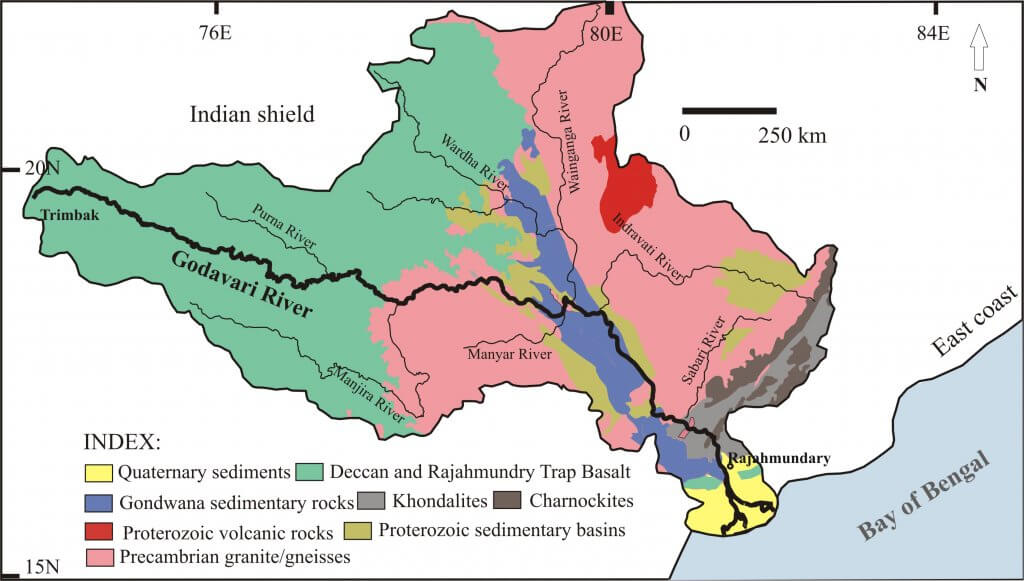
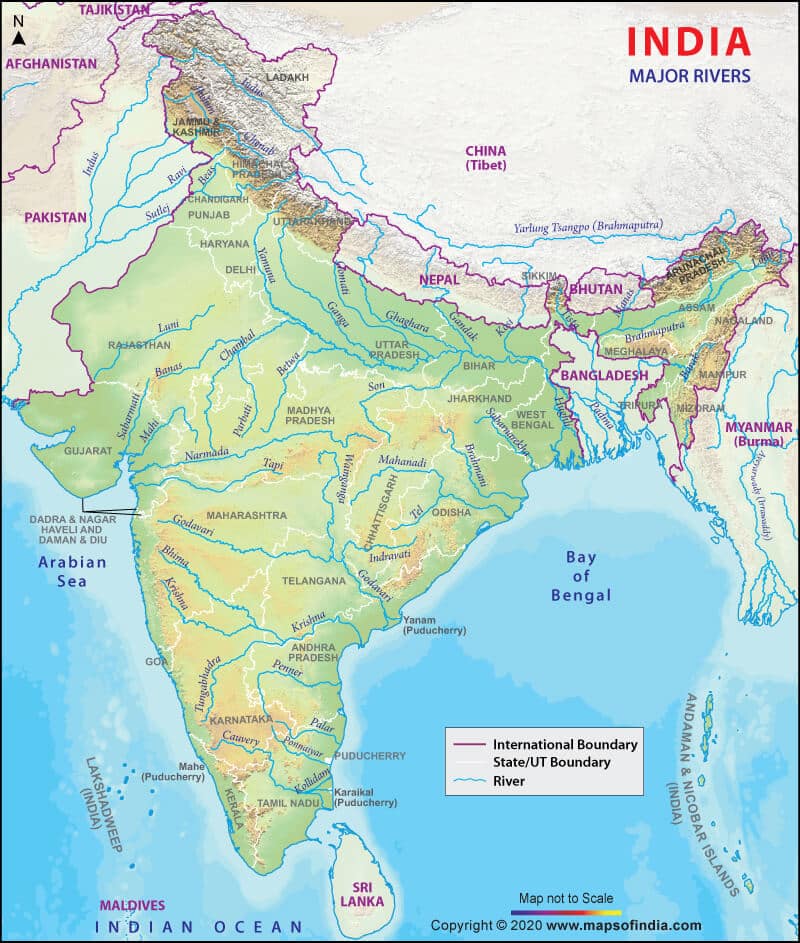
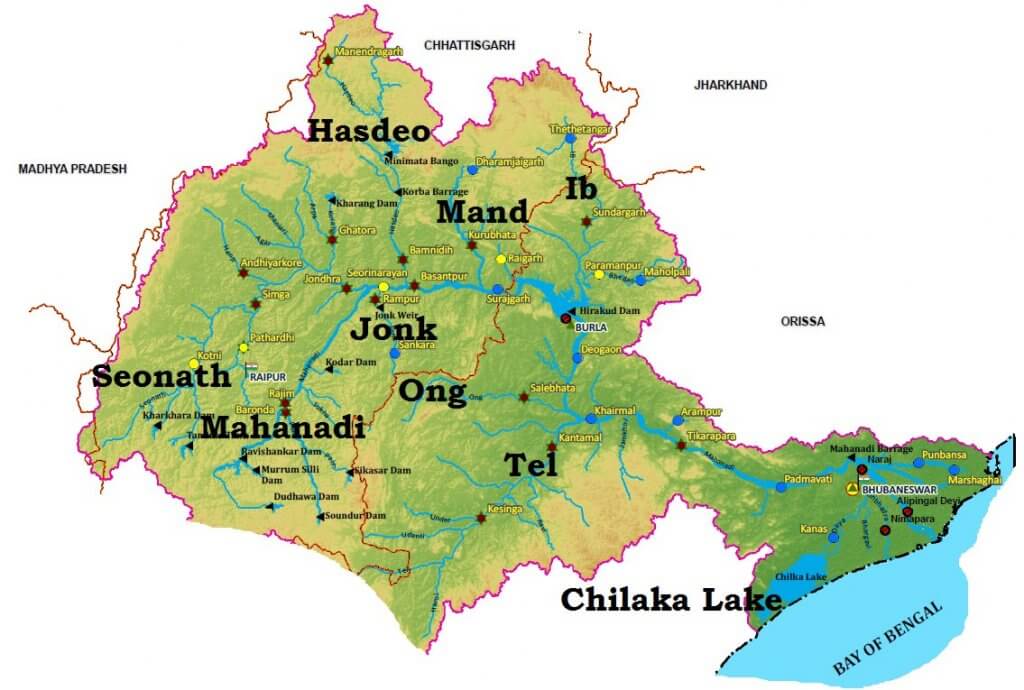
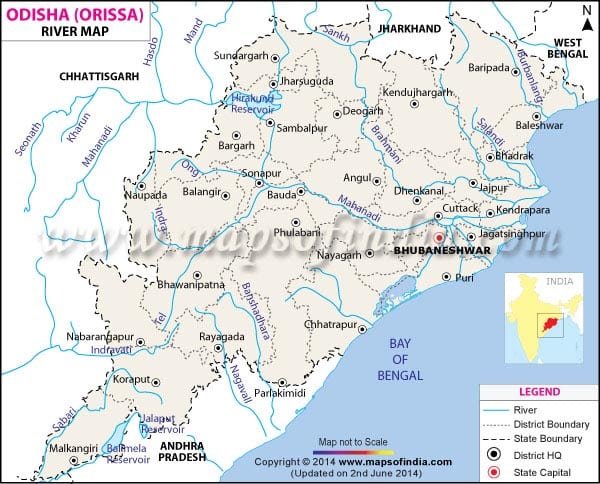
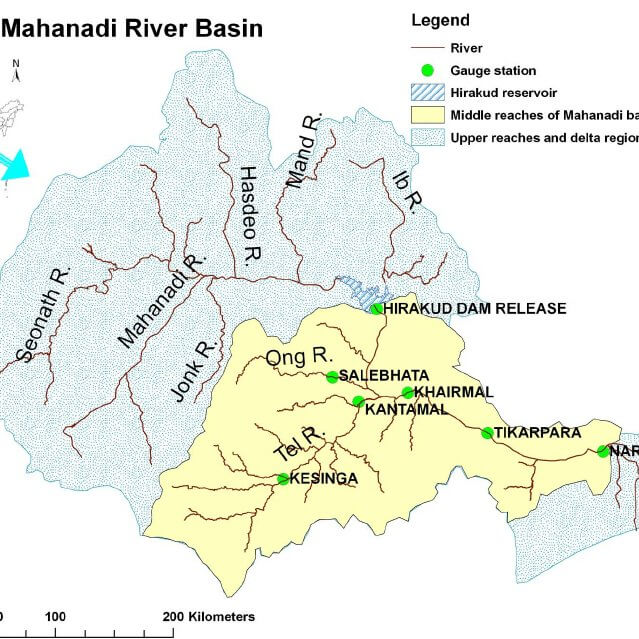
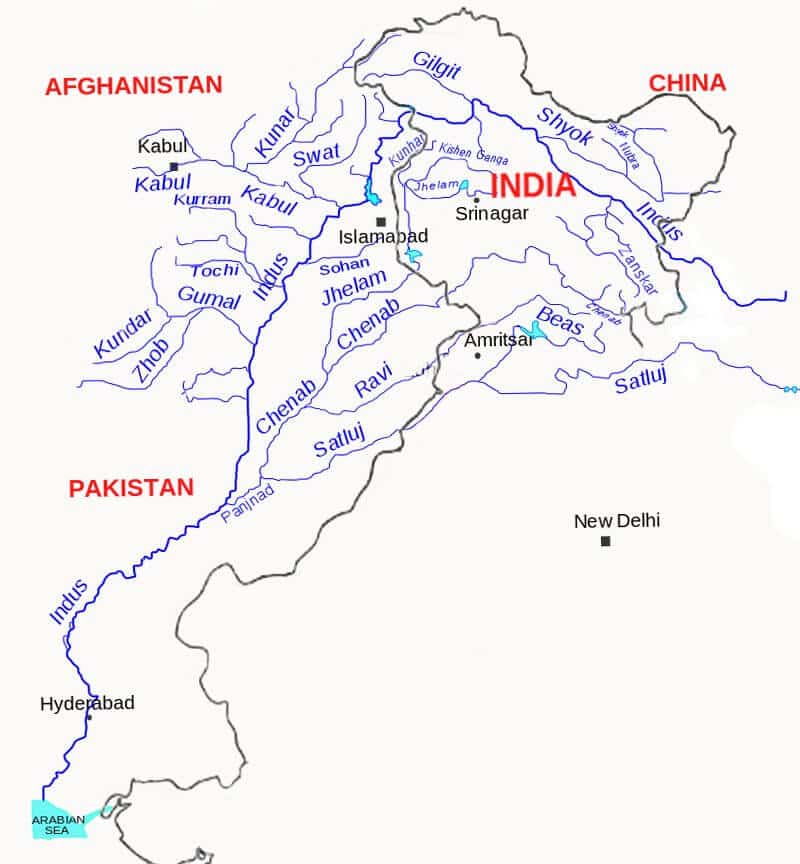
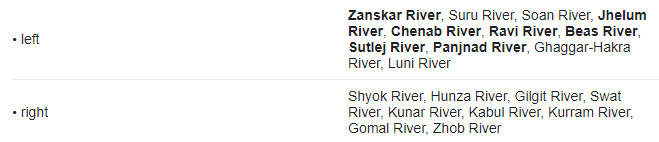
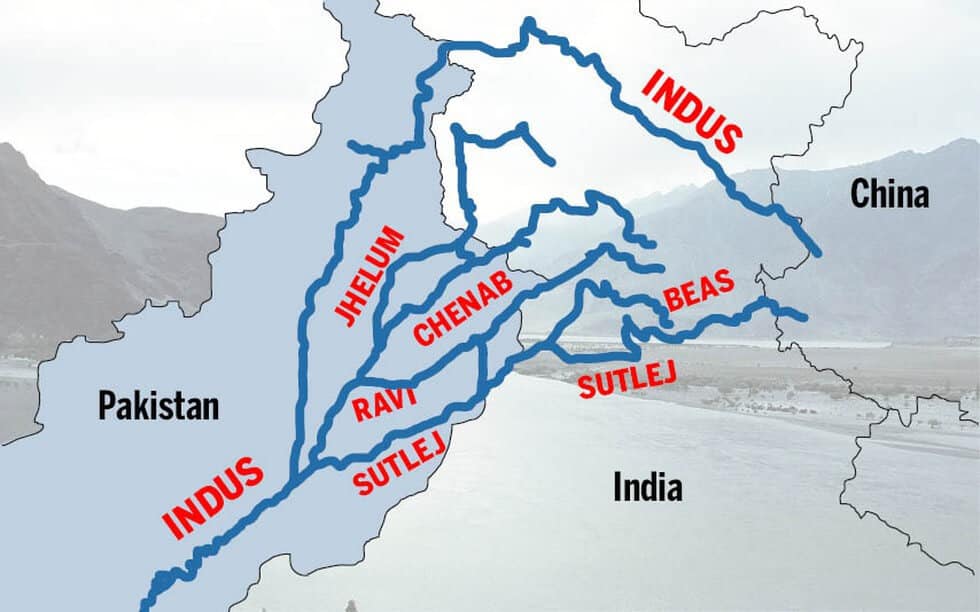
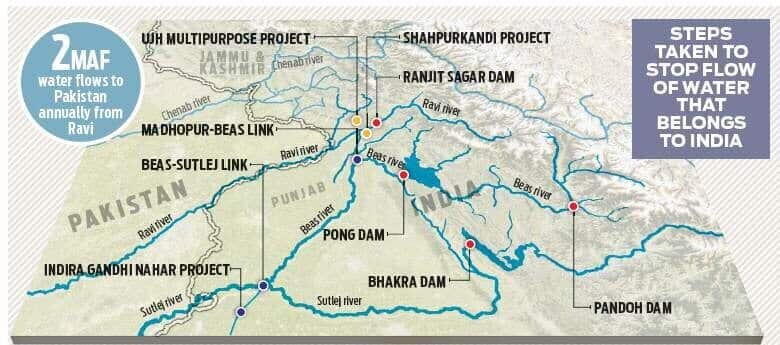
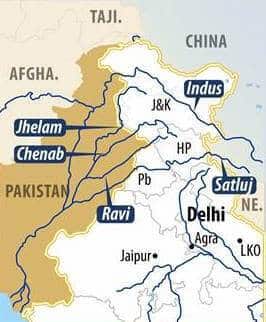
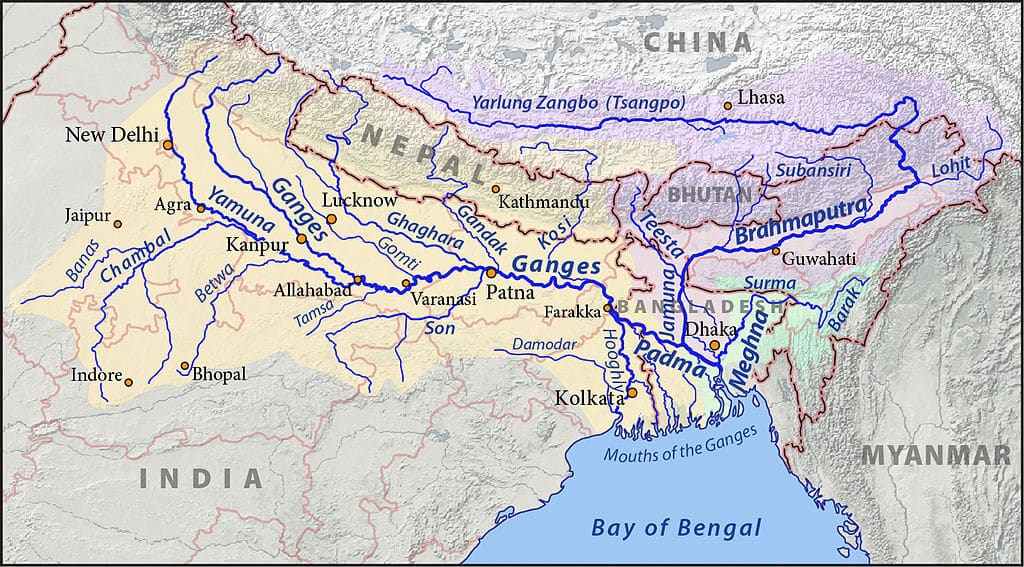
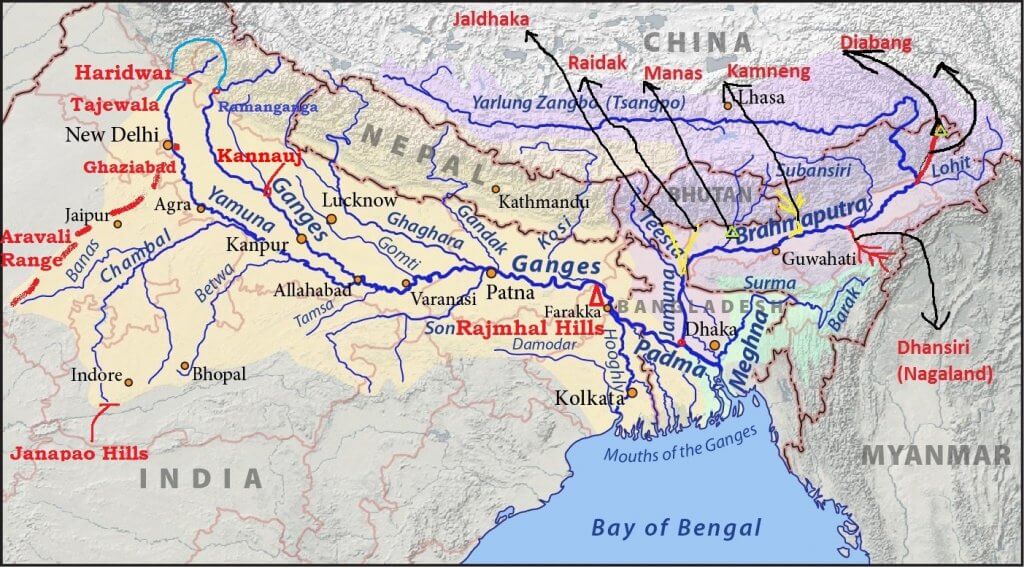

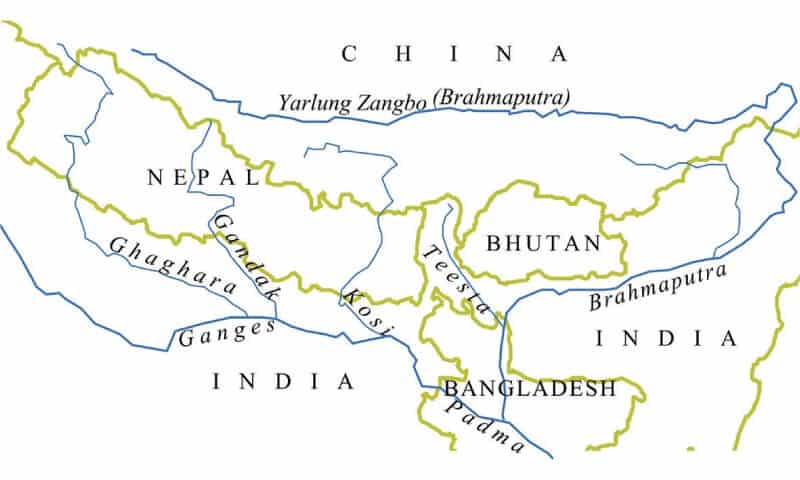
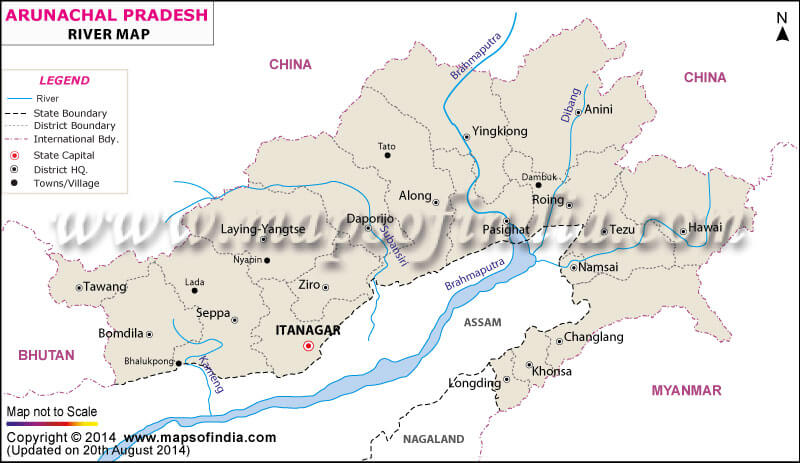
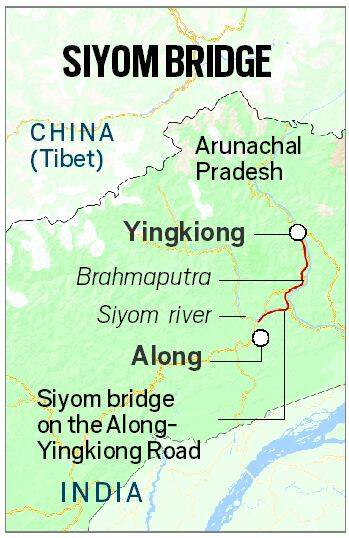

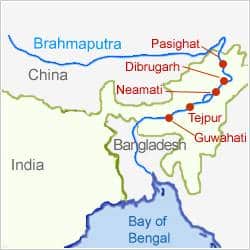
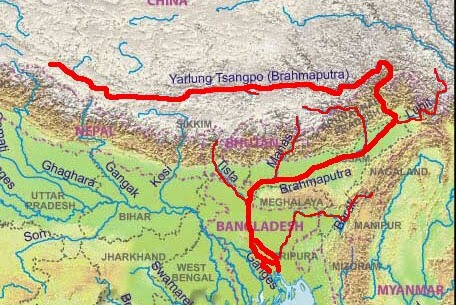
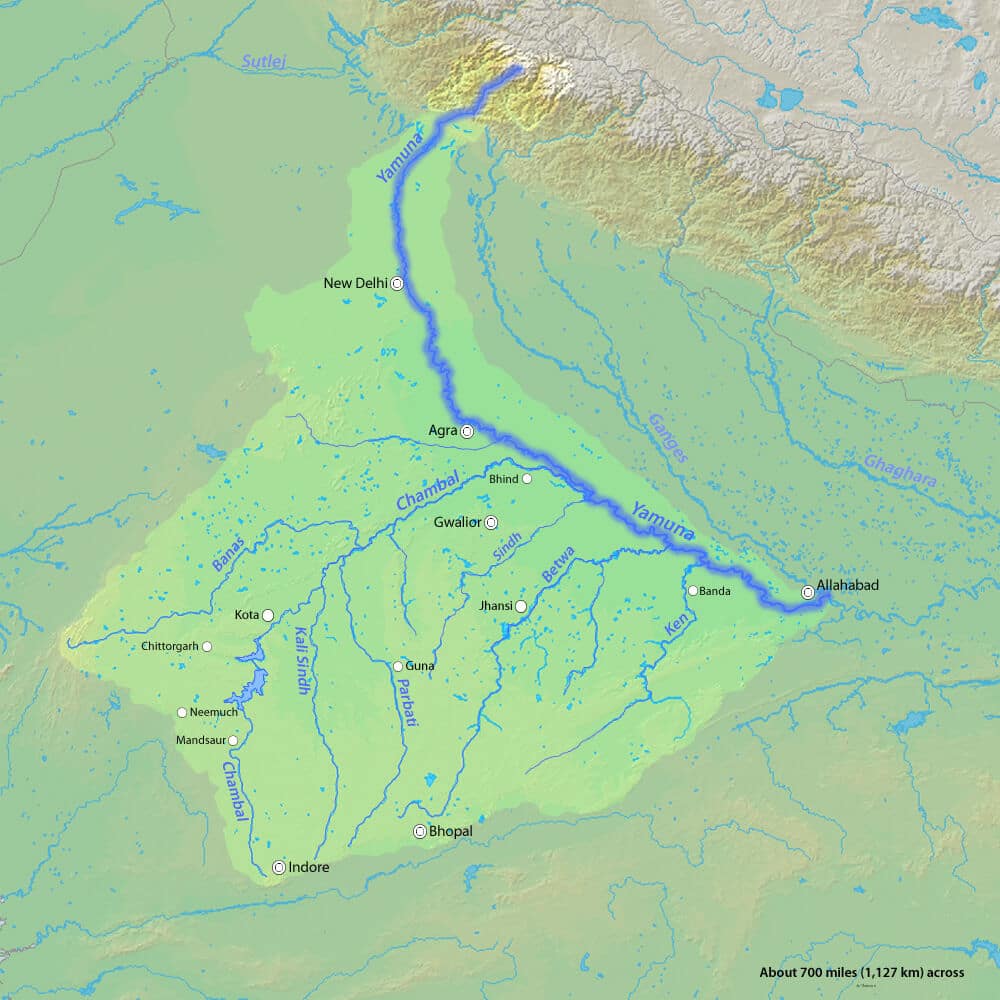
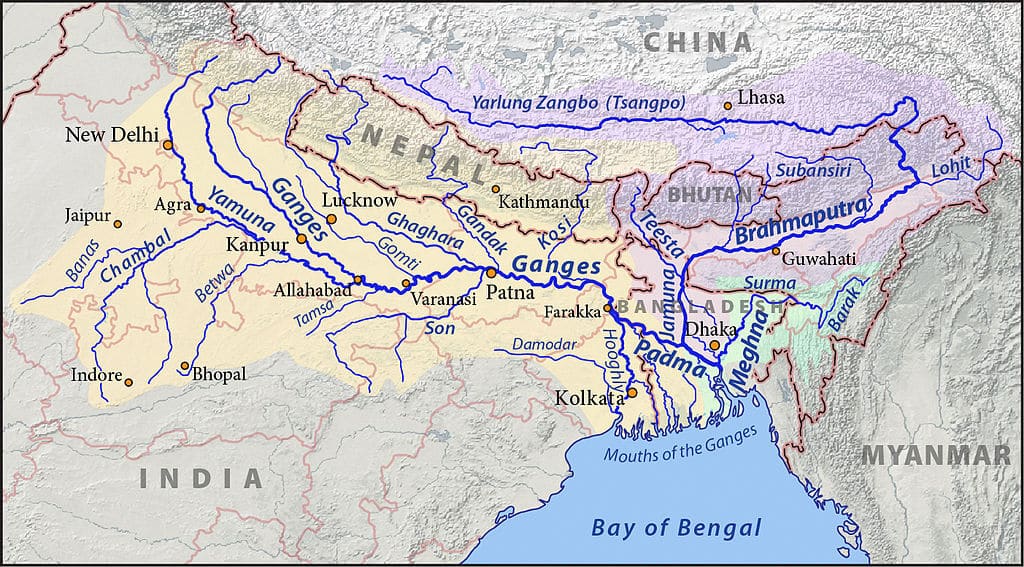
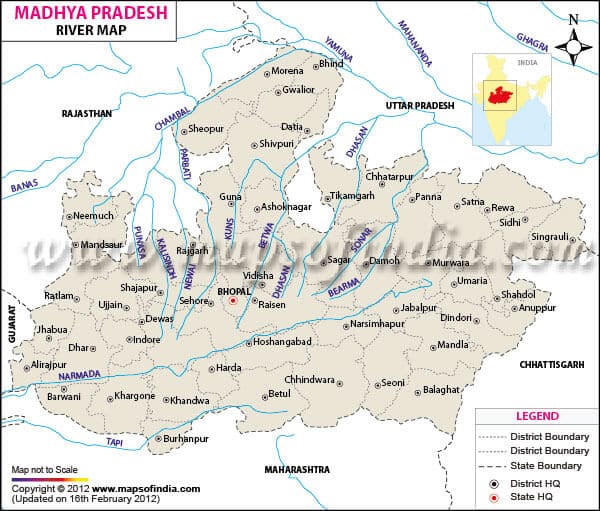
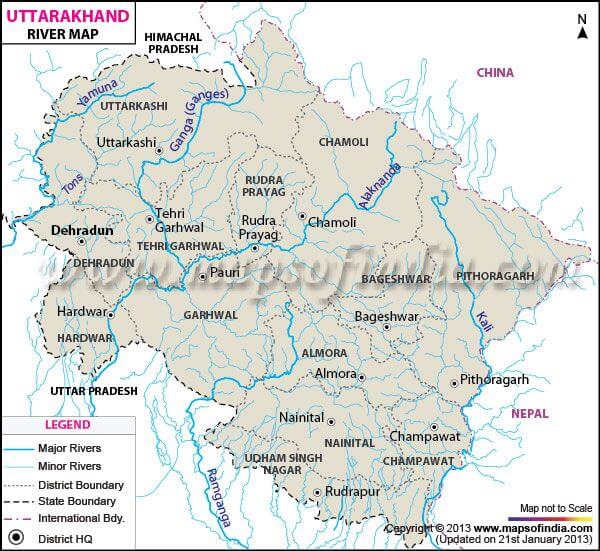
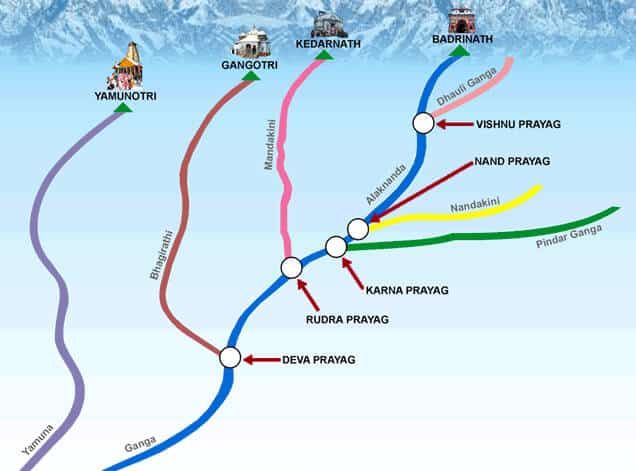
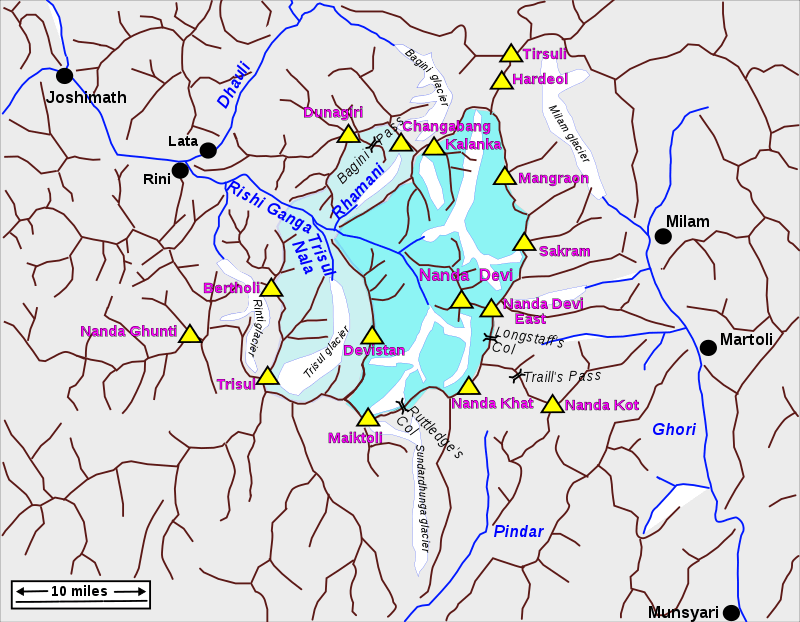

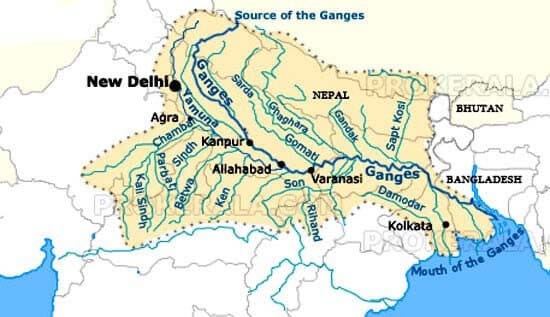
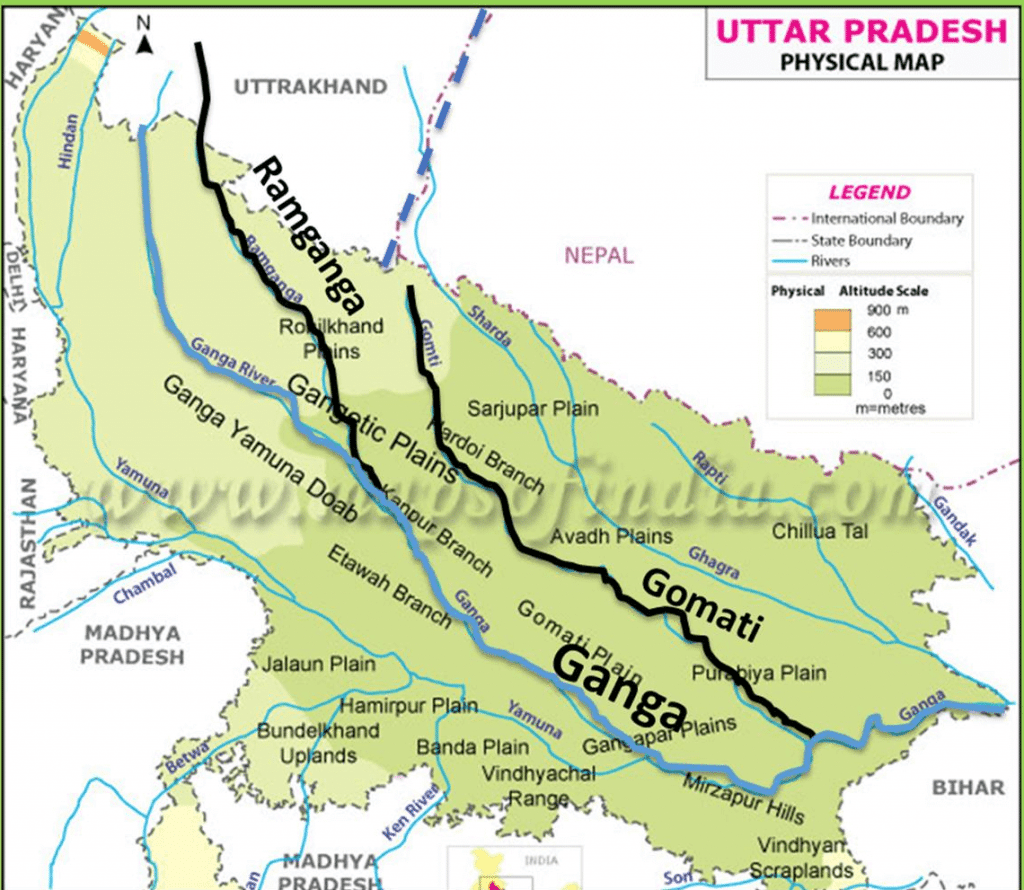
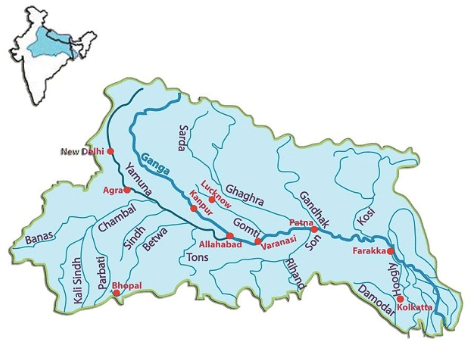

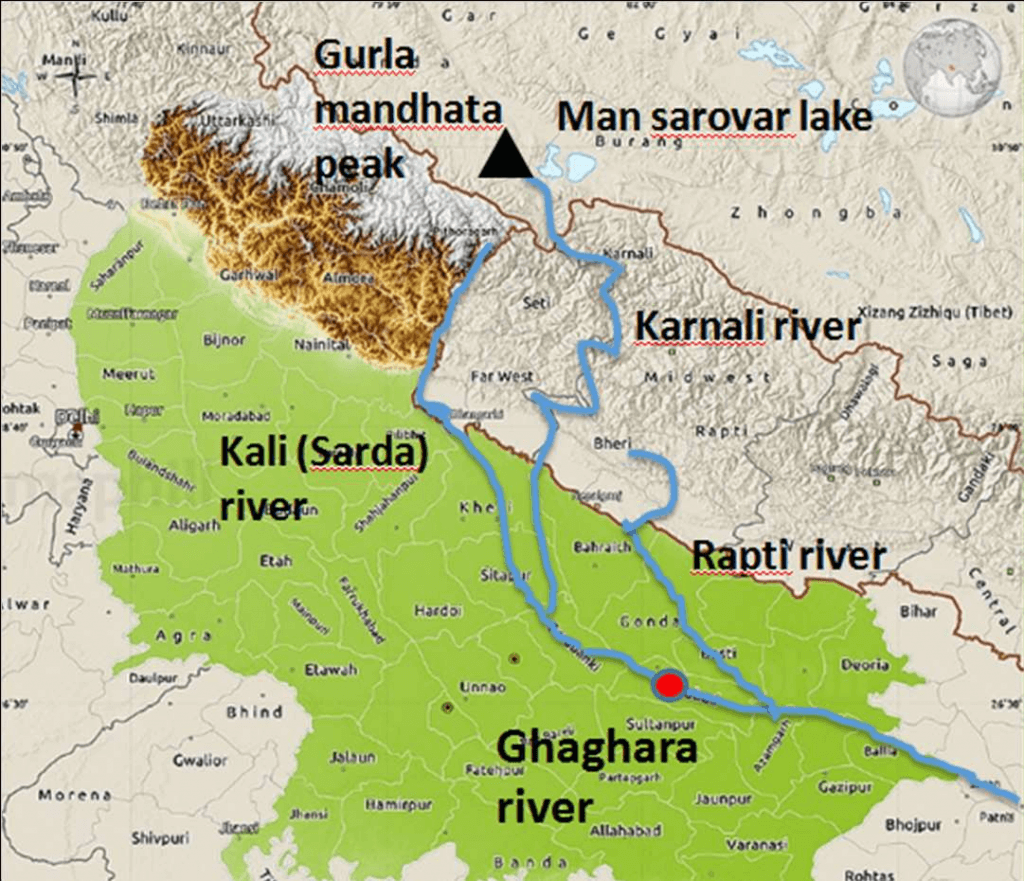
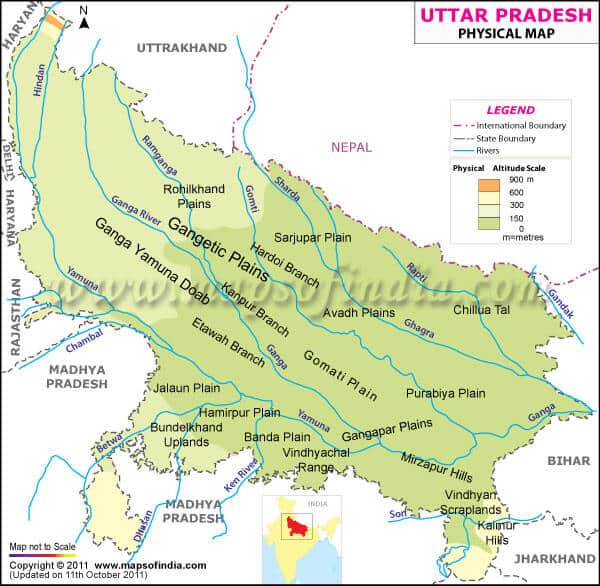
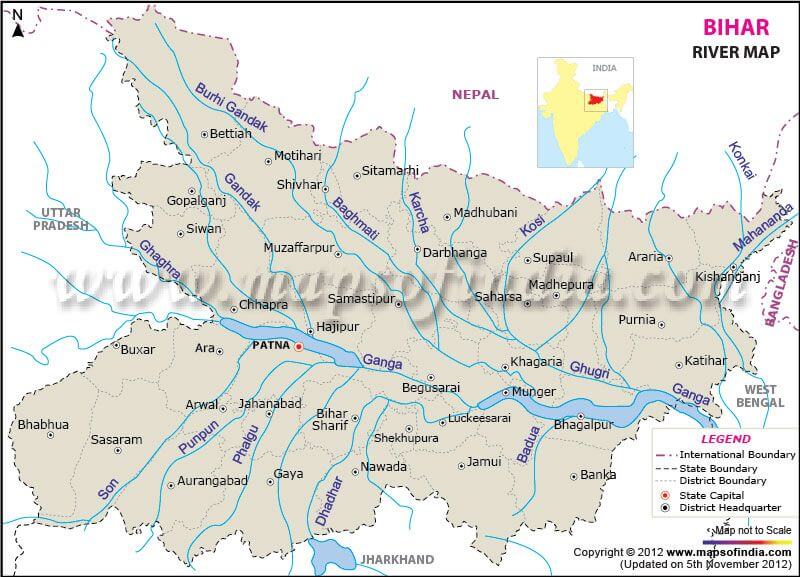
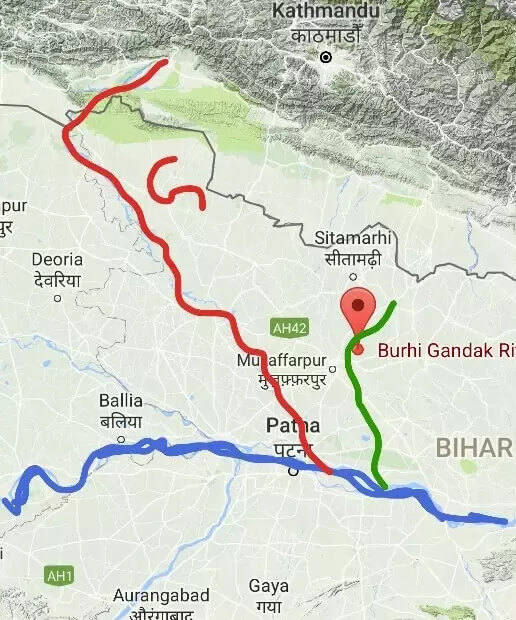
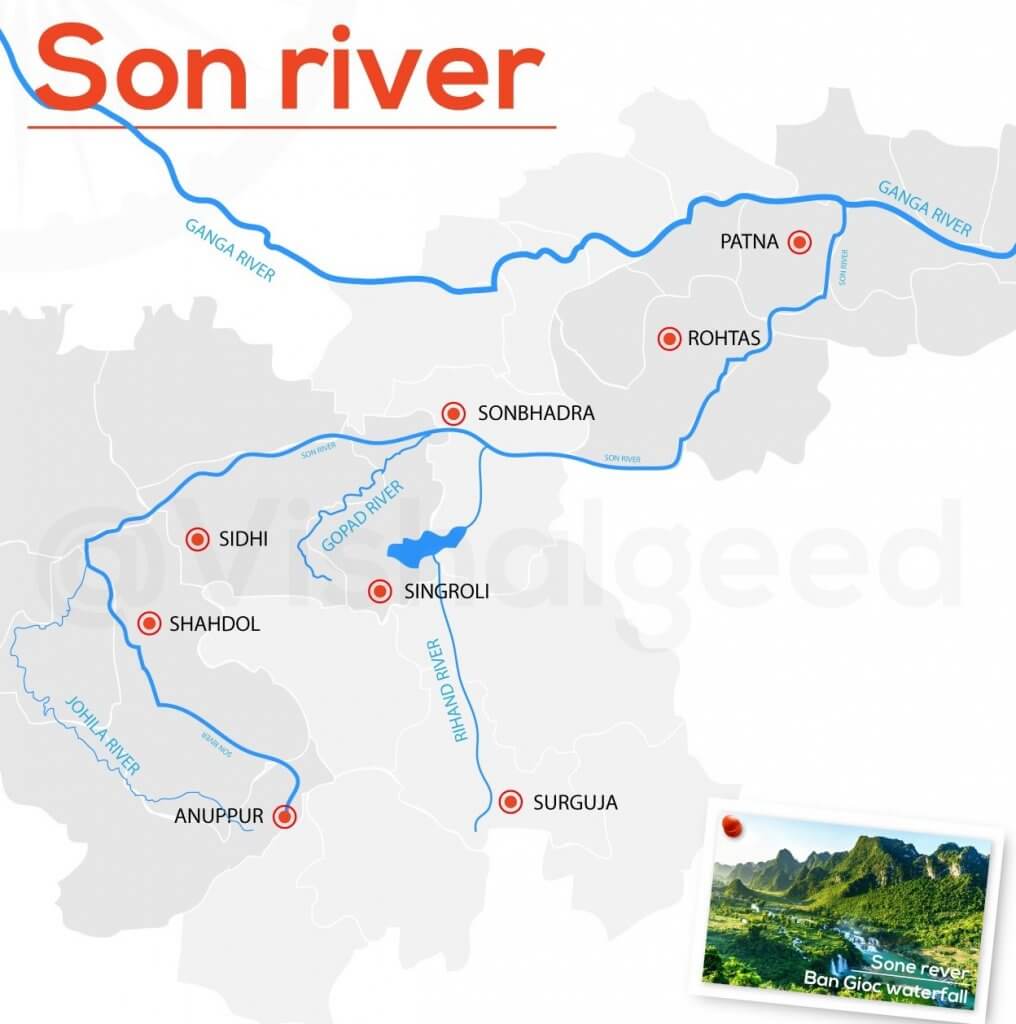
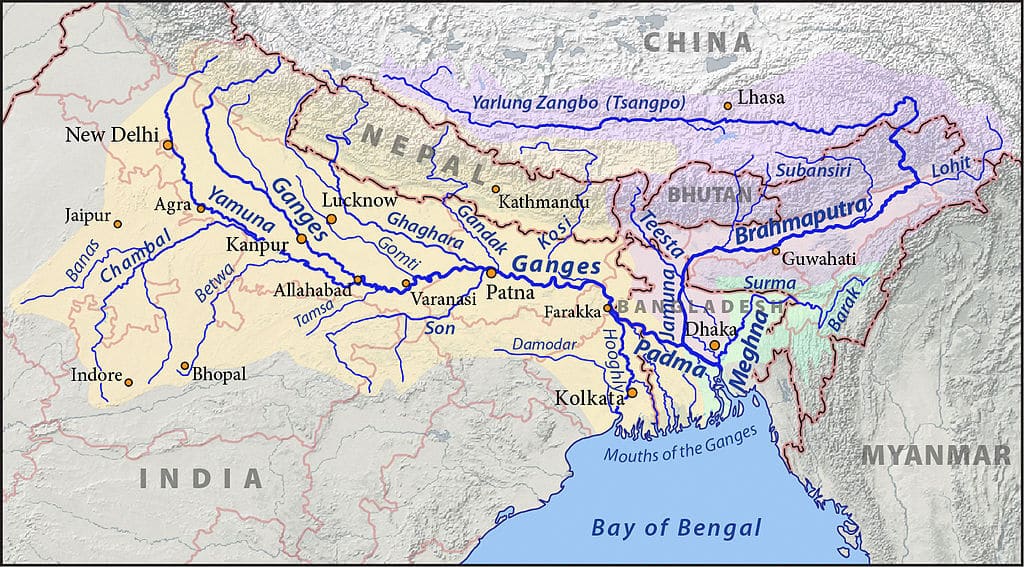
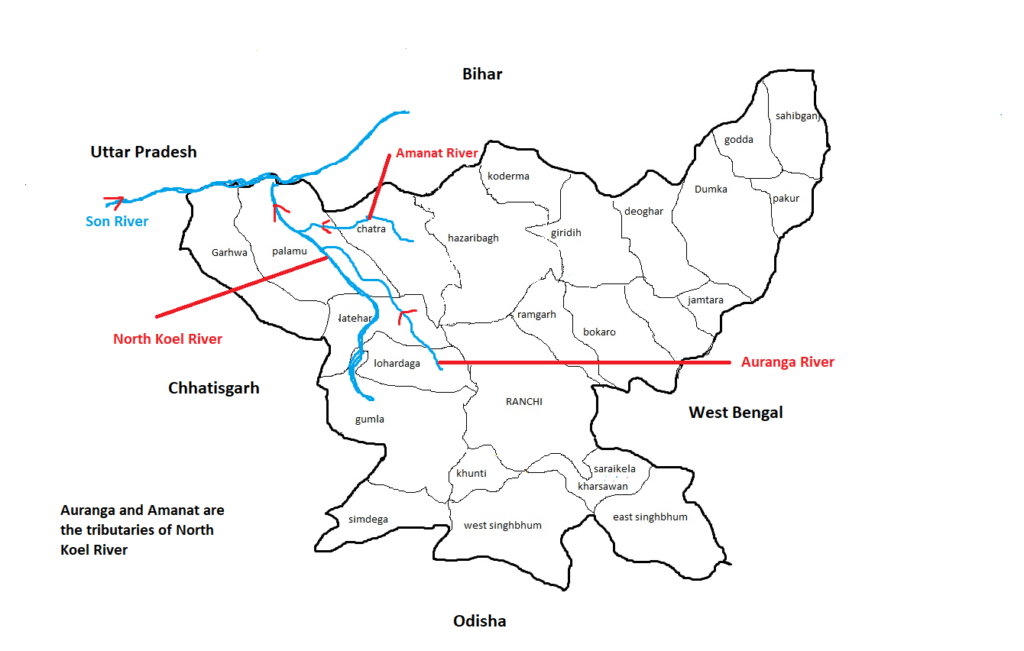
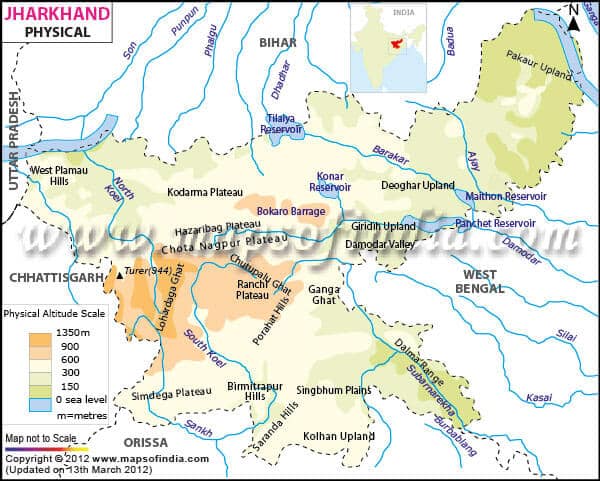
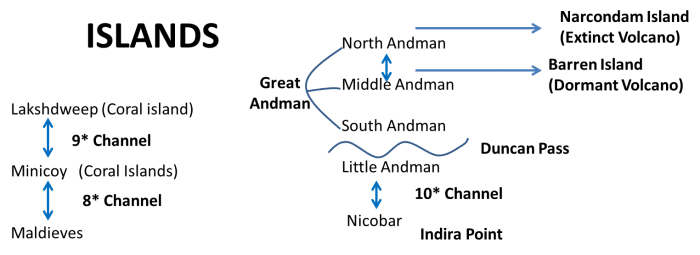
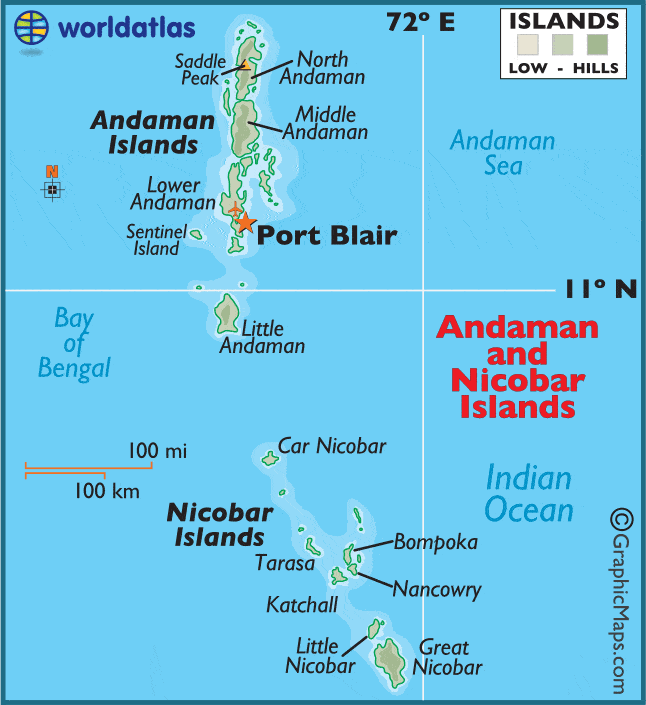
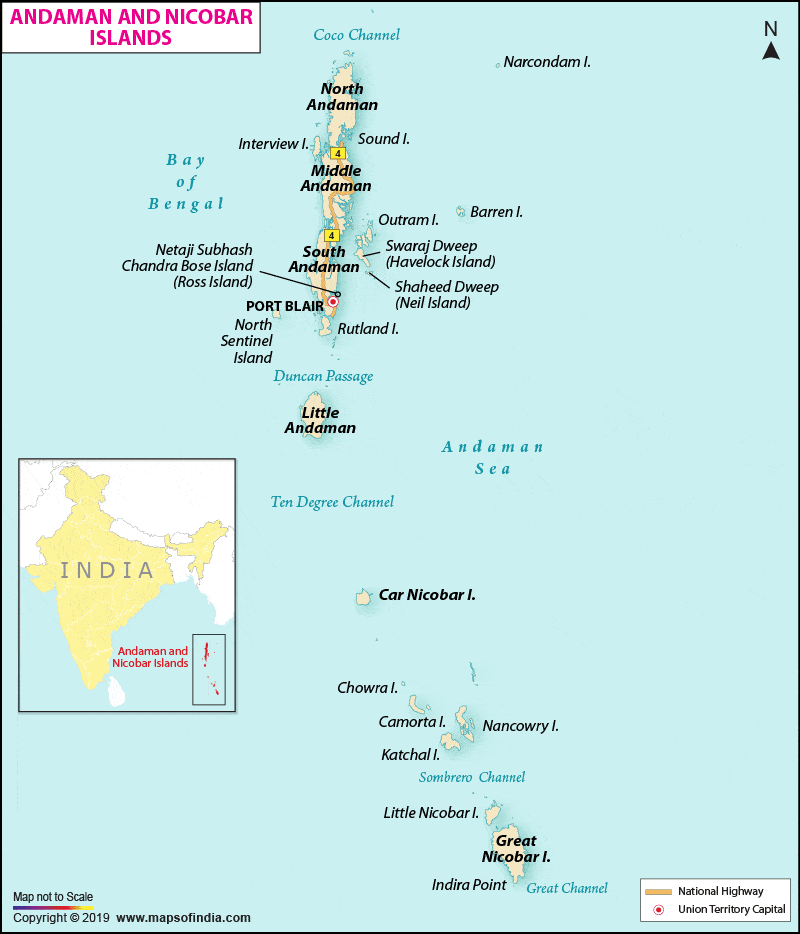
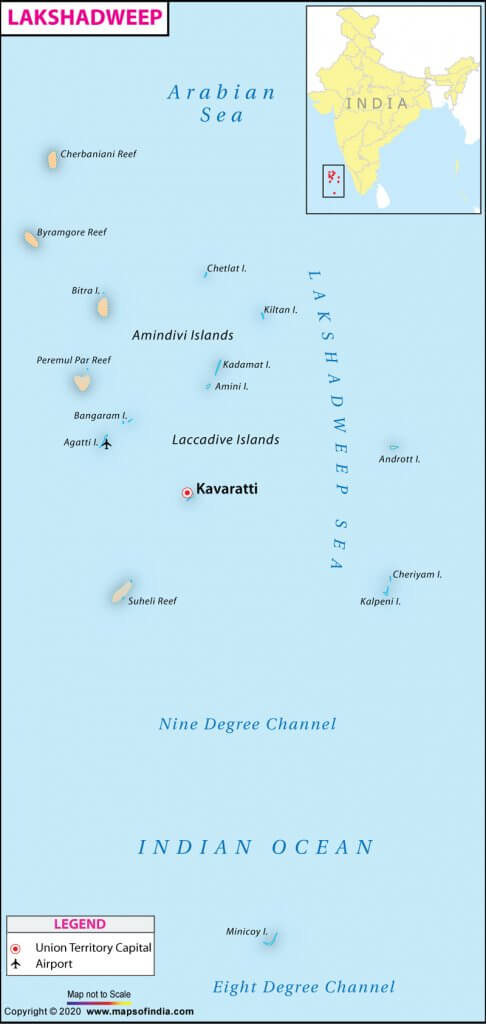
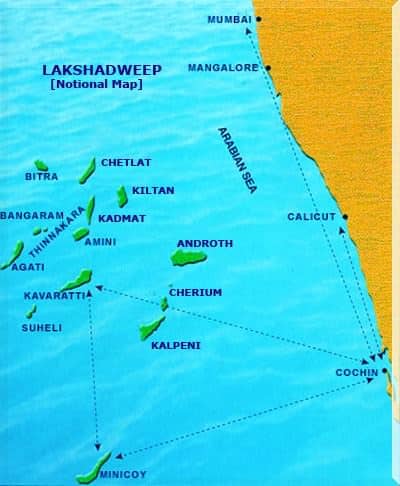
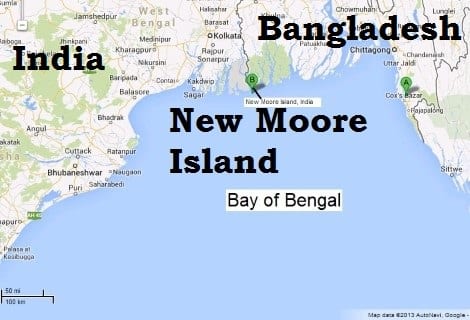
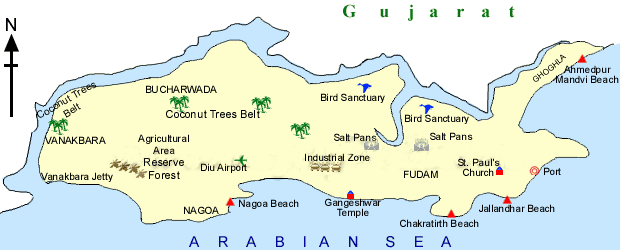
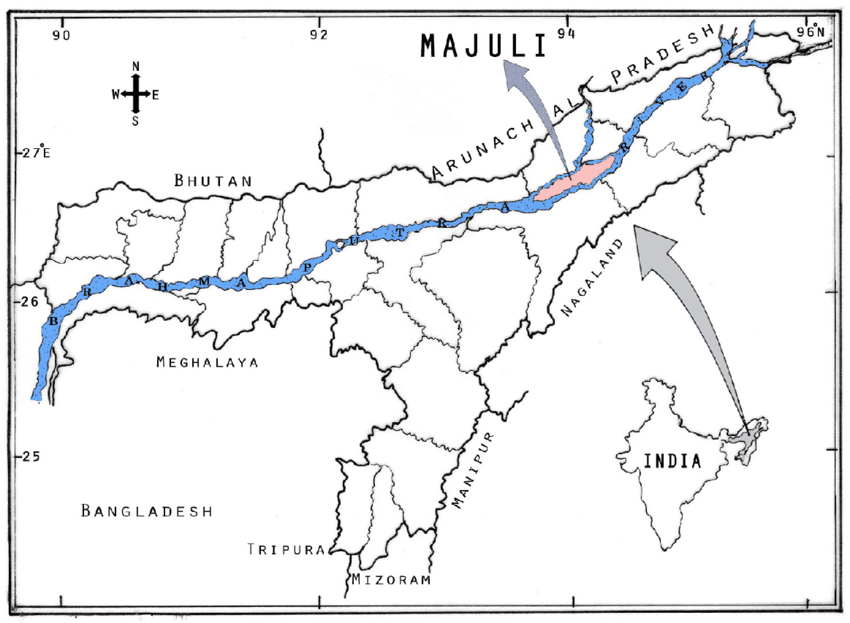
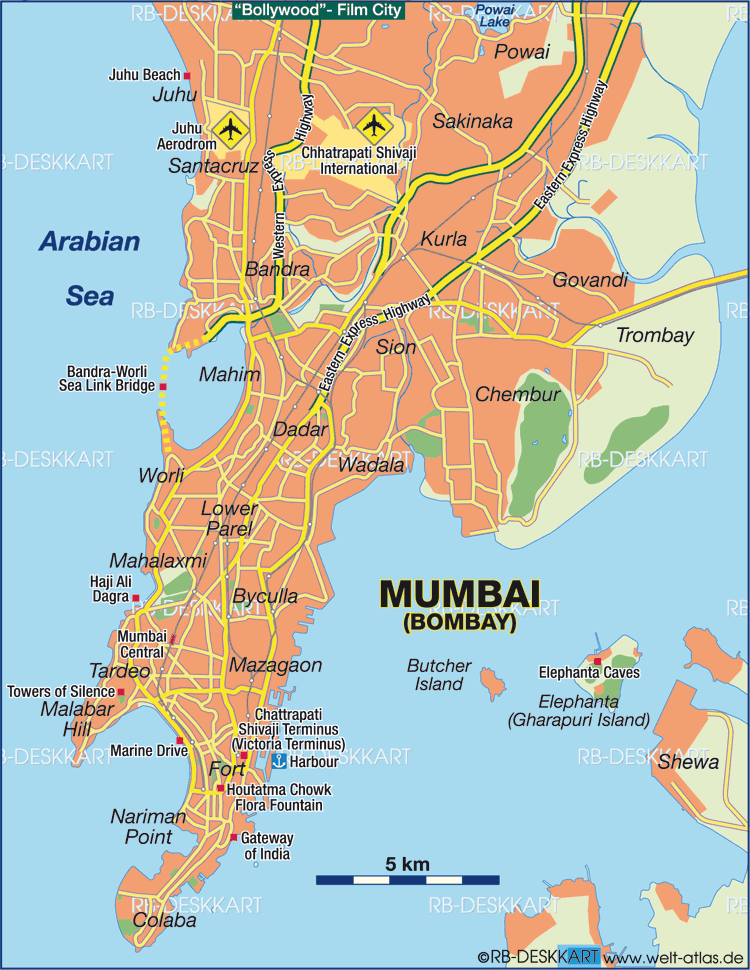
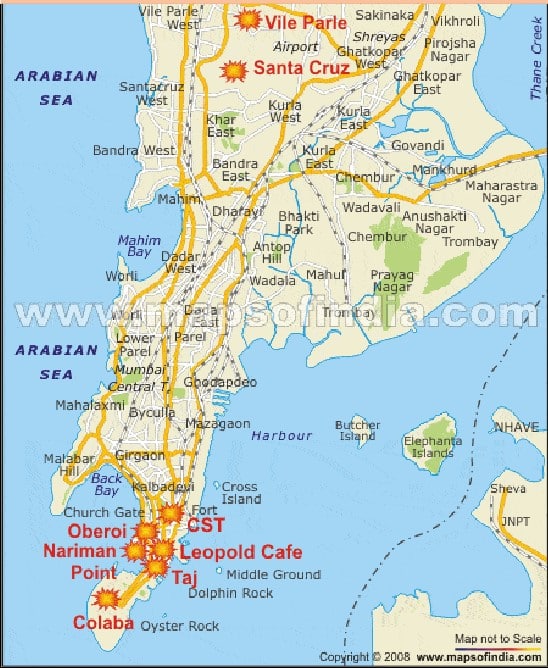
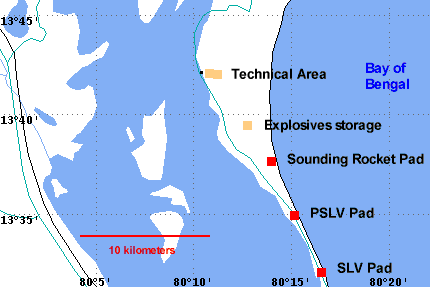
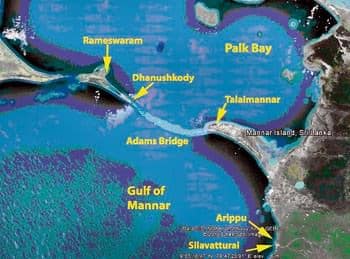
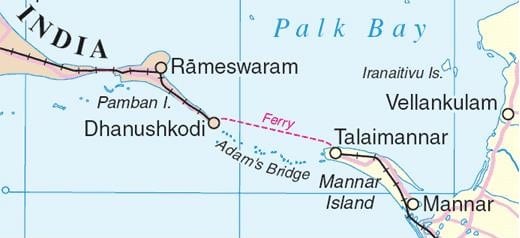
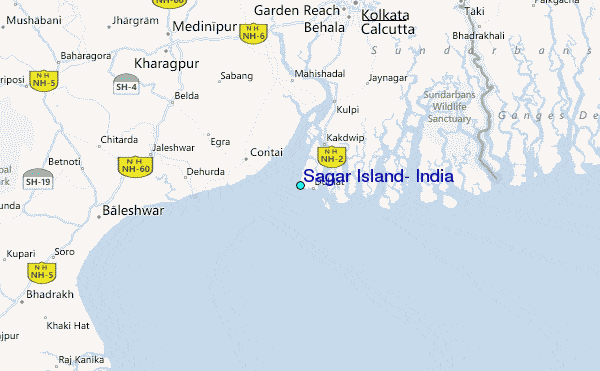
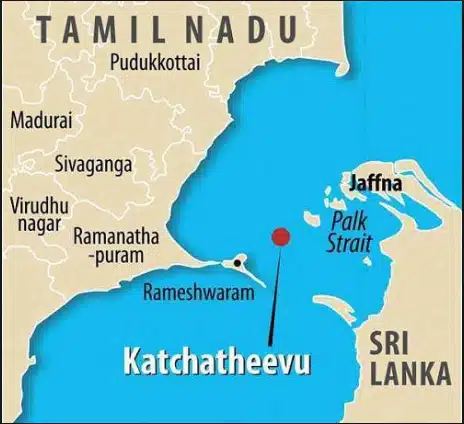
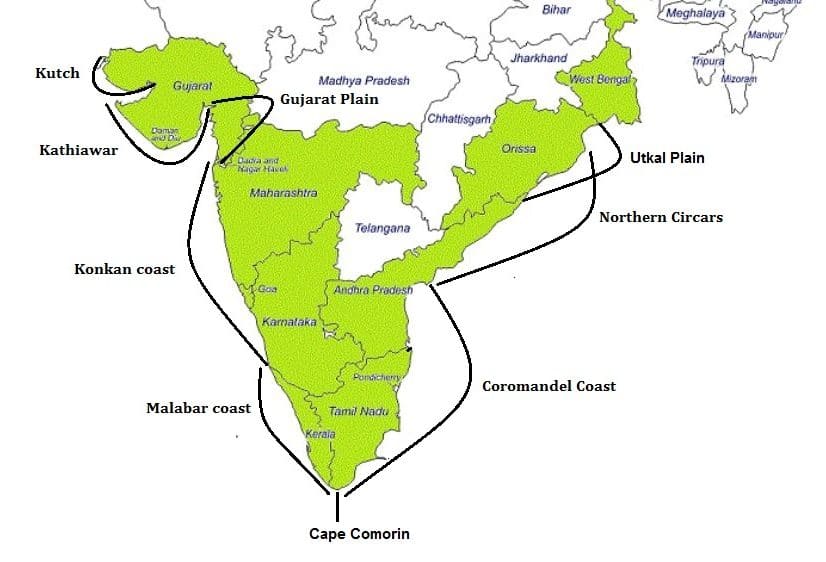
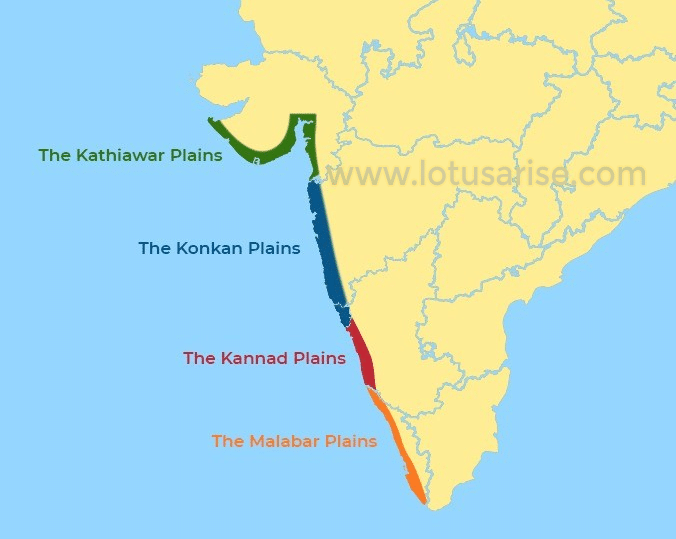
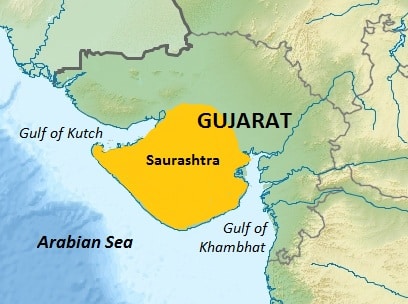
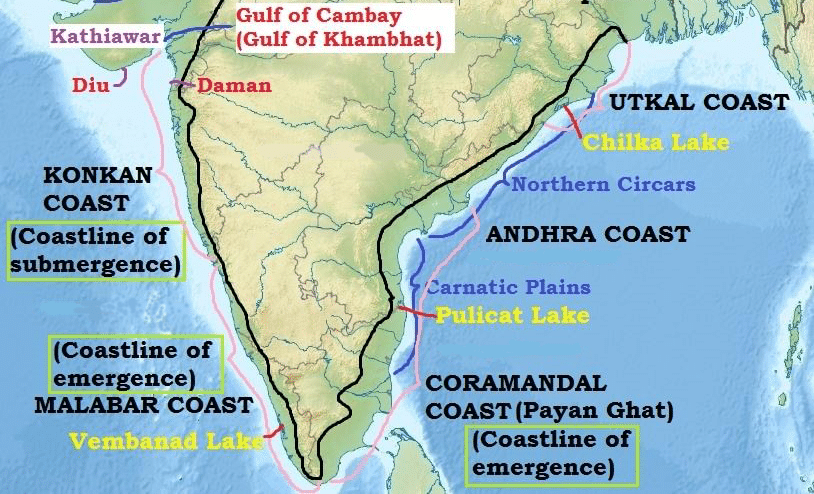
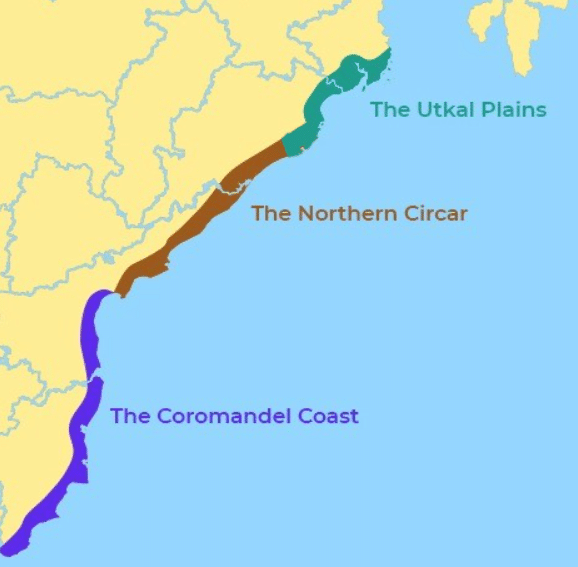
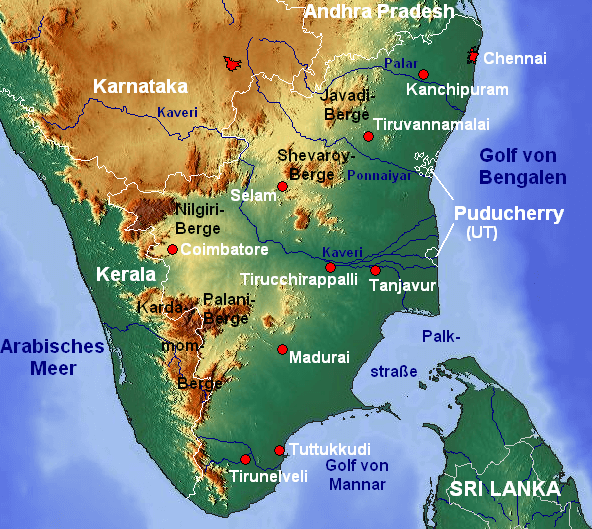
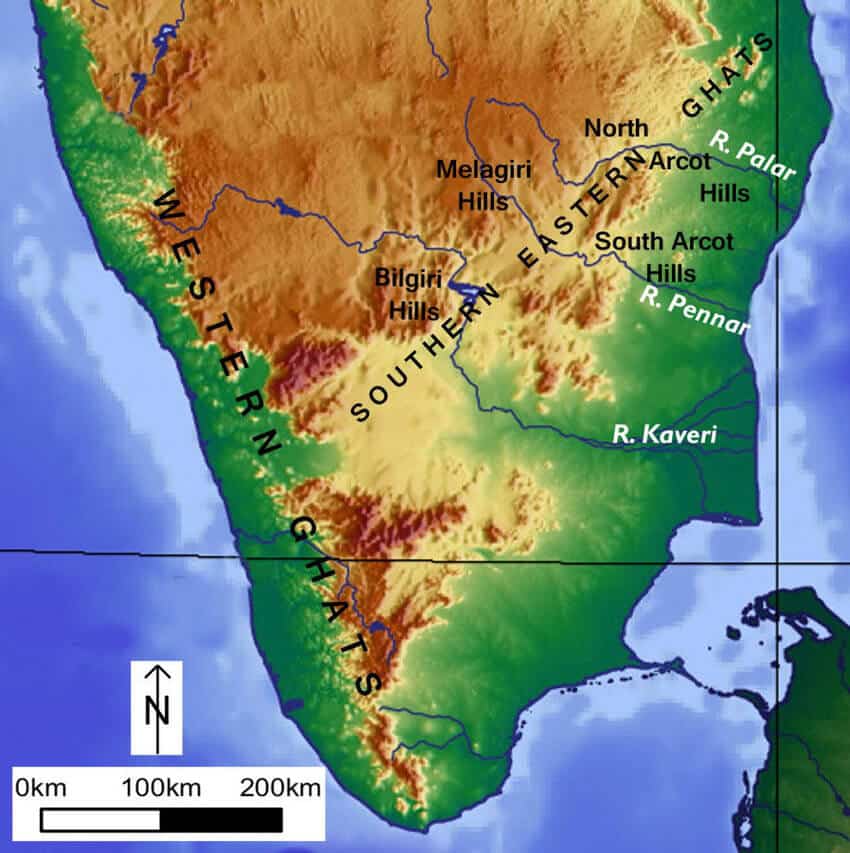
 आंध्र का मैदान (Andhra Plain)
आंध्र का मैदान (Andhra Plain)